阻塞队列
学习地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18b411M7xz?p=35
阻塞队列
阻塞队列,顾名思义,首先它是一个队列,而一个阻塞队列在数据结构中所起的作用大致如图所示:
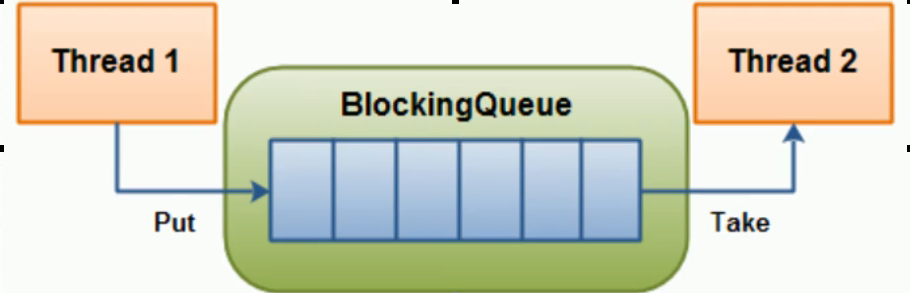
线程1往阻塞队列中添加元素,二线程2从队列中移除元素
当阻塞队列是空时,从队列中获取元素的操作将会被阻塞.
当阻塞队列是满时,往队列中添加元素的操作将会被阻塞.
同样
试图往已满的阻塞队列中添加新的线程同样也会被阻塞,直到其他线程从队列中移除一个或者多个元素或者全清空队列后使队列重新变得空闲起来并后续新增.
用处
在多线程领域:所谓阻塞,在某些情况下会挂起线程(即线程阻塞),一旦条件满足,被挂起的线程优惠被自动唤醒
为什么需要使用BlockingQueue
好处是我们不需要关心什么时候需要阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程,因为BlockingQueue都一手给你包办好了
在concurrent包 发布以前,在多线程环境下,我们每个程序员都必须自己去控制这些细节,尤其还要兼顾效率和线程安全,而这会给我们的程序带来不小的复杂度.
BlockingQueue的核心方法
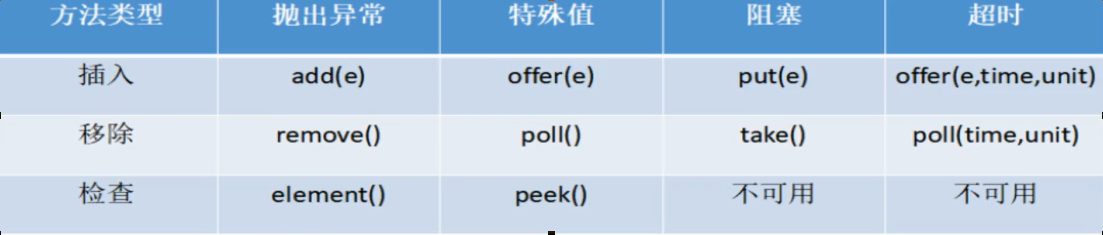
| 方法类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 抛出异常 | 当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里面add插入元素会抛IllegalStateException: Queue full 当阻塞队列空时,再往队列Remove元素时候回抛出NoSuchElementException |
| 特殊值 | 插入方法,成功返回true 失败返回false 移除方法,成功返回元素,队列里面没有就返回null |
| 一直阻塞 | 当阻塞队列满时,生产者继续往队列里面put元素,队列会一直阻塞直到put数据or响应中断退出 当阻塞队列空时,消费者试图从队列take元素,队列会一直阻塞消费者线程直到队列可用. |
| 超时退出 | 当阻塞队列满时,队列会阻塞生产者线程一定时间,超过后限时后生产者线程就会退出 |
抛出异常
当阻塞队列满时,再往队列里面add插入元素会抛IllegalStateException: Queue full
当阻塞队列空时,再往队列Remove元素时候回抛出NoSuchElementException
@Test
public void test1() {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
//往阻塞队列添加元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));//true
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));//true
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));//true
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d"));//java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
//从阻塞队列取元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.element());//a
//从阻塞队列移除元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());//a
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());//b
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());//c
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());//java.util.NoSuchElementException
}
特殊值
插入方法,成功返回true 失败返回false
移除方法,成功返回元素,队列里面没有就返回null
@Test
public void test2(){
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
//往阻塞队列添加元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));//true
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));//true
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));//true
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d"));//false
//从阻塞队列取元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());//a
//从阻塞队列移除元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());//a
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());//b
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());//c
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());//null
}
一直阻塞
当阻塞队列满时,生产者继续往队列里面put元素,队列会一直阻塞直到put数据or响应中断退出
当阻塞队列空时,消费者试图从队列take元素,队列会一直阻塞消费者线程直到队列可用.
@Test
public void test3() throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
//往阻塞队列添加元素
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
// blockingQueue.put("x");//一直阻塞
//从阻塞队列移除元素
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take();
blockingQueue.take();
// blockingQueue.take();//一直阻塞
}
超时退出
当阻塞队列满时,队列会阻塞生产者线程一定时间,超过后限时后生产者线程就会退出
@Test
public void test4() throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
//往阻塞队列添加元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//true
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//true
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//true
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//false
//从阻塞队列移除元素
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//a
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//b
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//c
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));//null
}
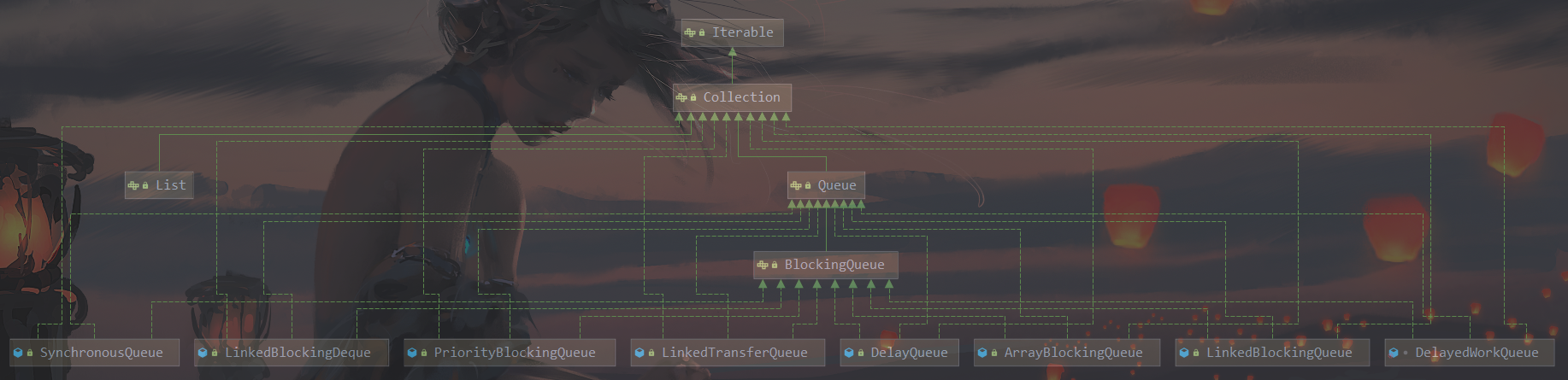
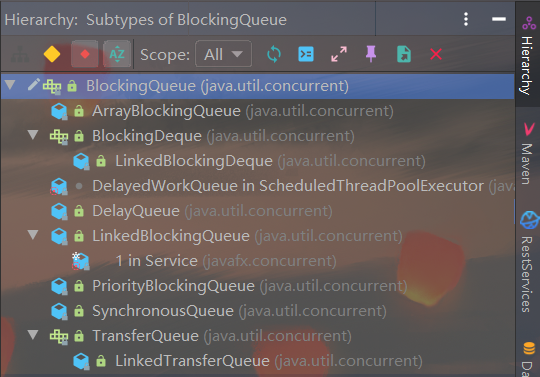
BlockingQueue种类分析
-
ArrayBlockingQueue: 由数组结构组成的有界阻塞队列.
-
LinkedBlockingDeque: 由链表结构组成的有界(但大小默认值Integer>MAX_VALUE)阻塞队列.
-
PriorityBlockingQueue:支持优先级排序的无界阻塞队列.
-
DelayQueue: 使用优先级队列实现的延迟无界阻塞队列.
-
SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,也即是单个元素的队列.
-
LinkedTransferQueue:由链表结构组成的无界阻塞队列.
-
LinkedBlockingDeque:由了解结构组成的双向阻塞队列.
ArrayBlockingQueue:是一个基于数组结构的有界阻塞队列,此队列按FIFO原则对元素进行排序
LinkedBlockingQueue:是一个基于链表结构的阻塞队列,此队列按FIFO排序元素,吞吐量高于ArrayBlockingQueue
SynchronousQueue:一个不存储元素的阻塞队列,每个插入操作必须等到另一个线程调用移出操作,否则插入操作一直处于阻塞状态,吞吐量通常要高
SynchronousQueue
SynchronousQueue没有容量
与其他BlcokingQueue不同,SynchronousQueue是一个不存储元素的BlcokingQueue
每个put操作必须要等待一个take操作,否则不能继续添加元素,反之亦然.
public class BlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tput 1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tput 2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\tput 3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "AAA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + blockingQueue.take());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + blockingQueue.take());
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "BBB").start();
}
}
AAA put 1
BBB 1
AAA put 2
BBB 2
AAA put 3
BBB 3
Synchronized和Lock的区别
-
原始构成
-
synchronized是关键字属于JVM层面,
-
monitorenter( 底层是通过monitor对象来完成,其实wait/notify等方法也依赖于monitor对象只有在同步块或方法中才能i漏wait/notify等方法
-
monitorexit
-
-
Lock是具体类(java. util. concurrent. locks. Lock)是api层面的锁
-
-
使用方法.
-
synchronized不需要用户去手动释放锁,当synchronized代码执行完后系统会自动让线程释放对锁的占用
-
ReentrantLock则需要用户去手动释放锁,若没有主动释放锁,就有可能导致出现死锁现象。
- 需要lock()和unlock()方法配合try/finally语句块来完成。
-
-
等待是否可中断
-
synchronized不可中断,除非抛出是常或者正常运行完成
-
ReentrantLock可中断
- 设置超时方法tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- lockInterruptibly()放代码块中,调用interrupt() 方法可中断
-
-
加锁是否公平
-
synchronized非公平锁
-
Reentrantlock两者都可以,默认公平锁,构造方法可以传入boolean值, true为公平锁,false 为非公平锁
-
-
锁绑定多个条件Condition
-
synchronized没有
-
ReentrantLock用来实现分组唤醒需要唤醒的线程们,可以精确唤醒,而不是像synchronized要么随机唤耀- 个线程要么唤醒全部线程。
-
锁绑定多个条件Condition
题目:多线程之间按顺序调用,实现A->B->C三个线程启动,要求如下:
A打印5次,B打印10次,C打印15次
紧接着
A打印5次,B打印10次,C打印15次
。。。。。
打印10轮
// LOCK -- await -- signal
class ShareResource {
private int number = 1;//A:1.B:2,C:3
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition c3 = lock.newCondition();
public void print5() {
lock.lock();
try {
//1判断
while (number != 1) {
c1.await();
}
//2干活
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
//3通知
number = 2;
c2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print10() {
lock.lock();
try {
//1判断
while (number != 2) {
c2.await();
}
//2干活
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
//3通知
number = 3;
c3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print15() {
lock.lock();
try {
//1判断
while (number != 3) {
c3.await();
}
//2干活
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + i);
}
//3通知
number = 1;
c1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class SyncAndReentrantLockDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareResource shareResource = new ShareResource();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.print5();
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.print10();
}
}, "B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
shareResource.print15();
}
}, "C").start();
}
}
应用:生产者消费者模式
传统版
//LOCK -- await -- signal
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 一个初始值为0的变量 两个线程交替操作 一个加1 一个减1来5轮
* <p>
* 1.线程操作资源类
* 2.判断 干活 通知
* 3.防止虚假唤醒机制
*/
public class ProdConsumerTraditionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareData shareData = new ShareData();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
try {
shareData.increment();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
try {
shareData.deIncrement();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BB").start();
}
}
/**
* 共享资源类
*/
class ShareData {
private int num = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
public void increment() throws Exception {
lock.lock();
try {
//判断
while (num != 0) {
//等待 不生产
condition.await();
}
//干活
num++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + num);
//通知唤醒
condition.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void deIncrement() throws Exception {
lock.lock();
try {
//判断
while (num == 0) {
//等待 不生产
condition.await();
}
//干活
num--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + num);
//通知唤醒
condition.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
阻塞队列版
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* volatile/CAS/atomicInteger/BlockQueue/线程交互/原子引用
**/
public class ProdConsumerBlockQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyResource myResource = new MyResource(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10));
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t生产线程启动");
try {
myResource.myProd();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "Prod").start();
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t消费线程启动");
try {
myResource.myConsumer();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "consumer").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("时间到,停止活动");
myResource.stop();
}
}
class MyResource {
/**
* 默认开启 进行生产消费的交互
*/
private volatile boolean flag = true;
/**
* 默认值是0
*/
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = null;
public MyResource(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
System.out.println(blockingQueue.getClass().getName());
}
public void myProd() throws Exception {
String data = null;
boolean returnValue;
while (flag) {
data = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet() + "";
returnValue = blockingQueue.offer(data, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (returnValue) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 插入队列数据" + data + "成功");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 插入队列数据" + data + "失败");
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t 生产停止 表示 flag = " + flag);
}
public void myConsumer() throws Exception {
String result = null;
while (flag) {
result = blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (null == result || "".equalsIgnoreCase(result)) {
flag = false;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "超过2m没有取到 消费退出");
return;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "消费队列" + result + "成功");
}
}
public void stop() throws Exception {
flag = false;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号