A Framework for Reinforcement Learning and Planning

发表时间:2020
文章要点:这篇文章是篇综述,主要从RL和planning的异同入手,总结了对解决MDP这类问题的公共因素,放到一起称作framework for reinforcement learning and planning (FRAP)的框架。首先文章提出,RL和planning的主要区别就是环境模型是已知的还是未知的,通常RL用在环境model未知的情况,planning用在model已知的情况,然后两者结合起来就是现在的model based RL。然后这个综述主要回答了六个问题:
- where to put our computational effort,
- where to make our next trial,
- how to estimate the cumulative return,
- how to back-up,
- how to represent the solution
- how to update the solution.
对于环境的区别,主要有reversible和irreversible。Reversible是说环境state可以重置和回访,就相当于可以时间倒流。具体可以分为Reversible analytic和Reversible sample。Reversible analytic就是说环境的转移概率完全是已知的,可以直接计算,Reversible sample就是不知道具体形式,但是可以query的形式去收集样本。然后irreversible就是说环境不能重置和回访某个状态,就相当于只能往前走,不能回头。然后RL通常就用在irreversible的场景下,planning用在reversible的场景下(RL fundamentally limits itself to irreversible sample environments, planning always assumes a reversible environment (either analytic or sample))。
先介绍了planning。先定义planning为any process that takes a model as input and produces or improves a policy for interacting with the modeled environment。包括Dynamic programming (DP),Heuristic search,Sample-based search,Gradient-based planning,Direct optimization。然后planning又可以分为open-loop和closed-loop,open-loop就是说先全部规划好,然后依次执行动作。closed-loop就是说每次执行一个动作,都要重新再planning一次。
然后介绍了Model-free reinforcement learning,主要介绍了Value and policy,On- and off-policy bootstrapping,Exploration,Generalization,Direct policy optimization。
然后说了下Model-based reinforcement learning,主要介绍了Sampling additional data,Multi-step approximate dynamic programming,Backward trials,Value gradients。
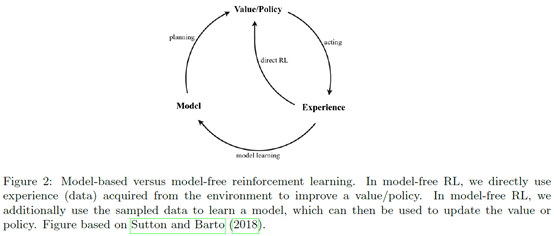
介绍了基本概念之后,就开始回答六个问题

-
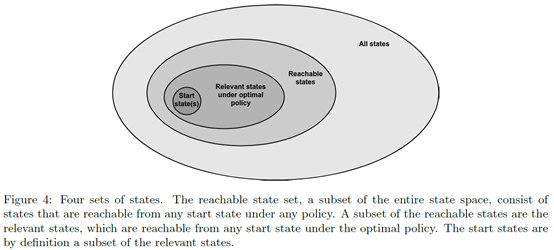
Where to put our computational effort主要就说在那些state上做计算,总共划分了四类:All states,Reachable states,Relevant states,Start states。
![]()
得出的结论就是,从Start states开始,考虑Reachable states,最后最优策略再将范围缩小到Relevant states。 -
Where to make the next trial包括的问题有Candidate set selection,Exploration,One versus two phase exploration,Reverse trials。
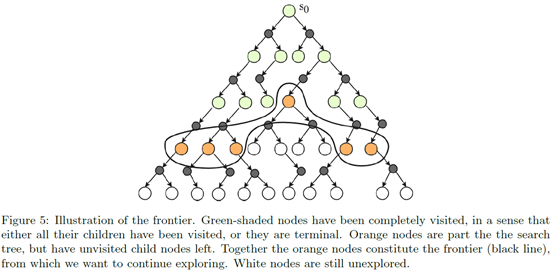
Candidate set selection就是说next trial在哪些状态上进行,主要分为两个方法:Step-wise和Frontier。Step-wise就是考虑当前状态下的所有可行动作。Frontier就是考虑那些最前沿的状态,比如树搜索里面那些叶节点。所以Step-wise在每个step都有一个新Candidate set,而Frontier在每个episode里只有一个Candidate set。Step-wise可能会重复探索相同的地方,而Frontier每次都会探索到新的地方,但是通常也会越来越大,比如建树就会越来越大。
![]()
Exploration主要就是说如何在candidate set里去选状态或者动作来探索。主要讲了Random exploration,Value-based exploration,State-based exploration。
One versus two phase exploration就是说前面的exploration都是一个阶段,exploration可以有两个阶段,first plan in our head, and then decide on an action in the real world,所以两个阶段分别是
![]()
这里多阶段的意思主要指不同阶段使用了不同的exploration策略(Multiple phases refers to the use of different exploration policies from the same state within one algorithm)。
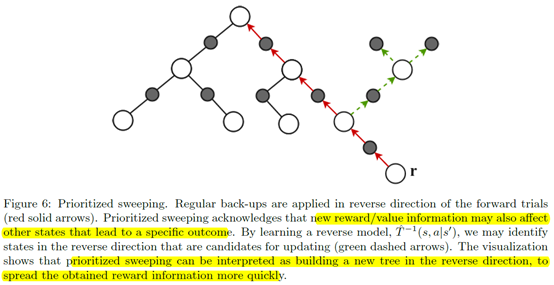
Reverse trials就是说前面的trials都是正向的,其实也可以反向trials,比如从后面的状态来推前面的promising的状态
![]()
-
How to estimate the cumulative return主要就是说如何估计值,包括Sample depth,Bootstrap function。
Sample depth就是说可以无穷步,可以1步,也可以n步,还可以用Reweighted的方式比如eligibility traces和importance sampling。Bootstrap function包括Learned value function和Heuristic。 -
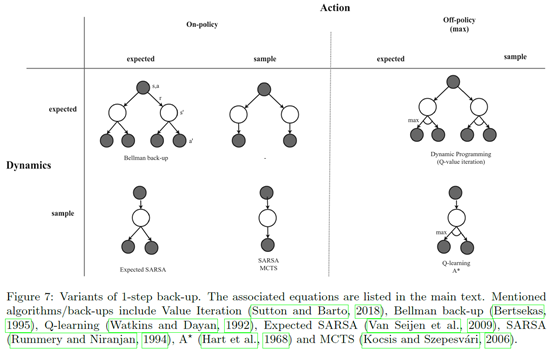
How to back-up就是说如何回溯
![]()
主要就要么是用算期望的方式,要么用采样的方式。具体的更新如下
![]()
-
How to represent the solution主要就是说近似什么值,和用什么函数来做。比如近似value,policy或者两个一起。函数的话可以用tabular,也可以用函数近似。
-
How to update the solution主要就是讲用什么loss以及update rules。Loss就是MSE,Cross-entropy policy loss之类的。update rules主要就是梯度更新,区别就是直接更新policy,还是policy结合value更新,或者policy结合model更新,或者model free更新等等。
最后文章总结了这些部分,并且指出the lines between planning and learning are
actually blurry, and frequently based on convention rather than necessity。
总结:提到了很多方向,以后可以关注关注,比如planning里的open-loop or closed-loop form;two phase exploration里面The first step (Plan) is of course only feasible when we have a reversible model; tree的表征是不是也可以做成连续的,而不是离散的节点。
疑问:无。

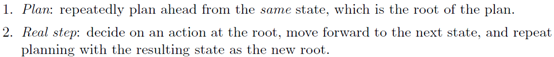
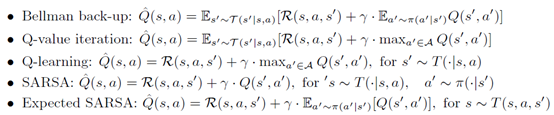

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号