二、
3、
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 union ww{ 5 char s[4]; 6 int k; 7 }; 8 9 struct node{ 10 int a,*b; 11 union ww c; 12 }; 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 int a[5],i,n=0x6162; 17 struct node s[5],*p; 18 for(i=0,p=s;i<5;i++,p++){ 19 p->b=a+i; 20 s[i].c.k=n++; 21 } 22 for(i=0;i<5;i++) 23 a[i]=i*10+10; 24 p=s; 25 printf("%d,",++*p->b); 26 printf("%d,",*++p->b); 27 printf("%c,",p++->c.s[0]); 28 printf("%d,",*++p->b); 29 printf("%c,",p->c.s[1]++); 30 printf("%x,",p++->c.k); 31 for(i=0,p=s;i<5;i++,p++) 32 printf("%d,",*p->b); 33 return 0; 34 }
运行结果:
丑就丑一点。。。有时间再整理

7、
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 int k; 7 char c='A'; 8 do{ 9 10 switch(c++){ 11 default : k=k*2;break; 12 case 'A':k++;break; 13 case 'B':k--; 14 case 'C':k+=2;break; 15 case 'D':k=k%2;continue; 16 } 17 k++; 18 }while(c<'F'); 19 printf("k=%d\n",k); 20 return 0; 21 }
运行结果:
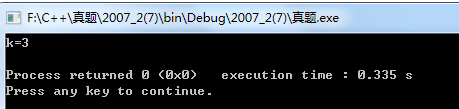
注意:
break语句在循环和switch语句中使用,用于终止最近的封闭代码块,如果在嵌套循环中,则只终止最近的循环。
continue语句在循环中使用,不能单独在switch中使用,可以在循环内的switch中使用,用于跳过当次循环,直接进入下一次循环。
比如:本题中continue后没经过k++;而是直接开始继续判断。而break;后是经过k++;的再进行判断。
8、
分析代码:
sub函数的功能是找数组中的最大整数的位置,这个位置是用数组的首元素的地址与偏移量*j来确定的,而这个偏移量保存在变量m中,所以main函数输出数组的最大元素为*(a+*n)<=>*(a+m)
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define N 10 4 int a[N]; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 void sub(int *,int *); 9 int i,*n,m=0,*t=a; 10 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 11 scanf("%d",a+i); 12 n=&m; 13 sub(t,n); 14 printf("%d",*(a+*n)); 15 return 0; 16 } 17 18 void sub(int *k,int *j){ 19 if(k<a+N){ 20 if(*k>*(a+*j)) 21 *j=k-a; 22 sub(k+1,j); 23 } 24 }
运行结果:
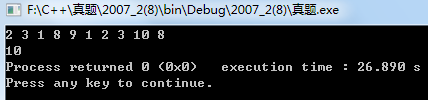
6、写出下面程序的功能(可举例说明程序的功能)
功能:检查在s1串中含有多少个s2这样的子串。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 5 int sub(char *s1,char *s2){ 6 int i,j,k,n=0; 7 for(i=0;*(s1+i);i++){ 8 for(j=i,k=0;*(s2+k)==*(s1+j)&&*(s1+j);k++,j++); 9 if(!*(s2+k)) 10 n++; 11 } 12 return n; 13 } 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 char s1[80],s2[80]; 18 int n; 19 gets(s1); 20 gets(s2); 21 printf("%d\n",sub(s1,s2)); 22 return 0; 23 }
运行结果如下:
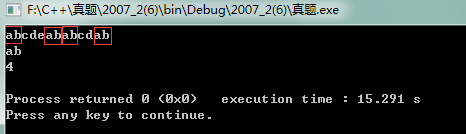
四、
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define N 3 4 #define M 5 5 6 float stu_ave(int (*p)[M]){ 7 int i,sum=0; 8 for(i=0;i<M;i++) 9 sum+=(*p)[i]; 10 return sum/5; 11 } 12 13 float cour_ave(int *pt){ 14 int i,sum=0; 15 for(i=0;i<N;i++,pt+=N) 16 sum+=*pt; 17 return sum/3; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 float stu_ave(int (*p)[M]); 22 float cour_ave(int *pt),(*p)(); 23 int score[N][M],i,j; 24 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 25 for(j=0;j<M;j++) 26 scanf("%d",&(*(score+i))[j]); 27 p=&stu_ave; 28 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 29 printf("%d:%f\n",i+1,(*p)(score+i)); 30 p=&cour_ave; 31 for(i=0;i<M;i++) 32 printf("%d:%f\n",i+1,(*p)(*score+i)); 33 return 0; 34 }
运行结果:
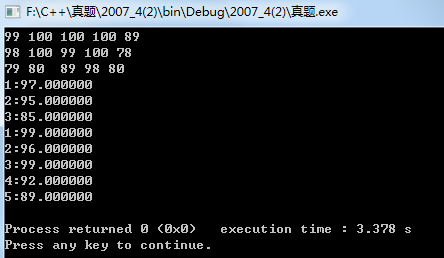
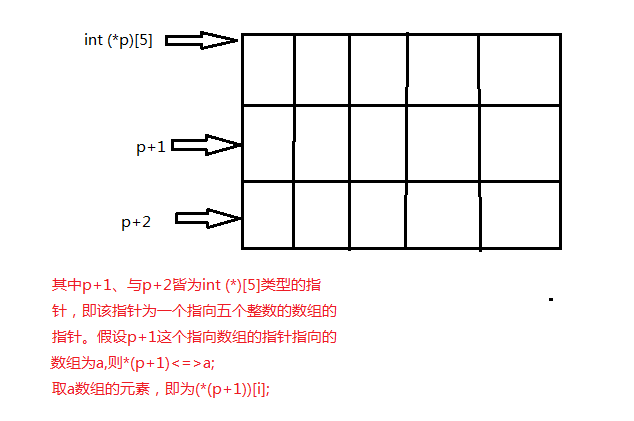
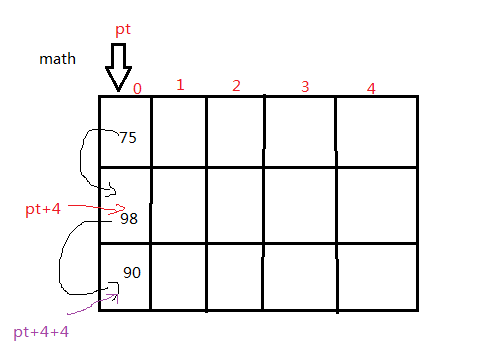
所以在统计每门课成绩的平均分时,只需要遍历第一个同学的所有有成绩就ok;
一、 单项:
五、编程序(每题15分,共30分)
若s1和s2是两个单链表存储的字符串,编程实现:找出串s1中第一个在串s2中出现的字符。若存在这样的字符将其从串s1中删除。
(这题我就不吐槽了,到底是只需要删除第一次出现的串s2,还是将s1串中含有s2串的都删除?哥们我好像理解题目意思理解错了。。。。)
要求:
(1)单个字符串链表的建立过程,写函数(create)实现,数据从键盘输入;
(2)查找及删除过程写一函数 (search)实现;
(3)主函数调用过程的create函数和search函数分别实现字符串链表的建立及查找功能,并在主函数中输出s1串的最后结果。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define SIZE sizeof(struct node) 4 struct node{ 5 char ch; 6 struct node *next; 7 }; 8 9 struct node * create(struct node *head){ 10 struct node *p,*q; 11 head=p=q=(struct node *)malloc(SIZE); 12 scanf("%c",&q->ch); 13 while(q->ch!='0'){ 14 p->next=q; 15 p=q; 16 q=(struct node *)malloc(SIZE); 17 scanf("%c",&q->ch); 18 } 19 p->next=NULL; 20 return head; 21 } 22 23 void Display(struct node *head){ 24 struct node *p=head; 25 while(p){ 26 printf("%c",p->ch); 27 p=p->next; 28 } 29 printf("\n"); 30 } 31 32 33 34 struct node * search(struct node *s1,struct node *s2){ 35 struct node *s1_head=(struct node *)malloc(SIZE); 36 s1_head->next=s1; 37 struct node *s1_pre=s1_head,*p=s1_head->next; 38 struct node *q; 39 struct node *begin,*end; 40 41 while(p){ 42 q=s2; 43 while(q&&(p->ch==q->ch)){//不知道为什么把这个判断的两个条件,把这个换个顺序就死循环。。。不知掉啊 44 p=p->next; 45 q=q->next; 46 } 47 48 if(q==NULL){ 49 //将结点删除 50 for(begin=s1_pre->next,end=p;begin<end;begin=begin->next) 51 free(begin); 52 53 s1_pre->next=p; 54 }else{ 55 s1_pre=p; 56 p=p->next; 57 } 58 } 59 s1=s1_head->next; 60 return s1; 61 62 } 63 int main() 64 { 65 struct node *s1,*s2; 66 s1=create(s1); 67 getchar(); 68 printf("s1:"); 69 Display(s1); 70 s2=create(s2); 71 getchar(); 72 printf("s2:"); 73 Display(s2); 74 s1=search(s1,s2); 75 printf("result:"); 76 Display(s1); 77 return 0; 78 }
运行结果:
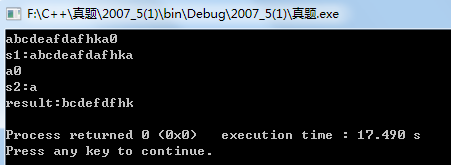
至于这个:
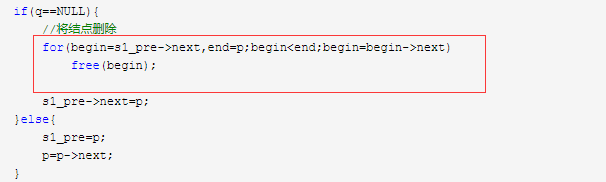
都可以,不过绿色图片的那个相对来说好一些。
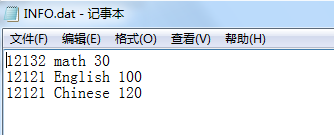
2.已知C: \goods\INFO. dat文件中存有数千种库存商品的信息,每种商品信息含三个内容:物资编号NO、商品名称和库存量NUM。
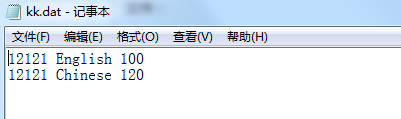
请编程通过检查全部库存量,在C盘goods目录下建立一个新的文件: KK. dat,它包括所有库存量大于50的商品编号、商品名称和库存量,并在屏幕上显示所有库存量大于50的商品名称。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 5 typedef struct goods{ 6 int no; 7 char name[20]; 8 int num; 9 }GOODS; 10 11 int main() 12 { 13 GOODS g; 14 FILE *in,*out; 15 char *p; 16 17 if((in=fopen("C:\\goods\\INFO.dat","r"))==NULL){ 18 printf("Can't open the file!\n"); 19 exit(1); 20 } 21 22 if((out=fopen("C:\\goods\\kk.dat","w+"))==NULL){ 23 printf("Can't open kk.dat.\n"); 24 exit(1); 25 } 26 27 fscanf(in,"%d%s%d",&g.no,p,&g.num); 28 strcpy(g.name,p); 29 while(!feof(in)){ 30 if(g.num>50){ 31 fprintf(out,"%d %s %d\n",g.no,g.name,g.num); 32 fprintf(stdout,"%d %s %d\n",g.no,g.name,g.num); 33 } 34 fscanf(in,"%d%s%d",&g.no,p,&g.num); 35 strcpy(g.name,p); 36 } 37 fclose(in); 38 fclose(out); 39 return 0; 40 }
运行结果:
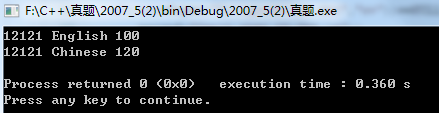
文件: