三、填空题
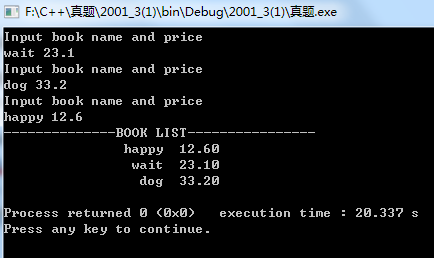
1、一下程序功能为:输入100本书的名称和单价,按照单价进行排序后输出。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define NUM 3//由于运行输入方便 所以将#define NUM 100 改成#define NUM 3 4 5 struct book{ 6 char name[20]; 7 float price; 8 }; 9 10 void sortbook(struct book term,struct book *pbook,int count){ 11 int k; 12 struct book *q,*pend=pbook; 13 for(k=0;k<count;k++,pend++);//用于移动pend到有序pbook数组的末端 14 15 for(;pbook<pend;pbook++) 16 if(pbook->price>term.price)//用于找插放的位置 这个条件说明是按照price从小到大排序 17 break; 18 19 for(q=pend-1;q>=pbook;q--) 20 *(q+1)=*q; 21 *pbook=term; 22 } 23 24 void printbook(struct book *pbook){ 25 printf("%20s %6.2f\n",pbook->name,pbook->price); 26 } 27 int main() 28 { 29 struct book term,books[NUM]; 30 int count; 31 32 for(count=0;count<NUM;count++){ 33 printf("Input book name and price\n"); 34 scanf("%s%f",term.name,&term.price); 35 sortbook(term,books,count); 36 } 37 printf("--------------BOOK LIST----------------\n"); 38 for(count=0;count<NUM;count++){ 39 printbook(&books[count]); 40 } 41 return 0; 42 }
运行结果:
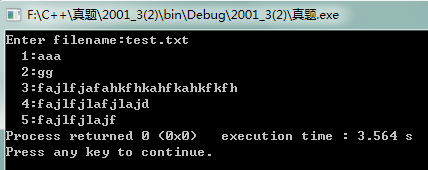
2、以下程序显示指定文件,在显示文件内容的同时加上行号。
技巧点在于:用flag变量来控制行号是否输出。
当flag=1时说明这一行已经读取完毕,要开始下一行了,输出 行号:读取的字符。当flag=0时,表示本行未读取完,还得继续读取,直接输出读取的字符即可,无效再加行号。
什么条件下改变flag?
由于fgets(char *buffer,int count,FILE *)函数,最多读取count-1个字符,假设count=20,则最多读取19个字符,最后一个位置buffer[19]用于存放'\0'.
当读取到'\n'时,结束读取,注意:fgets函数把'\n'读取了。
对于fget函数读取一行时读到什么时候停止?有三种情况
case1:遇到第一个换行符时,读完换行符后,停止。(没错,它读了换行符,和fscanf函数不一样)
case2:读取到字符个数为count-1时停止
case3:遇到文件结束符(换句话来说就是读取到文件结尾),然后fgets()函数会向末尾添加一个空字符以构成一个字符串。所以字符串的最大长度代表字符的最大数目再加上一个空字符。
综上:fgets函数读取一行到字符数组buffer时,字符串长度只有两种情况,strlen(buffer)==count-1 和strlen(buffer)<count-1
对于case1:读到遇到换行符为止,这种情况可能为strlen(buffer)<count-1或者strlen(buffer)==count-1且buffer[count-2]=='\n'
对于case2:strlen(buffer)==count-1
对于case3:strlen(buffer)<=count-1
也就是说:当strlen(buffer)<count-1||buffer[count-2]=='\n'时说明本行读取结束,flag置1代表下次读取完后前面要输出行号。否则,flag置0代表下次读取完直接输出无需输出行号
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 int main() 5 { 6 char s[20],filename[20]; 7 int flag=1,i=0,t=2; 8 FILE *fp; 9 printf("Enter filename:"); 10 gets(filename); 11 if((fp=fopen(filename,"r"))==NULL){ 12 printf("File open error!\n"); 13 exit(0); 14 } 15 16 while(!feof(fp)){ 17 while(fgets(s,20,fp)!=NULL){ 18 if(flag) 19 printf("%3d:%s",++i,s); 20 else 21 printf("%s",s); 22 if(strlen(s)!=19||s[18]=='\n') 23 flag=1; 24 else 25 flag=0; 26 } 27 } 28 fclose(fp); 29 return 0; 30 }
运行结果:
四、编程题
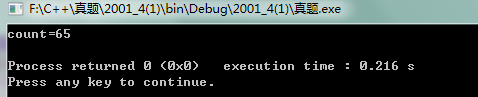
1.某人有10张3分的邮票和10张5分的邮票,问使用这些邮票可以组合出多少种不同面值的邮资。(例如:1张3分邮票加1张5分邮票可以组成8分的邮资:5张3分的邮票或3张5分的邮票都可以组成同样面值的邮资。)
算法:暴力枚举出所有的组合情况,借助组成的面值数组来进行统计,下标是组合的面值。把money数组中的数相加刚好是100,即100种组合情况。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 static int money[81];//因为10*3+10*5=80;从1-80开始存储 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int i,j; 9 int count=0;//面值种类个数 10 for(i=1;i<=10;i++){//3分 11 for(j=1;j<=10;j++){//5分 12 money[i*3+j*5]++; 13 } 14 15 } 16 for(i=8;i<=80;i++) 17 if(money[i]) 18 count++; 19 20 printf("count=%d\n",count); 21 return 0; 22 }
运行结果:
2.已知某数列前两项为2和3,其后继项根据前面最后两项的乘积,按下列规则生成:
(1)若乘积为一位数,则该乘积即为数列的后继项:
2)若乘积为二位数,则该乘积的十位数字和个位数字依次作为数列的两个后继项。
请编程序生成该数列的前N项,并求前N项的和。要求:生成该数列后继项及求和过程用函数实现,在主函数中调用该函数。

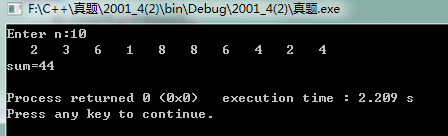
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define N 100 4 int a[N+1]; 5 void list_sum(int n){ 6 int count=2;//已经有两项了 7 int result,i; 8 int sum=0; 9 a[0]=2; 10 a[1]=3; 11 while(n>2&&count<n){ 12 result=a[count-1]*a[count-2]; 13 if(result>=10){ 14 a[count]=result/10; 15 a[count+1]=result%10; 16 count+=2; 17 }else{ 18 a[count]=result; 19 count++; 20 } 21 } 22 23 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 24 printf("%4d",a[i]); 25 sum+=a[i]; 26 } 27 printf("\nsum=%d\n",sum); 28 } 29 30 int main() 31 { 32 int n; 33 printf("Enter n:"); 34 scanf("%d",&n); 35 list_sum(n); 36 return 0; 37 }
运行结果:
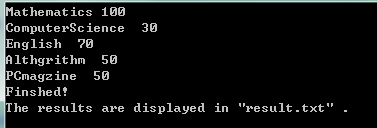
3.小刚假期同妈妈一起去书店,他选中了N本书,每本书的单价分别为p1,p2p3,...,pn元(均为整数)。不巧的是:妈妈只带了S (为整数)元钱,不够买这N本书(即: s<p1+p2+..+pn).为了让小刚过一个愉快的假期,妈妈同意将这S元钱全部用来买书。也就是小刚要从所选的N本书中选出M本,使得这M本的价格和刚好等于S.即:pi1+pi2+pi3+...+pim=S.请你编程序将所有满足这一条件的i1, i2, i3,..,im依次打印出来。
/*数据范例:data.txt*/
200
5
Mathematics 100
ComputerScience 30
English 70
Althgrithm 50
PCmagzine 50
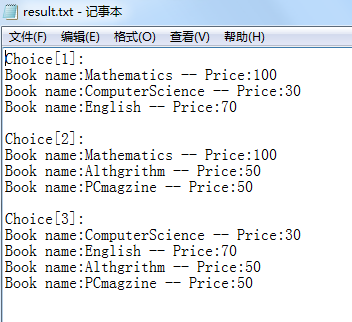
/*输出范例:result.txt*/
Choice[ 1]:
Book name: Mathematics -- Price: 100
Book name: ComputerScience -- Price: 30
Book name: English -- Price: 70
Choice[ 2]:
Book name: Mathematics -- Price: 100
Book name: Althgrithm -- Price: 50
Book name: PCmagzine -- Price: 50
Choice[ 3]:
Book name: ComputerScience -- Price: 30
Book name: English -- Price: 70
Book name: Althgrithm -- Price: 50
Book name: PCmagzine -- Price: 50

正式版:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define MAXN 100 4 5 6 typedef struct book{ 7 char name[20]; 8 int price; 9 }BOOK; 10 11 typedef struct stack{ 12 int top; 13 BOOK booklist[MAXN]; 14 }BOOKSTACK; 15 typedef unsigned long int ulint; 16 void selectbook(BOOK *books,int n,FILE *out); 17 void Push_stack(BOOKSTACK* package,BOOK a_book,int *top ); 18 int S,N;//带了S元 在N本中选取M本 19 20 int main() 21 { 22 FILE *fp,*out; 23 BOOK books[MAXN]; 24 int i; 25 if((fp=fopen("data.txt","r"))==NULL){ 26 printf("Cannot open the %s.\n","data.txt"); 27 exit(0); 28 } 29 30 if((out=fopen("result.txt","w"))==NULL){ 31 printf("Cannot open the %s.\n","result.txt"); 32 exit(0); 33 } 34 35 fscanf(fp,"%d%d",&S,&N); 36 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 37 fscanf(fp,"%s%d",books[i].name,&books[i].price); 38 39 selectbook(books,N,out); 40 fclose(fp); 41 fclose(out); 42 return 0; 43 } 44 45 46 47 /*共有N=5本书那么有00000-11111种选择 */ 48 void Push_stack(BOOKSTACK *package,BOOK a_book,int *top){ 49 package->booklist[(*top)++]=a_book; 50 } 51 52 void Print(BOOKSTACK packge,FILE *out,int *count){ 53 int i; 54 int len=packge.top; 55 fprintf(out,"Choice[%d]:\n",*count); 56 for(i=0;i<len;i++){ 57 fprintf(out,"Book name:%s -- Price:%d\n",packge.booklist[i].name,packge.booklist[i].price); 58 } 59 fprintf(out,"\n"); 60 } 61 62 void selectbook(BOOK *books,int n,FILE *out){ 63 int len=n; 64 ulint bit=1<<len; 65 ulint i,j,sum; 66 int count=0; 67 BOOKSTACK packge;//用于存放选择的书 68 69 for(i=1;i<bit;i++){ 70 //从1循环到2^N 71 sum=0; 72 packge.top=0; 73 for(j=0;j<len;j++){ 74 if((i&1<<j)!=0){ 75 //表示第j位已选 76 sum+=books[j].price; 77 78 Push_stack(&packge,books[j],&packge.top); 79 80 81 } 82 83 } 84 if(sum==S){ 85 count++; 86 Print(packge,out,&count); 87 } 88 } 89 printf("Finshed!\nThe results are displayed in \"result.txt\" .\n"); 90 91 }
运行结果已存入result.txt文件中.

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define MAXN 31 4 5 6 typedef struct book{ 7 char name[20]; 8 int price; 9 }BOOK; 10 11 typedef struct stack{ 12 int top; 13 BOOK booklist[MAXN]; 14 }BOOKSTACK; 15 16 void sortbook(BOOK *books,int n); 17 void selectbook(BOOK *books,int n); 18 BOOK Findcon(BOOK *books,int price,int n);//在books中查找出价格为x的书籍,并且返回这本书 19 20 void Push_stack(BOOKSTACK* package,BOOK a_book,int *top ); 21 int S,N;//带了S元 在N本中选取M本 22 23 int main() 24 { 25 FILE *fp; 26 BOOK books[MAXN]; 27 int i; 28 if((fp=fopen("data.txt","r"))==NULL){ 29 printf("Cannot open the file.\n"); 30 exit(0); 31 } 32 33 fscanf(fp,"%d%d",&S,&N); 34 /*printf("S=%d N=%d\n",S,N);*/ 35 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 36 fscanf(fp,"%s%d",books[i].name,&books[i].price); 37 /*for(i=0;i<N;i++) 38 printf("%s%4d\n",books[i].name,books[i].price);*/ 39 40 //对books根据price进行从小到大排序 41 sortbook(books,N); 42 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 43 printf("%s%4d\n",books[i].name,books[i].price); 44 45 selectbook(books,N);fclose(fp); 46 return 0; 47 } 48 49 void sortbook(BOOK *books,int n){ 50 int i,j,t;//用选择排序法从小到大排 51 BOOK temp; 52 for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){ 53 t=i; 54 for(j=i+1;j<n;j++){ 55 if(books[t].price>books[j].price) 56 t=j; 57 } 58 if(t!=i){ 59 temp=books[i]; 60 books[i]=books[t]; 61 books[t]=temp; 62 } 63 64 } 65 } 66 67 BOOK Findcon(BOOK *books,int price,int n){ 68 int low,high,mid; 69 low=0; 70 high=n-1; 71 while(low<high){ 72 mid=(low+high)/2; 73 if(books[mid].price>price) 74 high=mid-1; 75 else if(books[mid].price<price) 76 low=mid+1; 77 else 78 return books[mid]; 79 } 80 81 } 82 /*共有N=5本书那么有00000-11111种选择 */ 83 void Push_stack(BOOKSTACK *package,BOOK a_book,int *top){ 84 package->booklist[(*top)++]=a_book; 85 // printf("%s %d\n",a_book.name,a_book.price); 86 } 87 88 void Print(BOOKSTACK packge){ 89 int i; 90 int len=packge.top; 91 for(i=0;i<len;i++){ 92 printf("%s %4d\n",packge.booklist[i].name,packge.booklist[i].price); 93 } 94 } 95 void print0_1(int number){ 96 int mask=1<<4; 97 int i=16; 98 printf("number=%d\n",number); 99 for(;mask&&i;mask>>=1){ 100 printf("%d",number&mask?1:0); 101 i--; 102 } 103 printf("\n\n"); 104 } 105 void selectbook(BOOK *books,int n){ 106 int len=n; 107 int bit=1<<len; 108 int i,j,sum; 109 int count=0; 110 BOOKSTACK packge;//用于存放选择的书 111 112 for(i=1;i<bit;i++){ 113 //从1循环到2^N 114 sum=0; 115 packge.top=0; 116 for(j=0;j<len;j++){ 117 if((i&1<<j)!=0){ 118 //表示第j位已选 119 sum+=books[j].price; 120 // Print(packge); 121 Push_stack(&packge,books[j],&packge.top); 122 123 124 } 125 126 } 127 if(sum==S){ 128 count++; 129 printf("\n\n====================\n\n"); 130 print0_1(i); 131 printf("Choice[%d]:\n",count); 132 Print(packge); 133 printf("\n\n====================\n\n"); 134 135 } 136 } 137 138 139 }
方法二:用递归方法

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #define MAXN 31 4 5 6 typedef struct book{ 7 char name[20]; 8 int price; 9 }BOOK; 10 11 typedef struct stack{ 12 int top; 13 BOOK booklist[MAXN]; 14 }BOOKSTACK; 15 16 void sortbook(BOOK *books,int n); 17 void selectbook(BOOK *books,int pos,int n,int top,int sum); 18 BOOK Findcon(BOOK *books,int price,int n);//在books中查找出价格为x的书籍,并且返回这本书 19 20 void Push_stack(BOOKSTACK* package,BOOK a_book,int *top ); 21 int S,N;//带了S元 在N本中选取M本 22 int choice=1; 23 BOOKSTACK packge;//用于存放选择的书 24 FILE *in,*out; 25 int main() 26 { 27 28 BOOK books[MAXN]; 29 30 int i; 31 if((in=fopen("data.txt","r"))==NULL){ 32 printf("Cannot open the %s.\n","data.txt"); 33 exit(0); 34 } 35 36 if((out=fopen("result.txt","w"))==NULL){ 37 printf("Cannot open the %s.\n","result.txt"); 38 exit(0); 39 } 40 41 fscanf(in,"%d%d",&S,&N); 42 43 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 44 fscanf(in,"%s%d",books[i].name,&books[i].price); 45 46 for(i=0;i<N;i++) 47 printf("%s%4d\n",books[i].name,books[i].price); 48 sortbook(books,N); 49 selectbook(books,0,N,0,0); 50 fclose(in);fclose(out); 51 printf("Finshed!\nThe results are displayed in \"result.txt\" .\n"); 52 return 0; 53 } 54 55 void selectbook(BOOK *books,int pos,int n,int top,int sum){ 56 57 if(pos>=n||sum>=S){ 58 if(sum==S){ 59 packge.top=top; 60 fprintf(out,"\nChoice[%d]:\n",choice++); 61 Print(packge); 62 } 63 return ; 64 } 65 packge.booklist[top]=books[pos]; 66 selectbook(books,pos+1,n,top+1,sum+books[pos].price); 67 selectbook(books,pos+1,n,top,sum); 68 69 } 70 71 72 void Print(BOOKSTACK packge){ 73 int i; 74 int len=packge.top; 75 for(i=0;i<len;i++){ 76 fprintf(out,"Book name:%s -- Price:%d\n",packge.booklist[i].name,packge.booklist[i].price); 77 } 78 fprintf(out,"\n"); 79 } 80 81 void sortbook(BOOK *books,int n){ 82 int i,j,t;//用选择排序法从大到小排 83 BOOK temp; 84 for(i=0;i<n-1;i++){ 85 t=i; 86 for(j=i+1;j<n;j++){ 87 if(books[t].price<books[j].price) 88 t=j; 89 } 90 if(t!=i){ 91 temp=books[i]; 92 books[i]=books[t]; 93 books[t]=temp; 94 } 95 96 } 97 }
运行结果: