(central university of finance and economics)
1997年
1、
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int m,n; int two_f,three_f; two_f=2; three_f=3; printf("Enter m and n:\n"); printf("m="); scanf("%d",&m); printf("n="); scanf("%d",&n); while(m&&n){ if(two_f<three_f){ printf("%d ",two_f); two_f*=2; m--; }else{ printf("%d ",three_f); three_f*=3; n--; } } while(m){ printf("%d ",two_f); two_f*=2; m--; } while(n){ printf("%d ",three_f); three_f*=3; n--; } printf("\n"); return 0; }
2、
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include<malloc.h> 4 5 typedef struct number{ 6 struct number *next; 7 int number; 8 }NUM; 9 10 NUM* CreSinList(int a[],int n){ 11 int i; 12 NUM *head; 13 NUM *r,*p;//尾插法 14 head=(NUM *)malloc(sizeof(NUM)); 15 head->next=NULL; 16 head->number='\0'; 17 r=head; 18 19 for(i=0;i<n;i++){ 20 p=(NUM *)malloc(sizeof(NUM)); 21 p->number=a[i]; 22 p->next=NULL; 23 r->next=p; 24 r=p; 25 } 26 r->next=NULL; 27 return head; 28 } 29 30 void Del(NUM *pre,NUM *cur){ 31 printf("yes"); 32 pre->next=cur->next; 33 free(cur); 34 } 35 36 void Prin(NUM *cur){ 37 printf("%d ",cur->number); 38 } 39 int FindNum(NUM *head,NUM *pre,NUM *cur,int key){ 40 41 int find=0; 42 pre=head; 43 cur=pre->next; 44 while(cur!=NULL){ 45 if(cur->number==key){ 46 Prin(cur); 47 Del(pre,cur); 48 find=1; 49 break; 50 } 51 pre=cur; 52 cur=cur->next; 53 } 54 return find; 55 } 56 int main() 57 { 58 59 60 int a[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; 61 int n=sizeof(a)/sizeof(int); 62 int keynum; 63 int find=0; 64 NUM *head,*pre,*cur; 65 66 head=CreSinList(a,n); 67 //head=head->next;//(找了几十分钟就是多加了这条语句,导致运行完一个,头结点到一下个断了) 68 pre=head; 69 cur=head->next; 70 printf("Enter a integer(1-10) you want find:"); 71 scanf("%d",&keynum); 72 while(1){ 73 if(cur==NULL){ 74 printf("Sorry the List is NULL.\n"); 75 break; 76 } 77 find=FindNum(head,pre,cur,keynum); 78 if(find){ 79 printf("Find it,and already deleted!\n"); 80 }else{ 81 printf("there is not the number you had entered in the sort from low to high,please enter other number.\n"); 82 } 83 printf("Enter a integer(1-10) you want find:"); 84 scanf("%d",&keynum); 85 pre=head;//每次从开头找 86 cur=head->next; 87 } 88 return 0; 89 }
1999年
1.假设银行一年整存零取的月息为0.63%。现在某人手中有一笔钱,他打算在今后的五年中每年的年底取出1000元,到第五年时刚好取完,请算出他存钱时应存入多少。
注意:用的是单利率而不是复利率
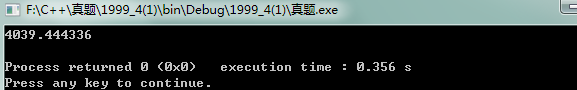
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 5 float f(int year){ 6 float money=0.0; 7 while(--year){ 8 money=(1000+money)/(1+0.0063*12); 9 } 10 return money; 11 } 12 13 int main() 14 { 15 float money=0.0; 16 money=f(6); 17 printf("%f\n",money); 18 return 0; 19 } 20 21 22 /* 23 int main(){ 24 int year=2; 25 float money=4039.444336; 26 while(year<=6){ 27 28 money=money*(1+0.0063*12)-1000; 29 if(fabs(money)<=1e-4) 30 money=0.0; 31 printf("year=%d money=%f\n",year,money); 32 year++; 33 } 34 return 0; 35 } 36 */
运行结果:
2.用一元人民币兑换成1分、2分和5分硬币,共有多少种不同的兑换方法。
方法一:暴力枚举法
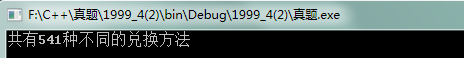
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 int count=0; 7 int i,j,k; 8 9 for(i=0;i<=100;i++){ 10 for(j=0;j<=50;j++){ 11 for(k=0;k<=20;k++){ 12 if(i+2*j+5*k==100) 13 count++; 14 } 15 } 16 } 17 printf("共有%d种不同的兑换方法\n",count); 18 return 0; 19 }
运行结果:
方法二:缩小枚举范围
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 int count=0; 7 int i,j,k; 8 9 for(i=0;i<=100;i++){ 10 for(j=0;j<=(100-i)/2;j++){ 11 for(k=0;k<=(100-i-2*j)/5;k++){ 12 if(i+2*j+5*k==100){ 13 count++; 14 printf("i=%d j=%d k=%d\n",i,j,k); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 printf("共有%d种不同的兑换方法\n",count); 20 return 0; 21 }
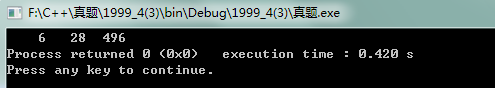
3.如果一个数恰好等于它的因子之和,则称该数为“完全数”。如: 6的因于是1、2、3,而6=1+2+3,则6是个“完全数”。试求出1.000以内的全部“完全数”。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 int sum; 7 8 int i=1,k=1; 9 for(i=1;i<1000;i++){ 10 sum=0;//判断i是否为完数 11 for(k=1;k<i;k++) 12 if(i%k==0)//此时k为i的一个因子 13 sum+=k; 14 if(sum==i) 15 printf("%5d",i); 16 } 17 return 0; 18 }
运行结果: