烟台CSP-S核心算法DAY 3
烟台CSP-S核心算法DAY 3
上午
二分函数
介绍经典的lower_bound和upper_bound的用法捏qwq
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 7;
int read()
{
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch > '9' || ch < '0')
{
if(ch == '-')
{
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
}
while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0')
{
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
long long Qmi(int a, int b, int p)
{
if(b == 0)
{
return 1%p;
}
if(b == 1)
{
return a%p;
}
long long ans = Qmi(a, b/2, p);
ans = ans*ans%p;
if(b % 2)
{
ans = ans*a%p;
}
return ans % p;
}
bool isprime(long long x)
{
if(x <= 1)
{
return false;
}
if(x == 2)
{
return true;
}
if(x % 2 == 0)
{
return false;
}
for(int i = 3; i <= sqrt(x); i += 2)
{
if(x % i == 0)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int a[MAXN];
set<int> se;
int main()
{
int n = 10;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
a[i] = i * i;
}
auto x = lower_bound(a + 1, a + n + 1, 15);
x--;
cout<<*x<<'\n';
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
se.insert(i*i);
}
auto y = se.lower_bound(15);
cout<<*y<<endl;
return 0;
}
DP
DP的基本三要素
1.状态
2.转移方程:状态之间的关系
3.初始化:边界状态如何计算
怎么定状态?
将题目中所有在变化的量定为状态
动态规划的本质就是在枚举所有情况
状态の例题壹式·qwq的野外旅行
基本的定状态
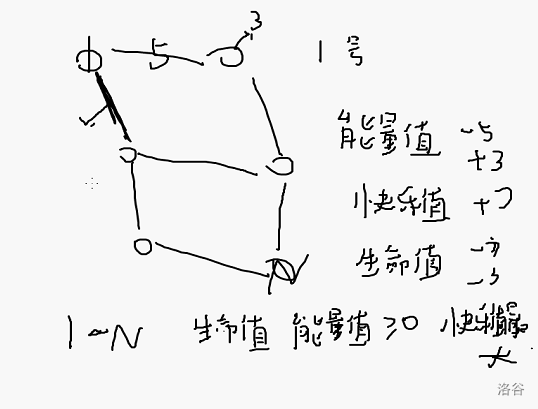
永远铭记:
将题目中所有在变化的量定为状态——zhx
于是我们简单得到

状态の例题贰式·qwq的足球队
一定不要惧怕六、七维的状态——zhx

Fibonacci数列
int main()
{//O(n)
f[0]=0;
f[1]=1;
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++)
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
cout << f[n] << "\n";
}
当然,这是一道很基础的DP(把入门组的小朋友抓起来也是可以完成的)
但是,我们最基础的Fibonacci DP是\(O(n)\)的
对于\(N \leq 1e9\)的数据,我们的代码就炸了
于是,我们考虑矩阵加速
矩阵优化DP(DDP、动态DP)
我们使用矩阵乘法优化DP的目的就是用一个矩阵(A矩阵、初始状态)乘上另一个矩阵(B矩阵)将状态向后推一个
但是我们怎么得到B矩阵
推出B矩阵的方法
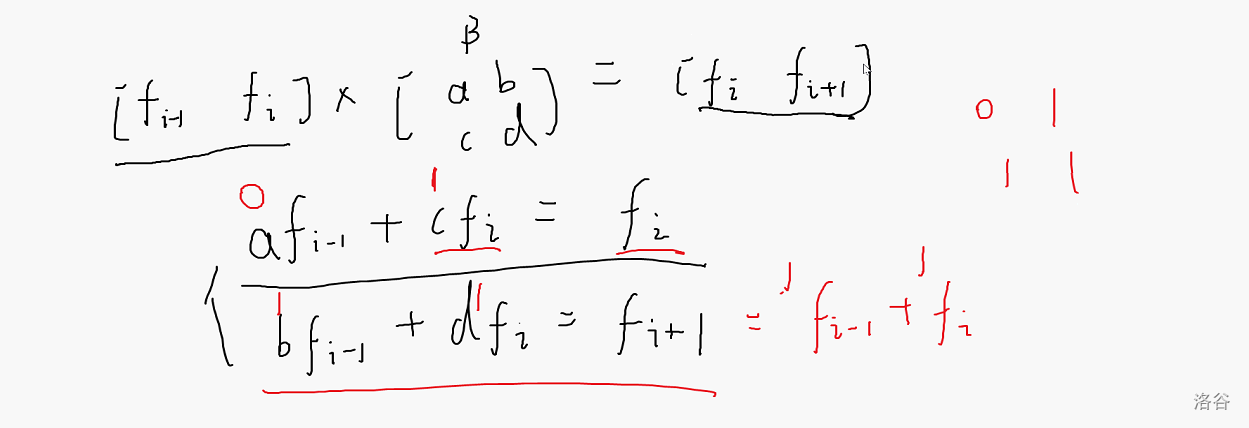
通过已知的A矩阵和C矩阵(状态)反推B矩阵
利用矩阵乘法的运算规律列出方程
然后待定系数法
矩阵加法
矩阵加法一般是指两个矩阵把其相对应元素加在一起的运算
当然,矩阵加法是简单且基本无作用的
于是,我们矩阵乘法
矩阵乘法
要求第一个矩阵的列数必须等于第二个矩阵的行数,它们的乘积定义为一个新矩阵,新矩阵的行数等于第一个矩阵的行数,列数等于第二个矩阵的列数
两矩阵的对应位置相乘,再求和,得到C矩阵的每个元素的值(A矩阵的每行与B矩阵的每列对应)
矩阵乘法CODE
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 7;
int read()
{
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch > '9' || ch < '0')
{
if(ch == '-')
{
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
}
while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0')
{
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
long long Qmi(int a, int b, int p)
{
if(b == 0)
{
return 1%p;
}
if(b == 1)
{
return a%p;
}
long long ans = Qmi(a, b/2, p);
ans = ans*ans%p;
if(b % 2)
{
ans = ans*a%p;
}
return ans % p;
}
bool isprime(long long x)
{
if(x <= 1)
{
return false;
}
if(x == 2)
{
return true;
}
if(x % 2 == 0)
{
return false;
}
for(int i = 3; i <= sqrt(x); i += 2)
{
if(x % i == 0)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
struct matrix
{
int n, m;
int a[110][110];
matrix()
{
n = m = 0;
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
}
}x, y, z;
matrix operator*(const matrix &x, const matrix &y)
{//O(n^3) 0.5112s
matrix z;
z.n = x.n;
z.m = y.m;
for(int i = 1; i <= z.n; i++)
{
for(int k = 1; k <= x.m; k++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= z.m; j++)
{
z.a[i][j] = z.a[i][j] + x.a[i][k] * y.a[k][j];
}
}
}
return z;
}
int main()
{
return 0;
}
这里有一个很有意思的问题
你会发现,我们遍历的顺序,即使在复杂度相同的情况下,也会对代码速度有大的变化——zhx
先观察事实
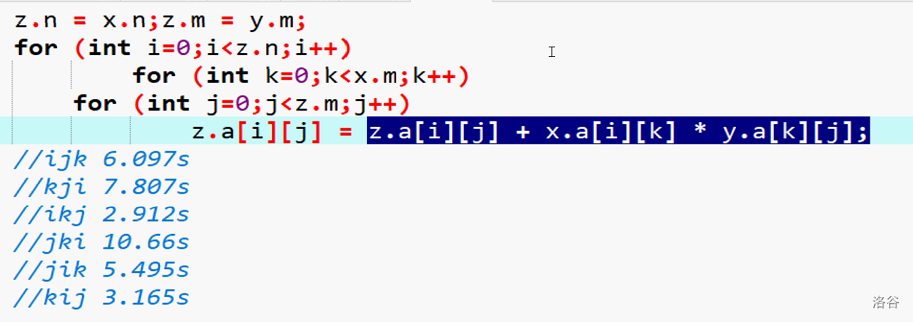
太不牛了!
遍历的顺序竟然对代码速度的快慢有关系!
但是我们发现他们的复杂度都是\(O(n^3)\)的
于是,我们不妨把评测鸡拆开,发现一个神奇的现象
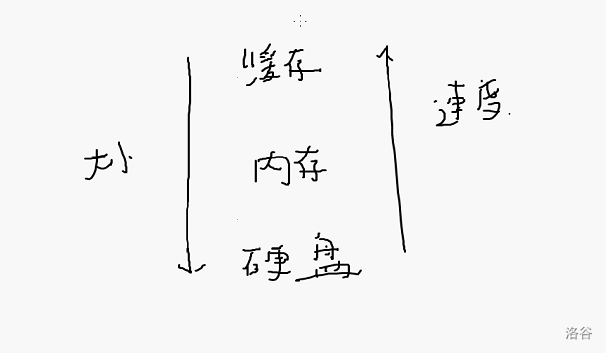
缓存很快!(比内存快约100倍)
我们来看机器工作原理
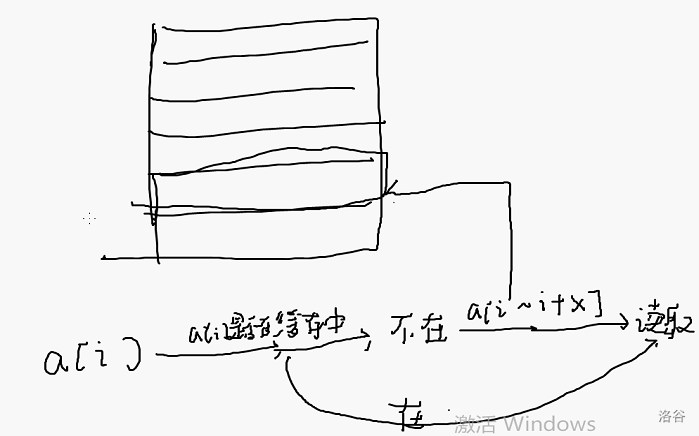
这很神奇!
∴我们要尽量按照数组定义的维度来枚举(可能会差3~4倍的速度)
单位矩阵的定义
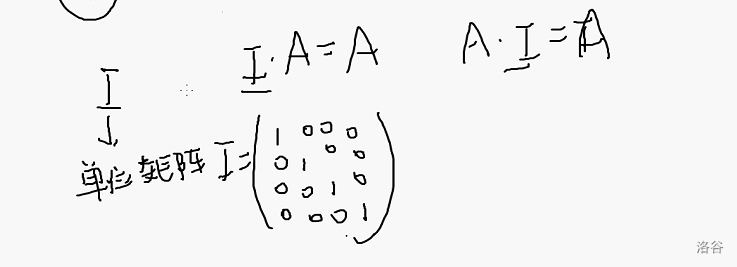
快速幂矩阵加速Fibonacci
由于我们使用了矩阵快速幂,所以我们求Fibonacci第n项的时间复杂度就变成了\(O(log N)\)的
这很牛!
CODE
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct matrix
{
int n,m;
int a[3][3];
matrix()
{
n=m=0;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
}
}A,B;
matrix operator*(const matrix &x,const matrix &y)
{//O(n^3)
//matrix z;
z.n = x.n;z.m = y.m;
for (int i=1;i<=z.n;i++)
for (int k=1;k<=x.m;k++)
for (int j=1;j<=z.m;j++)
z.a[i][j] = z.a[i][j] + x.a[i][k] * y.a[k][j];
return z;
}
matrix ksm(matrix a,int b)//计算a^b
{
if (b==0)
{
matrix c;
c.n=c.m=a.n;
for (int i=1;i<=c.n;i++)
c.a[i][i]=1;
return c;
}
matrix c = ksm(a,b/2);//c=a^(b/2)
c=c*c;
if (b&1) c=c*a;
return c;
}
int main()
{
A.n=1;A.m=2;
A.a[1][1]=0;A.a[1][2]=1;
B.n=2;B.m=2;
B.a[1][1]=0;B.a[1][2]=1;
B.a[2][1]=1;B.a[2][2]=1;
C = A * ksm(B,n);
cout << C.a[1][1] << "\n";
return 0;
}
例题

矩阵乘法优化DP的要求(特征)
1.\(f[i-1] -> f[i]\)
2.转移系数M与i无关
怎样推导式子
先升维,再降维,再观察矩阵乘法
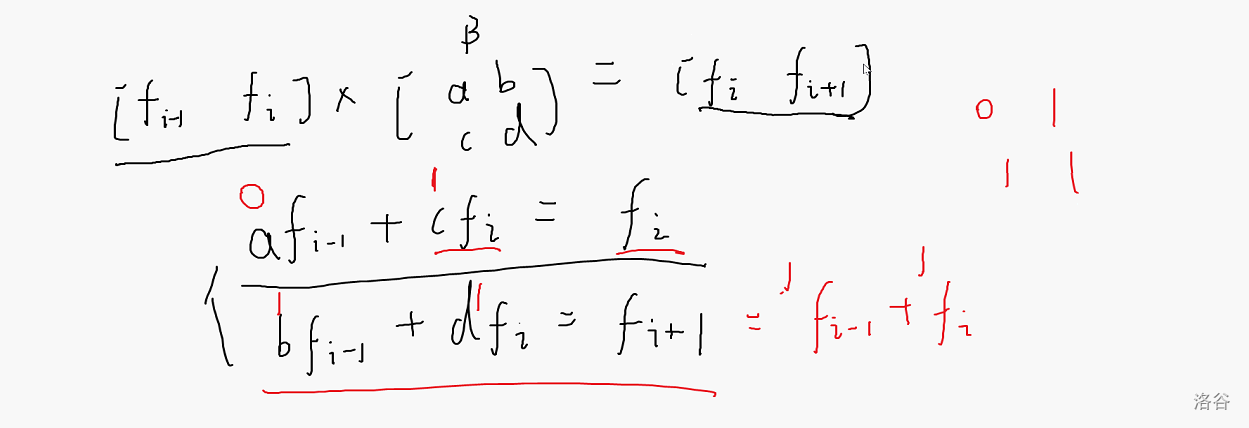
伟大的中午
踢球扭到大腿根了qwqwqwqwq
DPの类型
区间DP、树形DP、数位DP、状压DP、背包DP、排列DP、博弈DP、插头DP、一般DP
排列DP
1~n每个数都出现且只出现一次
1~n有\(n!\)种合法的排列
\(n!\)种排列有多少种能满足条件
排列DPの核心:插入(从大到小/从小到大)
排列DP状态的第一位都是插入到i了
(从小到大1~i 从大到小i~n)
例题

先设计出状态

我们简单地想到转移方程
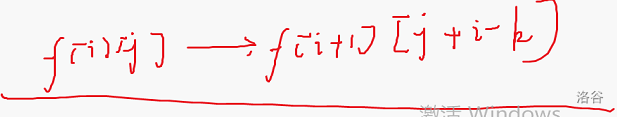
CODE(\(O(n^4)\))
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e5 + 7;
int read()
{
int x = 0, w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch > '9' || ch < '0')
{
if(ch == '-')
{
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
}
while(ch <= '9' && ch >= '0')
{
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x * w;
}
long long Qmi(int a, int b, int p)
{
if(b == 0)
{
return 1%p;
}
if(b == 1)
{
return a%p;
}
long long ans = Qmi(a, b/2, p);
ans = ans*ans%p;
if(b % 2)
{
ans = ans*a%p;
}
return ans % p;
}
bool isprime(long long x)
{
if(x <= 1)
{
return false;
}
if(x == 2)
{
return true;
}
if(x % 2 == 0)
{
return false;
}
for(int i = 3; i <= sqrt(x); i += 2)
{
if(x % i == 0)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int f[1001][1001];
int n;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
f[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= (i * (i-1)) >> 1; j++)
{
for(int k = 0; k <= i; k++)
{
f[i+1][j+i-k] += f[i][j];
}
}
}
return 0;
}
奇偶性优化(\(O(n^2)\))
int main()
{
cin>>n;
f[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= 1; j++)
{
for(int k = 0; k <= i; k++)
{
f[i+1][(j+i-k) % 2] += f[i][j];
}
}
}
return 0;
}
思路做法(\(O(n)\))
但是我们可以算出
1~n 有几个奇数、偶数,这样就优化到 \(O(n)\)了
数学(\(O(不知道反正更快)\))
\(\dfrac{n!}{2}\) qwq
正经的排列DP题——zhx
区间DP
区间DP的重点:区间
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/B2104
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/B2105
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3390
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1939
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2886
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4159
https://hydro.ac/p/bzoj-P3583
https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeChef-LEMOVIE#author=GPT_zh
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1775
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1880
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1063
https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-1651#author=DeepSeek_zh
https://vjudge.net/problem/HDU-4632#author=DeepSeek_zh
https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeChef-LEMOUSE#author=DeepSeek_zh


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号