FRCN文本检测(转)
[源码分析]Text-Detection-with-FRCN
<ul class="article_tags clearfix csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click" data-mod="popu_377" style="display: none;">
<li class="tit">标签:</li>
<!-- [endarticletags]-->
</ul>
<ul class="right_bar">
<li><button class="btn-noborder"><i class="icon iconfont icon-read"></i><span class="txt">659</span></button></li>
<li class="edit" style="display: none;">
<a class="btn-noborder" href="https://mp.csdn.net/postedit/78580970">
<i class="icon iconfont icon-bianji"></i><span class="txt">编辑</span>
</a>
</li>
<li class="del" style="display: none;">
<a class="btn-noborder" onclick="javascript:deleteArticle(fileName);return false;">
<i class="icon iconfont icon-shanchu"></i><span class="txt">删除</span>
</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div id="article_content" class="article_content csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click" data-mod="popu_519" data-dsm="post" style="overflow: hidden;">
<div class="htmledit_views">
<p><span style="white-space:pre;"></span><span style="white-space:pre;"></span><span style="white-space:pre;"></span><span style="white-space:pre;"></span><span style="font-size:12px;"><a href="https://github.com/jugg1024/Text-Detection-with-FRCN" target="_blank">Text-Detection-with-FRCN</a>项目是基于<a href="https://github.com/rbgirshick/py-faster-rcnn" target="_blank">py-faster-rcnn</a>项目在场景文字识别领域的扩展。对Text-Detection-with-FRCN的理解过程,本质上是对py-faster-rcnn的理解过程。我个人认为,初学者,尤其是对caffe还不熟悉的时候,在理解整个项目的过程中,会有以下困惑:</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">1.程序入口</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">2.数据是如何准备的?</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">3.整个网络是如何构建的?</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">4.整个网络是如何训练的?</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;"><span style="white-space:pre;"></span>那么,接下来,以我的理解,结合论文和源代码,一步步进行浅析。</span></p><p><br></p><p><span style="font-size:24px;">一.程序入口</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">训练阶段:</span></p><p><span style="font-size:18px;">入口一</span>:<span style="font-size:12px;">/py-faster-rcnn/experiments/scripts/faster_rcnn_end2end.sh</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">-- ></span></p><p><br></p><p><span style="font-size:18px;">入口二</span>: <span style="font-size:12px;">/py-faster-rcnn/tools/train_net.py</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">在train_net中:</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">1.定义数据格式,获得imdb,roidb;</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">2.开始训练网络。</span></p><p></p><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 923px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_1" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_1" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=1&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span>train_net(args.solver, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model, max_iters) </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">train_net(args.solver, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model, max_iters)</pre><p></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">train_net定义在/py-faster-rcnn/lib/fast_rcnn/train.py中</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">--></span></p><p><br></p><p><span style="font-size:18px;">入口三</span>:<span style="font-size:12px;">/py-faster-rcnn/lib/fast_rcnn/train.py</span></p><p><span style="font-size:12px;">在train_net函数中:</span></p><p></p><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 1207px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_2" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_2" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=2&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span>roidb = filter_roidb(roidb) </span></span></li><li class=""><span>sw = SolverWrapper(solver_prototxt, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=pretrained_model) </span></li><li class="alt"><span>model_paths = sw.train_model(max_iters) </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="keyword">return</span><span> model_paths </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">roidb = filter_roidb(roidb)
sw = SolverWrapper(solver_prototxt, roidb, output_dir, pretrained_model=pretrained_model)
model_paths = sw.train_model(max_iters)
return model_paths
这样,就开始对整个网络进行训练了。
在solver_prototxt中,定义了train_prototxt。在train_prototxt中,定义了各种层,这些层组合起来,形成了训练网络的结构。
-->
入口四:/py-faster-rcnn/models/coco_text/VGG16/faster_rcnn_end2end/train.prototxt
先举例说明形式:
1.自定义Caffe Python layer
- layer {
- name: 'input-data'
- type: 'Python'
- top: 'data'
- top: 'im_info'
- top: 'gt_boxes'
- python_param {
- module: 'roi_data_layer.layer'
- layer: 'RoIDataLayer'
- param_str: "'num_classes': 2"
- }
- }
layer {
name: 'input-data'
type: 'Python'
top: 'data'
top: 'im_info'
top: 'gt_boxes'
python_param {
module: 'roi_data_layer.layer'
layer: 'RoIDataLayer'
param_str: "'num_classes': 2"
}
}在自定义的caffe python layer中:type为’python';
python_param中:
module为模块名,通常也是文件名。module: 'roi_data_layer.layer':说明这一层定义在roi_data文件夹下面的layer中
layer为模块里的类名。layer:'RoIDataLayer':说明该类的名字为'RoIDataLayer'
param_str为传入该层的参数。
2.caffe中原有的定义好的层,一般用c++定义。
- layer {
- name: "conv1_1"
- type: "Convolution"
- bottom: "data"
- top: "conv1_1"
- param {
- lr_mult: 0
- decay_mult: 0
- }
- param {
- lr_mult: 0
- decay_mult: 0
- }
- convolution_param {
- num_output: 64
- pad: 1
- kernel_size: 3
- }
- }
layer {
name: "conv1_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1_1"
param {
lr_mult: 0
decay_mult: 0
}
param {
lr_mult: 0
decay_mult: 0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 64
pad: 1
kernel_size: 3
}
}入口一: /py-faster-rcnn/tools/train_net.py
在train_net中:
获得imdb,roidb:imdb, roidb = combined_roidb(args.imdb_name)
进入位于 /py-faster-rcnn/tools/train_net.py,combined_roidb中:- def combined_roidb(imdb_names):
- def get_roidb(imdb_name):
- imdb = get_imdb(imdb_name)
- print 'Loaded dataset
{:s}for training'.format(imdb.name) - imdb.set_proposal_method(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD)
- print 'Set proposal method: {😒}'.format(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD)
- roidb = get_training_roidb(imdb)
- return roidb
- roidbs = [get_roidb(s) for s in imdb_names.split('+')]
- roidb = roidbs[0]
- if len(roidbs) > 1:
- for r in roidbs[1:]:
- roidb.extend(r)
- imdb = datasets.imdb.imdb(imdb_names)
- else:
- imdb = get_imdb(imdb_names)
- return imdb, roidb
def combined_roidb(imdb_names):
def get_roidb(imdb_name):
imdb = get_imdb(imdb_name)
print 'Loaded dataset{:s}for training'.format(imdb.name)
imdb.set_proposal_method(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD)
print 'Set proposal method: {😒}'.format(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD)
roidb = get_training_roidb(imdb)
return roidbroidbs = [get_roidb(s) for s in imdb_names.split('+')] roidb = roidbs[0] if len(roidbs) > 1: for r in roidbs[1:]: roidb.extend(r) imdb = datasets.imdb.imdb(imdb_names) else: imdb = get_imdb(imdb_names) return imdb, roidb</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">先看imdb是如何产生的,然后看如何借助imdb产生roidb:</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">进入位于 /py-faster-rcnn/lib/datasets/factory.py,get_imdb中:</span><br></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 3614px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_6" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_6" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=6&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> get_imdb(name): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="comment">"""Get an imdb (image database) by name."""</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">if</span><span> </span><span class="keyword">not</span><span> __sets.has_key(name): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">raise</span><span> KeyError(</span><span class="string">'Unknown dataset: {}'</span><span>.format(name)) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">return</span><span> __sets[name]() </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def get_imdb(name): """Get an imdb (image database) by name.""" if not __sets.has_key(name): raise KeyError('Unknown dataset: {}'.format(name)) return __sets[name]()</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">由此可见,get_imdb函数的实现原理:_sets是一个字典,字典的key是数据集的名称,字典的value是一个lambda表达式(即一个函数指针)。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">在前面的文章中提到过,这里已经将coco_text数据集转化为pascal_voc数据集的格式。因此,这里使用的数据集的名称为pascal_voc。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">在faster_rcnn_end2end.sh中,定义了:</span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 3893px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_7" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_7" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=7&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span>case $DATASET </span><span class="keyword">in</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> pascal_voc) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> TRAIN_IMDB=<span class="string">"voc_2007_trainval"</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> TEST_IMDB=<span class="string">"voc_2007_test"</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> PT_DIR=<span class="string">"coco_text"</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> ITERS=<span class="number">70000</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> ;; </span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">case $DATASET inpascal_voc)
TRAIN_IMDB="voc_2007_trainval"
TEST_IMDB="voc_2007_test"
PT_DIR="coco_text"
ITERS=70000
;;
- # Set up voc_<year><split> using selective search "fast" mode
- for year in ['2007', '2012']:
- for split in ['train', 'val', 'trainval', 'test']:
- name = 'voc{}{}'.format(year, split)
- _sets[name] = (lambda split=split, year=year: pascal_voc(split, year))
# Set up voc<year><split> using selective search "fast" mode所以,这里实际执行的是pascal_voc函数。
for year in ['2007', '2012']:
for split in ['train', 'val', 'trainval', 'test']:
name = 'voc_{}{}'.format(year, split)
_sets[name] = (lambda split=split, year=year: pascal_voc(split, year))
- class pascal_voc(imdb):
- def init(self, image_set, year, devkit_path=None):
- imdb.init(self, 'voc' + year + '' + image_set)
- self._year = year
- self._image_set = image_set
- # self._devkit_path = self._get_default_path() if devkit_path is None </span>
- # else devkit_path
- self._devkit_path = os.path.join(cfg.ROOT_DIR, '..', 'datasets', 'train_data')
- self._data_path = os.path.join(self._devkit_path, 'formatted_dataset')
- self._classes = ('background', # always index 0
- 'text')
- self._class_to_ind = dict(zip(self.classes, xrange(self.num_classes)))
- self._image_ext = '.jpg'
- self._image_index = self._load_image_set_index()
- # Default to roidb handler
- self._roidb_handler = self.selective_search_roidb
- self._salt = str(uuid.uuid4())
- self._comp_id = 'comp4'
- # PASCAL specific config options
- self.config = {'cleanup' : True,
- 'use_salt' : True,
- 'use_diff' : False,
- 'matlab_eval' : False,
- 'rpn_file' : None,
- 'min_size' : 2}
- assert os.path.exists(self._devkit_path),
- 'VOCdevkit path does not exist: {}'.format(self._devkit_path)
- assert os.path.exists(self.data_path),
- 'Path does not exist: {}'.format(self.data_path)
class pascal_voc(imdb):
def init(self, image_set, year, devkit_path=None):
imdb.init(self, 'voc' + year + '' + image_set)
self._year = year
self._image_set = image_set
# self._devkit_path = self._get_default_path() if devkit_path is None
# else devkit_path
self._devkit_path = os.path.join(cfg.ROOT_DIR, '..', 'datasets', 'train_data')
self._data_path = os.path.join(self._devkit_path, 'formatted_dataset')
self._classes = ('background', # always index 0
'text')
self._class_to_ind = dict(zip(self.classes, xrange(self.num_classes)))
self._image_ext = '.jpg'
self._image_index = self._load_image_set_index()
# Default to roidb handler
self._roidb_handler = self.selective_search_roidb
self._salt = str(uuid.uuid4())
self._comp_id = 'comp4'# PASCAL specific config options self.config = {'cleanup' : True, 'use_salt' : True, 'use_diff' : False, 'matlab_eval' : False, 'rpn_file' : None, 'min_size' : 2} assert os.path.exists(self._devkit_path), \ 'VOCdevkit path does not exist: {}'.format(self._devkit_path) assert os.path.exists(self._data_path), \ 'Path does not exist: {}'.format(self._data_path)</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">在pascal_voc的构造函数中,定义了imdb的结构,那么roidb与imdb有什么关系呢?</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">回到 /py-faster-rcnn/tools/train_net.py的combined_roidb中:</span><br><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 5137px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_10" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_10" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=10&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span>imdb = get_imdb(imdb_name) </span></span></li><li class=""><span><span class="keyword">print</span><span> </span><span class="string">'Loaded dataset `{:s}` for training'</span><span>.format(imdb.name) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span>imdb.set_proposal_method(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD) </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="keyword">print</span><span> </span><span class="string">'Set proposal method: {:s}'</span><span>.format(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span>roidb = get_training_roidb(imdb) </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="keyword">return</span><span> roidb </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;"> imdb = get_imdb(imdb_name) print 'Loaded dataset `{:s}` for training'.format(imdb.name) imdb.set_proposal_method(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD) print 'Set proposal method: {:s}'.format(cfg.TRAIN.PROPOSAL_METHOD) roidb = get_training_roidb(imdb) return roidb</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">其中,set_proposal_method方法在/py-faster-rcnn/lib/datasets/imdb.py中:</span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 5357px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_11" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_11" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=11&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> set_proposal_method(</span><span class="special">self</span><span>, method): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> method = eval(<span class="string">'self.'</span><span> + method + </span><span class="string">'_roidb'</span><span>) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="special">self</span><span>.roidb_handler = method </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def set_proposal_method(self, method): method = eval('self.' + method + '_roidb') self.roidb_handler = method</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">所以set_proposal_method是用于设置生成proposal的方法。</span></div><div><br></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">get_training_roidb方法在/py-faster-rcnn/lib/fast-rcnn/train.py中:</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 5599px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_12" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_12" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=12&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> get_training_roidb(imdb): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="comment">"""Returns a roidb (Region of Interest database) for use in training."""</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">if</span><span> cfg.TRAIN.USE_FLIPPED: </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">print</span><span> </span><span class="string">'Appending horizontally-flipped training examples...'</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> imdb.append_flipped_images() </span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">print</span><span> </span><span class="string">'done'</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">print</span><span> </span><span class="string">'Preparing training data...'</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> rdl_roidb.prepare_roidb(imdb) </span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">print</span><span> </span><span class="string">'done'</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">return</span><span> imdb.roidb </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def get_training_roidb(imdb): """Returns a roidb (Region of Interest database) for use in training.""" if cfg.TRAIN.USE_FLIPPED: print 'Appending horizontally-flipped training examples...' imdb.append_flipped_images() print 'done' print 'Preparing training data...' rdl_roidb.prepare_roidb(imdb) print 'done' return imdb.roidb</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">get_training_roidb方法中包含了两个方法:append_flipped_images() 和prepare_roidb()方法。<br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">a) append_flipped_images():对imdb中涉及到的图像做了一个水平镜像,使得trainval中的图片的数量加倍。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">b) prepare_roidb():定义roidb的相关信息。</span><br></div><div><br></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">其中,append_flipped_images()方法定义在/py-faster-rcnn/lib/datasets/imdb.py中:</span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 6022px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_13" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_13" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=13&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> append_flipped_images(</span><span class="special">self</span><span>): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> num_images = <span class="special">self</span><span>.num_images </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> widths = <span class="special">self</span><span>._get_widths() </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">for</span><span> i </span><span class="keyword">in</span><span> xrange(num_images): </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> boxes = <span class="special">self</span><span>.roidb[i][</span><span class="string">'boxes'</span><span>].copy() </span></span></li><li class=""><span> oldx1 = boxes[:, <span class="number">0</span><span>].copy() </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> oldx2 = boxes[:, <span class="number">2</span><span>].copy() </span></span></li><li class=""><span> boxes[:, <span class="number">0</span><span>] = widths[i] - oldx2 - </span><span class="number">1</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> boxes[:, <span class="number">2</span><span>] = widths[i] - oldx1 - </span><span class="number">1</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">assert</span><span> (boxes[:, </span><span class="number">2</span><span>] >= boxes[:, </span><span class="number">0</span><span>]).all() </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> entry = {<span class="string">'boxes'</span><span> : boxes, </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="string">'gt_overlaps'</span><span> : </span><span class="special">self</span><span>.roidb[i][</span><span class="string">'gt_overlaps'</span><span>], </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="string">'gt_classes'</span><span> : </span><span class="special">self</span><span>.roidb[i][</span><span class="string">'gt_classes'</span><span>], </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="string">'flipped'</span><span> : </span><span class="special">True</span><span>} </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="special">self</span><span>.roidb.append(entry) </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="special">self</span><span>._image_index = </span><span class="special">self</span><span>._image_index * </span><span class="number">2</span><span> </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def append_flipped_images(self): num_images = self.num_images widths = self._get_widths() for i in xrange(num_images): boxes = self.roidb[i]['boxes'].copy() oldx1 = boxes[:, 0].copy() oldx2 = boxes[:, 2].copy() boxes[:, 0] = widths[i] - oldx2 - 1 boxes[:, 2] = widths[i] - oldx1 - 1 assert (boxes[:, 2] >= boxes[:, 0]).all() entry = {'boxes' : boxes, 'gt_overlaps' : self.roidb[i]['gt_overlaps'], 'gt_classes' : self.roidb[i]['gt_classes'], 'flipped' : True} self.roidb.append(entry) self._image_index = self._image_index * 2</pre><div><br></div><span style="font-size:12px;">prepare_roidb()方法定义在/py-faster-rcnn/lib/roi_data_layer/roidb.py中:</span><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 6415px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_14" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_14" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=14&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> prepare_roidb(imdb): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="comment">"""Enrich the imdb's roidb by adding some derived quantities that</span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"> are useful for training. This function precomputes the maximum</span> </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="comment"> overlap, taken over ground-truth boxes, between each ROI and</span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"> each ground-truth box. The class with maximum overlap is also</span> </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="comment"> recorded.</span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"> """</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> sizes = [PIL.Image.open(imdb.image_path_at(i)).size </span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">for</span><span> i </span><span class="keyword">in</span><span> xrange(imdb.num_images)] </span></span></li><li class=""><span> roidb = imdb.roidb </span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">for</span><span> i </span><span class="keyword">in</span><span> xrange(len(imdb.image_index)): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> roidb[i][<span class="string">'image'</span><span>] = imdb.image_path_at(i) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> roidb[i][<span class="string">'width'</span><span>] = sizes[i][</span><span class="number">0</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class=""><span> roidb[i][<span class="string">'height'</span><span>] = sizes[i][</span><span class="number">1</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># need gt_overlaps as a dense array for argmax</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> gt_overlaps = roidb[i][<span class="string">'gt_overlaps'</span><span>].toarray() </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># max overlap with gt over classes (columns)</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> max_overlaps = gt_overlaps.max(axis=<span class="number">1</span><span>) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># gt class that had the max overlap</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> max_classes = gt_overlaps.argmax(axis=<span class="number">1</span><span>) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> roidb[i][<span class="string">'max_classes'</span><span>] = max_classes </span></span></li><li class=""><span> roidb[i][<span class="string">'max_overlaps'</span><span>] = max_overlaps </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># sanity checks</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="comment"># max overlap of 0 => class should be zero (background)</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> zero_inds = np.where(max_overlaps == <span class="number">0</span><span>)[</span><span class="number">0</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">assert</span><span> all(max_classes[zero_inds] == </span><span class="number">0</span><span>) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># max overlap > 0 => class should not be zero (must be a fg class)</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> nonzero_inds = np.where(max_overlaps > <span class="number">0</span><span>)[</span><span class="number">0</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">assert</span><span> all(max_classes[nonzero_inds] != </span><span class="number">0</span><span>) </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def prepare_roidb(imdb): """Enrich the imdb's roidb by adding some derived quantities that are useful for training. This function precomputes the maximum overlap, taken over ground-truth boxes, between each ROI and each ground-truth box. The class with maximum overlap is also recorded. """ sizes = [PIL.Image.open(imdb.image_path_at(i)).size for i in xrange(imdb.num_images)] roidb = imdb.roidb for i in xrange(len(imdb.image_index)): roidb[i]['image'] = imdb.image_path_at(i) roidb[i]['width'] = sizes[i][0] roidb[i]['height'] = sizes[i][1] # need gt_overlaps as a dense array for argmax gt_overlaps = roidb[i]['gt_overlaps'].toarray() # max overlap with gt over classes (columns) max_overlaps = gt_overlaps.max(axis=1) # gt class that had the max overlap max_classes = gt_overlaps.argmax(axis=1) roidb[i]['max_classes'] = max_classes roidb[i]['max_overlaps'] = max_overlaps # sanity checks # max overlap of 0 => class should be zero (background) zero_inds = np.where(max_overlaps == 0)[0] assert all(max_classes[zero_inds] == 0) # max overlap > 0 => class should not be zero (must be a fg class) nonzero_inds = np.where(max_overlaps > 0)[0] assert all(max_classes[nonzero_inds] != 0)</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">由此可见,<span style="color:#ff0000;">roidb是imdb的一个成员变量,roidb是一个list(list的每个元素对应一张图片)</span>。其中,list中的每个元素是一个字典,字典中存放的key包括:boxes, gt_overlaps, gt_classes, flipped, seg_areas, image, width, height, max_classes, max_overlaps。至此,就利用我们提供的数据集,准备好了roidb的相关信息。<br><br><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">那么,真正读取数据到内存的地方是在哪儿呢?</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">在/py-faster-rcnn/lib/roi_data_layer/layer.py文件中:</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">在RoIDataLayer类的forward(self,bottom,top)函数中,</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">利用blobd = self._get_next_minibatch(roidb, num_classes),产生了需要的blobs.</span></div><div><br></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">_get_next_minibatch函数调用了minibatch.py文件中的get_minibatch(roidb, num_classes)函数。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">get_minibatch函数又调用了同为minibatch.py文件中的_get_image_blob(roidb, scale_inds)函数。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 7360px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_15" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_15" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=15&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> _get_image_blob(roidb, scale_inds): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="comment">"""Builds an input blob from the images in the roidb at the specified</span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"> scales.</span> </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="comment"> """</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> num_images = len(roidb) </span></li><li class=""><span> processed_ims = [] </span></li><li class="alt"><span> im_scales = [] </span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">for</span><span> i </span><span class="keyword">in</span><span> xrange(num_images): </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> im = cv2.imread(roidb[i][<span class="string">'image'</span><span>]) </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">if</span><span> roidb[i][</span><span class="string">'flipped'</span><span>]: </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> im = im[:, ::-<span class="number">1</span><span>, :] </span></span></li><li class=""><span> target_size = cfg.TRAIN.SCALES[scale_inds[i]] </span></li><li class="alt"><span> im, im_scale = prep_im_for_blob(im, cfg.PIXEL_MEANS, target_size, </span></li><li class=""><span> cfg.TRAIN.MAX_SIZE) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> im_scales.append(im_scale) </span></li><li class=""><span> processed_ims.append(im) </span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def _get_image_blob(roidb, scale_inds): """Builds an input blob from the images in the roidb at the specified scales. """ num_images = len(roidb) processed_ims = [] im_scales = [] for i in xrange(num_images): im = cv2.imread(roidb[i]['image']) if roidb[i]['flipped']: im = im[:, ::-1, :] target_size = cfg.TRAIN.SCALES[scale_inds[i]] im, im_scale = prep_im_for_blob(im, cfg.PIXEL_MEANS, target_size, cfg.TRAIN.MAX_SIZE) im_scales.append(im_scale) processed_ims.append(im)</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">通过cv2.imread,实现了将图片读取到内存。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">在_get_image_blob函数中,可以看到图片会被缩放到预先定义的size。其中,短边为cfg.TRAIN.SCALES,长边最长不能超过cfg.TRAIN.MAX_SIZE。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">回到get_minibatch函数中,可以看到:</span></div><div><br></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 7904px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_16" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_16" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=16&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"># Get the input image blob, formatted for caffe</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> im_blob, im_scales = _get_image_blob(roidb, random_scale_inds) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li><li class=""><span> blobs = {<span class="string">'data'</span><span>: im_blob} </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span>..... </span></li><li class=""><span> blobs[<span class="string">'im_info'</span><span>] = np.array( </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> [[im_blob.shape[<span class="number">2</span><span>], im_blob.shape[</span><span class="number">3</span><span>], im_scales[</span><span class="number">0</span><span>]]], </span></span></li><li class=""><span> dtype=np.float32) </span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;"> # Get the input image blob, formatted for caffe im_blob, im_scales = _get_image_blob(roidb, random_scale_inds) blobs = {'data': im_blob}......
blobs['im_info'] = np.array(
[[im_blob.shape[2], im_blob.shape[3], im_scales[0]]],
dtype=np.float32)
也就是,对于一副任意大小的P×Q图像(假设P为短边,Q为长边),首先reshape到M×N,其中M由cfg.TRAIN.SCALES决定,N由cfg.TRAIN.MAX_SIZE决定。blob中的data为reshape后的图像。im_info=[M,N,scale_factor]则保存了此次缩放的所有信息。
- layer {
- name: "rpn_conv/3x3"
- type: "Convolution"
- bottom: "conv5_3"
- top: "rpn/output"
- param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
- param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
- convolution_param {
- num_output: 512
- kernel_size: 3 pad: 1 stride: 1
- weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
- bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
- }
- }
layer {
name: "rpn_conv/3x3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv5_3"
top: "rpn/output"
param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 512
kernel_size: 3 pad: 1 stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
}
}- layer {
- name: "rpn_cls_score"
- type: "Convolution"
- bottom: "rpn/output"
- top: "rpn_cls_score"
- param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
- param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
- convolution_param {
- num_output: 18 # 2(bg/fg) 9(anchors)
- kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
- weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
- bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
- }
- }
- layer {
- name: "rpn_bbox_pred"
- type: "Convolution"
- bottom: "rpn/output"
- top: "rpn_bbox_pred"
- param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
- param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
- convolution_param {
- num_output: 36 # 4 * 9(anchors)
- kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
- weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
- bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
- }
- }
layer {
name: "rpn_cls_score"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "rpn/output"
top: "rpn_cls_score"
param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 18 # 2(bg/fg) * 9(anchors)
kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
}
}
layer {
name: "rpn_bbox_pred"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "rpn/output"
top: "rpn_bbox_pred"
param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 36 # 4 * 9(anchors)
kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
}
}

- layer {
- name: 'rpn-data'
- type: 'Python'
- bottom: 'rpn_cls_score'
- bottom: 'gt_boxes'
- bottom: 'im_info'
- bottom: 'data'
- top: 'rpn_labels'
- top: 'rpn_bbox_targets'
- top: 'rpn_bbox_inside_weights'
- top: 'rpn_bbox_outside_weights'
- python_param {
- module: 'rpn.anchor_target_layer'
- layer: 'AnchorTargetLayer'
- param_str: "'feat_stride': 16"
- }
- }
layer {
name: 'rpn-data'
type: 'Python'
bottom: 'rpn_cls_score'
bottom: 'gt_boxes'
bottom: 'im_info'
bottom: 'data'
top: 'rpn_labels'
top: 'rpn_bbox_targets'
top: 'rpn_bbox_inside_weights'
top: 'rpn_bbox_outside_weights'
python_param {
module: 'rpn.anchor_target_layer'
layer: 'AnchorTargetLayer'
param_str: "'feat_stride': 16"
}
}- array([[ -83., -39., 100., 56.],
- [-175., -87., 192., 104.],
- [-359., -183., 376., 200.],
- [ -55., -55., 72., 72.],
- [-119., -119., 136., 136.],
- [-247., -247., 264., 264.],
- [ -35., -79., 52., 96.],
- [ -79., -167., 96., 184.],
- [-167., -343., 184., 360.]])
array([[ -83., -39., 100., 56.],
[-175., -87., 192., 104.],
[-359., -183., 376., 200.],
[ -55., -55., 72., 72.],
[-119., -119., 136., 136.],
[-247., -247., 264., 264.],
[ -35., -79., 52., 96.],
[ -79., -167., 96., 184.],
[-167., -343., 184., 360.]])
这个是rpn/output输出的feature map的(0,0)位置的anchor坐标。其中每行的4个值[x1,y1,x2,y2]代表矩阵左上角和右下角点的坐标。一共有9行,代表feature map中的每个点都会生成9个anchors。
- def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],
- scales=2np.arange(3, 6)):
- """
- Generate anchor (reference) windows by enumerating aspect ratios X
- scales wrt a reference (0, 0, 15, 15) window.
- """
- base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1
- ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios)
- anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales)
- for i in xrange(ratio_anchors.shape[0])])
- return anchors
def generate_anchors(base_size=16, ratios=[0.5, 1, 2],
scales=2np.arange(3, 6)):
"""
Generate anchor (reference) windows by enumerating aspect ratios X
scales wrt a reference (0, 0, 15, 15) window.
"""base_anchor = np.array([1, 1, base_size, base_size]) - 1 ratio_anchors = _ratio_enum(base_anchor, ratios) anchors = np.vstack([_scale_enum(ratio_anchors[i, :], scales) for i in xrange(ratio_anchors.shape[0])]) return anchors</pre><div><br></div><span style="font-size:12px;">b)设置不同的长宽比和面积</span><br><br></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 11932px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_22" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_22" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=22&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="comment">"""</span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"> Enumerate a set of anchors for each aspect ratio wrt an anchor.</span> </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="comment"> """</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) </span></li><li class=""><span> size = w * h </span></li><li class="alt"><span> size_ratios = size / ratios </span></li><li class=""><span> ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios)) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> hs = np.round(ws * ratios) </span></li><li class=""><span> anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">return</span><span> anchors </span></span></li><li class=""><span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> _scale_enum(anchor, scales): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="comment">"""</span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"> Enumerate a set of anchors for each scale wrt an anchor.</span> </span></li><li class=""><span><span class="comment"> """</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li><li class=""><span> w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> ws = w * scales </span></li><li class=""><span> hs = h * scales </span></li><li class="alt"><span> anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) </span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">return</span><span> anchors </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def _ratio_enum(anchor, ratios): """ Enumerate a set of anchors for each aspect ratio wrt an anchor. """ w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) size = w * h size_ratios = size / ratios ws = np.round(np.sqrt(size_ratios)) hs = np.round(ws * ratios) anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) return anchorsdef _scale_enum(anchor, scales):
"""
Enumerate a set of anchors for each scale wrt an anchor.
"""w, h, x_ctr, y_ctr = _whctrs(anchor) ws = w * scales hs = h * scales anchors = _mkanchors(ws, hs, x_ctr, y_ctr) return anchors</pre><div><br></div><span style="font-size:12px;">(2)生成feature map的其他位置的anchor坐标:</span><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><span style="font-size:12px;">在/py-faster-rcnn/lib/rpn/anchor_target_layer.py中:</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">a)计算偏移量</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;color:#ff0000;">计算偏移量的原理:<span style="font-size:12px;">原图</span>的大小是<span style="font-size:12px;">feature map</span>的16倍,因此,计算feature map其他位置的anchors,相对于(0,0)位置的anchors在原图的偏移量,需要将其在feature map中相对于(0,0)的偏移量×16。</span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 12581px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_23" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_23" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=23&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"># 1. Generate proposals from bbox deltas and shifted anchors</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> shift_x = np.arange(<span class="number">0</span><span>, width) * </span><span class="special">self</span><span>._feat_stride </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> shift_y = np.arange(<span class="number">0</span><span>, height) * </span><span class="special">self</span><span>._feat_stride </span></span></li><li class=""><span> shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> shifts = np.vstack((shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(), </span></li><li class=""><span> shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel())).transpose() </span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;"># 1. Generate proposals from bbox deltas and shifted anchors shift_x = np.arange(0, width) * self._feat_stride shift_y = np.arange(0, height) * self._feat_stride shift_x, shift_y = np.meshgrid(shift_x, shift_y) shifts = np.vstack((shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel(), shift_x.ravel(), shift_y.ravel())).transpose() </pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">b)累积得到anchors</span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 12818px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_24" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_24" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=24&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"># add A anchors (1, A, 4) to</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span><span class="comment"># cell K shifts (K, 1, 4) to get</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"># shift anchors (K, A, 4)</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span><span class="comment"># reshape to (K*A, 4) shifted anchors</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span>A = <span class="special">self</span><span>._num_anchors </span></span></li><li class=""><span>K = shifts.shape[<span class="number">0</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span>all_anchors = (<span class="special">self</span><span>._anchors.reshape((</span><span class="number">1</span><span>, A, </span><span class="number">4</span><span>)) + </span></span></li><li class=""><span> shifts.reshape((<span class="number">1</span><span>, K, </span><span class="number">4</span><span>)).transpose((</span><span class="number">1</span><span>, </span><span class="number">0</span><span>, </span><span class="number">2</span><span>))) </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span>all_anchors = all_anchors.reshape((K * A, <span class="number">4</span><span>)) </span></span></li><li class=""><span>total_anchors = int(K * A) </span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;"> # add A anchors (1, A, 4) to # cell K shifts (K, 1, 4) to get # shift anchors (K, A, 4) # reshape to (K*A, 4) shifted anchors A = self._num_anchors K = shifts.shape[0] all_anchors = (self._anchors.reshape((1, A, 4)) + shifts.reshape((1, K, 4)).transpose((1, 0, 2))) all_anchors = all_anchors.reshape((K * A, 4)) total_anchors = int(K * A)</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">c)过滤掉不在原图内的anchors</span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 13107px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_25" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_25" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=25&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="comment"># only keep anchors inside the image</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> inds_inside = np.where( </span></li><li class="alt"><span> (all_anchors[:, <span class="number">0</span><span>] >= -</span><span class="special">self</span><span>._allowed_border) & </span></span></li><li class=""><span> (all_anchors[:, <span class="number">1</span><span>] >= -</span><span class="special">self</span><span>._allowed_border) & </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> (all_anchors[:, <span class="number">2</span><span>] < im_info[</span><span class="number">1</span><span>] + </span><span class="special">self</span><span>._allowed_border) & </span><span class="comment"># width</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> (all_anchors[:, <span class="number">3</span><span>] < im_info[</span><span class="number">0</span><span>] + </span><span class="special">self</span><span>._allowed_border) </span><span class="comment"># height</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> )[<span class="number">0</span><span>] </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;"># only keep anchors inside the image inds_inside = np.where( (all_anchors[:, 0] >= -self._allowed_border) & (all_anchors[:, 1] >= -self._allowed_border) & (all_anchors[:, 2] < im_info[1] + self._allowed_border) & # width (all_anchors[:, 3] < im_info[0] + self._allowed_border) # height )[0]
- if not cfg.TRAIN.RPN_CLOBBER_POSITIVES:
- # assign bg labels first so that positive labels can clobber them
- labels[max_overlaps < cfg.TRAIN.RPN_NEGATIVE_OVERLAP] = 0
- # fg label: for each gt, anchor with highest overlap
- labels[gt_argmax_overlaps] = 1
- # fg label: above threshold IOU
- labels[max_overlaps >= cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_OVERLAP] = 1
- if cfg.TRAIN.RPN_CLOBBER_POSITIVES:
- # assign bg labels last so that negative labels can clobber positives
- labels[max_overlaps < cfg.TRAIN.RPN_NEGATIVE_OVERLAP] = 0
if not cfg.TRAIN.RPN_CLOBBER_POSITIVES:
# assign bg labels first so that positive labels can clobber them
labels[max_overlaps < cfg.TRAIN.RPN_NEGATIVE_OVERLAP] = 0# fg label: for each gt, anchor with highest overlap labels[gt_argmax_overlaps] = 1 # fg label: above threshold IOU labels[max_overlaps >= cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_OVERLAP] = 1 if cfg.TRAIN.RPN_CLOBBER_POSITIVES: # assign bg labels last so that negative labels can clobber positives labels[max_overlaps < cfg.TRAIN.RPN_NEGATIVE_OVERLAP] = 0
(2)筛选anchors
- # subsample positive labels if we have too many
- num_fg = int(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_FG_FRACTION * cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE)
- fg_inds = np.where(labels 1)[0]
- if len(fg_inds) > num_fg:
- disable_inds = npr.choice(
- fg_inds, size=(len(fg_inds) - num_fg), replace=False)
- labels[disable_inds] = -1
- # subsample negative labels if we have too many
- num_bg = cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE - np.sum(labels 1)
- bg_inds = np.where(labels == 0)[0]
- if len(bg_inds) > num_bg:
- disable_inds = npr.choice(
- bg_inds, size=(len(bg_inds) - num_bg), replace=False)
- labels[disable_inds] = -1
# subsample positive labels if we have too many
num_fg = int(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_FG_FRACTION * cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE)
fg_inds = np.where(labels == 1)[0]
if len(fg_inds) > num_fg:
disable_inds = npr.choice(
fg_inds, size=(len(fg_inds) - num_fg), replace=False)
labels[disable_inds] = -1# subsample negative labels if we have too many num_bg = cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BATCHSIZE - np.sum(labels == 1) bg_inds = np.where(labels == 0)[0] if len(bg_inds) > num_bg: disable_inds = npr.choice( bg_inds, size=(len(bg_inds) - num_bg), replace=False) labels[disable_inds] = -1</pre><br><span style="font-size:12px;">3.生成rpn_bbox_targets</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">论文原文:”ti is a vector representing the 4 parameterized coordinates of the predicted bounding box, and t∗ i is that of the ground-truth box associated with a positive anchor.“</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">这里提到t(i)与t(*i)都是经过parameterized的bounding box的坐标。</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">那么,具体是如何parameterized的呢?</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><img src="https://img-blog.csdn.net/20171121101809735?watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQvdTAxMzI1MDQxNg==/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fill/I0JBQkFCMA==/dissolve/70/gravity/Center" alt=""><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;">源码中的实现:</span></div><div><br><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 14831px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_28" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_28" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=28&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span>bbox_targets = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), </span><span class="number">4</span><span>), dtype=np.float32) </span></span></li><li class=""><span>bbox_targets = _compute_targets(anchors, gt_boxes[argmax_overlaps, :]) </span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;"> bbox_targets = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32) bbox_targets = _compute_targets(anchors, gt_boxes[argmax_overlaps, :])
- def _compute_targets(ex_rois, gt_rois):
- """Compute bounding-box regression targets for an image."""
- assert ex_rois.shape[0] gt_rois.shape[0]
- assert ex_rois.shape[1] 4
- assert gt_rois.shape[1] == 5
- return bbox_transform(ex_rois, gt_rois[:, :4]).astype(np.float32, copy=False)
def _compute_targets(ex_rois, gt_rois):
"""Compute bounding-box regression targets for an image."""assert ex_rois.shape[0] == gt_rois.shape[0] assert ex_rois.shape[1] == 4 assert gt_rois.shape[1] == 5 return bbox_transform(ex_rois, gt_rois[:, :4]).astype(np.float32, copy=False)</pre><span style="font-size:12px;">来看一看/py-faster-rcnn/lib/fast_rcnn/bbox_transform.py中的bbox_transform函数:</span></div><div><span style="font-size:12px;"><br></span></div><div><div class="dp-highlighter bg_python"><div class="bar"><div class="tools"><b>[python]</b> <a href="#" class="ViewSource" title="view plain" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('ViewSource',this);return false;" target="_self">view plain</a><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_168"> <a href="#" class="CopyToClipboard" title="copy" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('CopyToClipboard',this);return false;" target="_self">copy</a><div style="position: absolute; left: 245px; top: 15213px; width: 16px; height: 16px; z-index: 99;"><embed id="ZeroClipboardMovie_30" src="https://csdnimg.cn/public/highlighter/ZeroClipboard.swf" loop="false" menu="false" quality="best" bgcolor="#ffffff" width="16" height="16" name="ZeroClipboardMovie_30" align="middle" allowscriptaccess="always" allowfullscreen="false" type="application/x-shockwave-flash" pluginspage="http://www.macromedia.com/go/getflashplayer" flashvars="id=30&width=16&height=16" wmode="transparent"></div></span><span class="tracking-ad" data-mod="popu_169"> <a href="#" class="PrintSource" title="print" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('PrintSource',this);return false;" target="_self">print</a></span><a href="#" class="About" title="?" onclick="dp.sh.Toolbar.Command('About',this);return false;" target="_self">?</a></div></div><ol start="1" class="dp-py"><li class="alt"><span><span class="keyword">def</span><span> bbox_transform_inv(boxes, deltas): </span></span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">if</span><span> boxes.shape[</span><span class="number">0</span><span>] == </span><span class="number">0</span><span>: </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="keyword">return</span><span> np.zeros((</span><span class="number">0</span><span>, deltas.shape[</span><span class="number">1</span><span>]), dtype=deltas.dtype) </span></span></li><li class=""><span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span> boxes = boxes.astype(deltas.dtype, copy=<span class="special">False</span><span>) </span></span></li><li class=""><span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span> widths = boxes[:, <span class="number">2</span><span>] - boxes[:, </span><span class="number">0</span><span>] + </span><span class="number">1.0</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> heights = boxes[:, <span class="number">3</span><span>] - boxes[:, </span><span class="number">1</span><span>] + </span><span class="number">1.0</span><span> </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> ctr_x = boxes[:, <span class="number">0</span><span>] + </span><span class="number">0.5</span><span> * widths </span></span></li><li class=""><span> ctr_y = boxes[:, <span class="number">1</span><span>] + </span><span class="number">0.5</span><span> * heights </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li><li class=""><span> dx = deltas[:, <span class="number">0</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> dy = deltas[:, <span class="number">1</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class=""><span> dw = deltas[:, <span class="number">2</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> dh = deltas[:, <span class="number">3</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] </span></span></li><li class=""><span> </span></li><li class="alt"><span> pred_ctr_x = dx * widths[:, np.newaxis] + ctr_x[:, np.newaxis] </span></li><li class=""><span> pred_ctr_y = dy * heights[:, np.newaxis] + ctr_y[:, np.newaxis] </span></li><li class="alt"><span> pred_w = np.exp(dw) * widths[:, np.newaxis] </span></li><li class=""><span> pred_h = np.exp(dh) * heights[:, np.newaxis] </span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li><li class=""><span> pred_boxes = np.zeros(deltas.shape, dtype=deltas.dtype) </span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># x1</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> pred_boxes[:, <span class="number">0</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] = pred_ctr_x - </span><span class="number">0.5</span><span> * pred_w </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># y1</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> pred_boxes[:, <span class="number">1</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] = pred_ctr_y - </span><span class="number">0.5</span><span> * pred_h </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># x2</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> pred_boxes[:, <span class="number">2</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] = pred_ctr_x + </span><span class="number">0.5</span><span> * pred_w </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> <span class="comment"># y2</span><span> </span></span></li><li class=""><span> pred_boxes[:, <span class="number">3</span><span>::</span><span class="number">4</span><span>] = pred_ctr_y + </span><span class="number">0.5</span><span> * pred_h </span></span></li><li class="alt"><span> </span></li><li class=""><span> <span class="keyword">return</span><span> pred_boxes </span></span></li></ol></div><pre class="python" name="code" style="display: none;">def bbox_transform_inv(boxes, deltas): if boxes.shape[0] == 0: return np.zeros((0, deltas.shape[1]), dtype=deltas.dtype) boxes = boxes.astype(deltas.dtype, copy=False) widths = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0] + 1.0 heights = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] + 1.0 ctr_x = boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * widths ctr_y = boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * heights dx = deltas[:, 0::4] dy = deltas[:, 1::4] dw = deltas[:, 2::4] dh = deltas[:, 3::4] pred_ctr_x = dx * widths[:, np.newaxis] + ctr_x[:, np.newaxis] pred_ctr_y = dy * heights[:, np.newaxis] + ctr_y[:, np.newaxis] pred_w = np.exp(dw) * widths[:, np.newaxis] pred_h = np.exp(dh) * heights[:, np.newaxis] pred_boxes = np.zeros(deltas.shape, dtype=deltas.dtype) # x1 pred_boxes[:, 0::4] = pred_ctr_x - 0.5 * pred_w # y1 pred_boxes[:, 1::4] = pred_ctr_y - 0.5 * pred_h # x2 pred_boxes[:, 2::4] = pred_ctr_x + 0.5 * pred_w # y2 pred_boxes[:, 3::4] = pred_ctr_y + 0.5 * pred_h return pred_boxes
- bbox_inside_weights = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32)
- bbox_inside_weights[labels 1, :] = np.array(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BBOX_INSIDE_WEIGHTS)
bbox_inside_weights = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32)因此,rpn_bbox_inside_weights就是公式里面的p(i),对于正样本为1,对于负样本为0。
bbox_inside_weights[labels == 1, :] = np.array(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_BBOX_INSIDE_WEIGHTS)
- bbox_outside_weights = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32)
- if cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT < 0:
- # 实现均匀取样
- # uniform weighting of examples (given non-uniform sampling)
- num_examples = np.sum(labels >= 0)
- positive_weights = np.ones((1, 4)) 1.0 / num_examples
- negative_weights = np.ones((1, 4)) 1.0 / num_examples
- else:
- assert ((cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT > 0) &
- (cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT < 1))
- positive_weights = (cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT /
- np.sum(labels 1))
- negative_weights = ((1.0 - cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT) /
- np.sum(labels 0))
- bbox_outside_weights[labels 1, :] = positive_weights
- bbox_outside_weights[labels == 0, :] = negative_weights
bbox_outside_weights = np.zeros((len(inds_inside), 4), dtype=np.float32)在cfg文件里面,cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT为-1,因此这里是对正负样本的权重都除以样本总数,相当于实现了1/Nreg的功能。
if cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT < 0:
# 实现均匀取样
# uniform weighting of examples (given non-uniform sampling)
num_examples = np.sum(labels >= 0)
positive_weights = np.ones((1, 4)) * 1.0 / num_examples
negative_weights = np.ones((1, 4)) * 1.0 / num_examples
else:
assert ((cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT > 0) &
(cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT < 1))
positive_weights = (cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT /
np.sum(labels == 1))
negative_weights = ((1.0 - cfg.TRAIN.RPN_POSITIVE_WEIGHT) /
np.sum(labels == 0))
bbox_outside_weights[labels == 1, :] = positive_weights
bbox_outside_weights[labels == 0, :] = negative_weights
- layer {
- name: "rpn_cls_score"
- type: "Convolution"
- bottom: "rpn/output"
- top: "rpn_cls_score"
- param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
- param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
- convolution_param {
- num_output: 18 # 2(bg/fg) * 9(anchors)
- kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
- weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
- bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
- }
- }
layer {
name: "rpn_cls_score"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "rpn/output"
top: "rpn_cls_score"
param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 18 # 2(bg/fg) * 9(anchors)
kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
}
}- layer {
- bottom: "rpn_cls_score"
- top: "rpn_cls_score_reshape"
- name: "rpn_cls_score_reshape"
- type: "Reshape"
- reshape_param { shape { dim: 0 dim: 2 dim: -1 dim: 0 } }
- }
- layer {
- name: "rpn_cls_prob"
- type: "Softmax"
- bottom: "rpn_cls_score_reshape"
- top: "rpn_cls_prob"
- }
- layer {
- name: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
- type: 'Reshape'
- bottom: 'rpn_cls_prob'
- top: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
- reshape_param { shape { dim: 0 dim: 18 dim: -1 dim: 0 } }
- }
layer {
bottom: "rpn_cls_score"
top: "rpn_cls_score_reshape"
name: "rpn_cls_score_reshape"
type: "Reshape"
reshape_param { shape { dim: 0 dim: 2 dim: -1 dim: 0 } }
}
layer {
name: "rpn_cls_prob"
type: "Softmax"
bottom: "rpn_cls_score_reshape"
top: "rpn_cls_prob"
}
layer {
name: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
type: 'Reshape'
bottom: 'rpn_cls_prob'
top: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
reshape_param { shape { dim: 0 dim: 18 dim: -1 dim: 0 } }
}




观察上面4个公式发现,需要学习的是dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)这四个变换。当输入的anchor A与GT相差较小时,可以认为这种变换是一种线性变换, 那么就可以用线性回归来建模对窗口进行微调(注意,只有当anchors A和GT比较接近时,才能使用线性回归模型,否则就是复杂的非线性问题了)。对应于Faster RCNN原文,平移量(tx, ty)与尺度因子(tw, th)如下:
接下来的问题就是如何通过线性回归获得dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)了。线性回归就是给定输入的特征向量X, 学习一组参数W, 使得经过线性回归后的值跟真实值Y非常接近,即Y=WX。对于该问题,输入X是一张经过卷积获得的feature map,定义为Φ;同时还有训练传入的GT,即(tx, ty, tw, th)。输出是dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)四个变换。那么目标函数可以表示为:
其中Φ(A)是对应anchor的feature map组成的特征向量,w是需要学习的参数,d(A)是得到的预测值(表示 x,y,w,h,也就是每一个变换对应一个上述目标函数)。为了让预测值(tx, ty, tw, th)与真实值差距最小,设计损失函数:
函数优化目标为:
- layer {
- name: "rpn_bbox_pred"
- type: "Convolution"
- bottom: "rpn/output"
- top: "rpn_bbox_pred"
- param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
- param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
- convolution_param {
- num_output: 36 # 4 9(anchors)
- kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
- weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
- bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
- }
- }
layer {
name: "rpn_bbox_pred"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "rpn/output"
top: "rpn_bbox_pred"
param { lr_mult: 1.0 }
param { lr_mult: 2.0 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 36 # 4 * 9(anchors)
kernel_size: 1 pad: 0 stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "gaussian" std: 0.01 }
bias_filler { type: "constant" value: 0 }
}
}- layer {
- name: 'proposal'
- type: 'Python'
- bottom: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
- bottom: 'rpn_bbox_pred'
- bottom: 'im_info'
- top: 'rpn_rois'
- # top: 'rpn_scores'
- python_param {
- module: 'rpn.proposal_layer'
- layer: 'ProposalLayer'
- param_str: "'feat_stride': 16"
- }
- }
layer {
name: 'proposal'
type: 'Python'
bottom: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
bottom: 'rpn_bbox_pred'
bottom: 'im_info'
top: 'rpn_rois'
top: 'rpn_scores'
python_param {
module: 'rpn.proposal_layer'
layer: 'ProposalLayer'
param_str: "'feat_stride': 16"
}
}
- 生成anchors,利用[dx(A),dy(A),dw(A),dh(A)]对所有的anchors做bbox regression回归(这里的anchors生成和训练时完全一致)也就是说,前面的网络是对anchor进行训练,而proposal层是用来生成anchor。
- 按照输入的foreground softmax scores由大到小排序anchors,提取前pre_nms_topN(e.g. 6000)个anchors,即提取修正位置后的foreground anchors。
- 限定超出图像边界的foreground anchors为图像边界(防止后续roi pooling时proposal超出图像边界)
- 剔除非常小(width<threshold or height<threshold)的foreground anchors
- 进行nonmaximum suppression
- 再次按照nms后的foreground softmax scores由大到小排序fg anchors,提取前post_nms_topN(e.g. 300)结果作为proposal输出。
缩进RoI Pooling层则负责收集proposal,并计算出proposal feature maps,送入后续网络。从图2中可以看到Rol pooling层有2个输入:
- 原始的feature maps
- RPN输出的proposal boxes(大小各不相同)
1)为何需要RoI Pooling
先来看一个问题:对于传统的CNN(如AlexNet,VGG),当网络训练好后输入的图像尺寸必须是固定值,同时网络输出也是固定大小的vector or matrix。如果输入图像大小不定,这个问题就变得比较麻烦。有2种解决办法:
- 从图像中crop一部分传入网络
- 将图像warp成需要的大小后传入网络
crop与warp破坏图像原有结构信息
两种办法的示意图如图,可以看到无论采取那种办法都不好,要么crop后破坏了图像的完整结构,要么warp破坏了图像原始形状信息。回忆RPN网络生成的proposals的方法:对foreground anchors进行bound box regression,那么这样获得的proposals也是大小形状各不相同,即也存在上述问题。所以Faster RCNN中提出了RoI Pooling解决这个问题。
2)RoI Pooling原理
缩进
分析之前先来看看RoI Pooling Layer的train.prototxt的定义:
- layer {
- name: "roi_pool5"
- type: "ROIPooling"
- bottom: "conv5_3"
- bottom: "rois"
- top: "pool5"
- roi_pooling_param {
- pooled_w: 7
- pooled_h: 7
- spatial_scale: 0.0625 # 1/16
- }
- }
layer {
name: "roi_pool5"
type: "ROIPooling"
bottom: "conv5_3"
bottom: "rois"
top: "pool5"
roi_pooling_param {
pooled_w: 7
pooled_h: 7
spatial_scale: 0.0625 # 1/16
}
}其中有新参数pooled_w=pooled_h=7。
RoI Pooling layer forward过程:在之前有明确提到:proposal=[x1, y1, x2, y2]是对应MxN尺度的,所以首先使用spatial_scale参数将其映射回(M/16)x(N/16)大小的feature maps尺度;之后将每个proposal水平和竖直都分为7份,对每一份都进行max pooling处理。这样处理后,即使大小不同的proposal,输出结果都是7x7大小,实现了fixed-length output(固定长度输出)。
proposal示意图
- template <typename Dtype>
- void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>>& bottom,
- const vector<Blob<Dtype>>& top) {
- //conv5-3信息
- const Dtype bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
- //rois信息
- const Dtype bottom_rois = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
- //Number of ROIs
- int num_rois = bottom[1]->num();
- //样本大小
- int batch_size = bottom[0]->num();
- int top_count = top[0]->count();
- //初始化top_data 和 argmax_data两个数组
- //caffe_set(const int N, const Dtype alpha, Dtype argmax_data);
- Dtype top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
- caffe_set(top_count, Dtype(-FLT_MAX), top_data);
- int argmax_data = max_idx_.mutable_cpu_data();
- caffe_set(top_count, -1, argmax_data);
- // For each ROI R=[batch_index x1 y1 x2 y2]: max pool over R
- for (int n = 0; n < num_rois; ++n) {
- int roi_batch_ind = bottom_rois[0];
- //将生成的rois的坐标映射到原来的feature map上
- //rois中只包含了坐标信息,而不包含feature map信息
- int roi_start_w = round(bottom_rois[1] spatial_scale_);
- int roi_start_h = round(bottom_rois[2] spatial_scale_);
- int roi_end_w = round(bottom_rois[3] spatial_scale_);
- int roi_end_h = round(bottom_rois[4] spatial_scale_);
- CHECK_GE(roi_batch_ind, 0);
- CHECK_LT(roi_batch_ind, batch_size);
- //每一个region在feature map上对应的大小
- int roi_height = max(roi_end_h - roi_start_h + 1, 1);
- int roi_width = max(roi_end_w - roi_start_w + 1, 1);
- //每一个sub region的大小
- const Dtype bin_size_h = static_cast<Dtype>(roi_height) / static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_height_);
- const Dtype bin_size_w = static_cast<Dtype>(roi_width) / static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_width_);
- const Dtype batch_data = bottom_data + bottom[0]->offset(roi_batch_ind);
- for(int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
- for(int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
- for(int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
- // Compute pooling region for this output unit:
- // start (included) = floor(ph roi_height / pooled_height__)
- // end (excluded) = ceil((ph+1) roi_height / pooled_height_)
- //floor(x):取小于等于x的整数,ceil(x):取大于x的整数
- //取得每一个sub region的起点终点坐标
- int hstart = static_cast<int>(floor(static_cast<DType>(ph) bin_size_h));
- int wstart = static_cast<int>(floor(static_cast<DType>(pw) bin_size_w));
- int hend = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<DType>(ph+1) bin_size_h));
- int wend = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<DType>(pw+1) bin_size_w));
- hstart = min(max(hstart + roi_start_h, 0), height_);
- hend = min(max(hend + roi_start_h, 0), height_);
- wstart = min(max(wstart + roi_start_w, 0), width_);
- wend = min(max(wend + roi_start_w, 0), width_);
- //剔除无效的roi
- bool is_empty = (hend <= hstart) || (wend <= wstart);
- //池化区域的编号
- const int pool_index = ph pooled_width_ + pw;
- if(is_empty){
- //如果该区域无效,则将池化结果设为0
- top_data[pool_index] = 0;
- //将最大区域的index设为-1
- argmax_data[pool_index] = -1;
- }
- //进行最大池化操作
- //pool_index:77的某一个池化区域的索引,index:feature map某一点的索引
- for(int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
- for(int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w){
- //计算在feature map中的索引
- const int index = h width_ + w;
- if(batch_data[index] > top_data[pool_index]){
- top_data[pool_index] = batch_data[index];
- argmax_data[pool_index] = index;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- //Increment all data pointers by one channel
- //也就是,将指针指向下一个channel
- batch_data += bottom[0]->offset(0,1);
- top_data += top[0]->offset(0,1);
- argmax_data += max_idx_.offset(0,1);
- }
- //Increment ROI data pointer
- bottom_rois += bottom[1]->offset(1);
- }
- }
template <typename Dtype>
void ROIPoolingLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>>& top) {
//conv5-3信息
const Dtype bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
//rois信息
const Dtype* bottom_rois = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
//Number of ROIs
int num_rois = bottom[1]->num();
//样本大小
int batch_size = bottom[0]->num();
int top_count = top[0]->count();//初始化top_data 和 argmax_data两个数组
//caffe_set(const int N, const Dtype alpha, Dtype* argmax_data);
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(top_count, Dtype(-FLT_MAX), top_data);
int* argmax_data = max_idx_.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(top_count, -1, argmax_data);// For each ROI R=[batch_index x1 y1 x2 y2]: max pool over R
for (int n = 0; n < num_rois; ++n) {
int roi_batch_ind = bottom_rois[0];
//将生成的rois的坐标映射到原来的feature map上
//rois中只包含了坐标信息,而不包含feature map信息
int roi_start_w = round(bottom_rois[1] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_start_h = round(bottom_rois[2] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_end_w = round(bottom_rois[3] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_end_h = round(bottom_rois[4] * spatial_scale_);
CHECK_GE(roi_batch_ind, 0);
CHECK_LT(roi_batch_ind, batch_size);//每一个region在feature map上对应的大小 int roi_height = max(roi_end_h - roi_start_h + 1, 1); int roi_width = max(roi_end_w - roi_start_w + 1, 1); //每一个sub region的大小 const Dtype bin_size_h = static_cast<Dtype>(roi_height) / static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_height_); const Dtype bin_size_w = static_cast<Dtype>(roi_width) / static_cast<Dtype>(pooled_width_); const Dtype* batch_data = bottom_data + bottom[0]->offset(roi_batch_ind); for(int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) { for(int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) { for(int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) { // Compute pooling region for this output unit: // start (included) = floor(ph * roi_height / pooled_height__) // end (excluded) = ceil((ph+1) * roi_height / pooled_height_) //floor(x):取小于等于x的整数,ceil(x):取大于x的整数 //取得每一个sub region的起点终点坐标 int hstart = static_cast<int>(floor(static_cast<DType>(ph) * bin_size_h)); int wstart = static_cast<int>(floor(static_cast<DType>(pw) * bin_size_w)); int hend = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<DType>(ph+1) * bin_size_h)); int wend = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<DType>(pw+1) * bin_size_w)); hstart = min(max(hstart + roi_start_h, 0), height_); hend = min(max(hend + roi_start_h, 0), height_); wstart = min(max(wstart + roi_start_w, 0), width_); wend = min(max(wend + roi_start_w, 0), width_); //剔除无效的roi bool is_empty = (hend <= hstart) || (wend <= wstart); //池化区域的编号 const int pool_index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw; if(is_empty){ //如果该区域无效,则将池化结果设为0 top_data[pool_index] = 0; //将最大区域的index设为-1 argmax_data[pool_index] = -1; } //进行最大池化操作 //pool_index:7*7的某一个池化区域的索引,index:feature map某一点的索引 for(int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) { for(int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w){ //计算在feature map中的索引 const int index = h * width_ + w; if(batch_data[index] > top_data[pool_index]){ top_data[pool_index] = batch_data[index]; argmax_data[pool_index] = index; } } } } } //Increment all data pointers by one channel //也就是,将指针指向下一个channel batch_data += bottom[0]->offset(0,1); top_data += top[0]->offset(0,1); argmax_data += max_idx_.offset(0,1); } //Increment ROI data pointer bottom_rois += bottom[1]->offset(1); }}
roi_height:region proposal的高度
缩进Classification部分利用已经获得的proposal feature maps,通过full connect层与softmax计算每个proposal具体属于哪个类别,输出cls_prob概率向量;同时再次利用bounding box regression获得每个proposal的位置偏移量bbox_pred,用于回归更加精确的目标检测框。Classification部分网络结构如下图。

从RoI Pooling获取到7x7=49大小的proposal feature maps后,送入后续网络,可以看到做了如下2件事:
- 通过全连接和softmax对proposals进行分类;
- 再次对proposals进行bounding box regression,获取更高精度的rect box。
全连接层示意图
其计算公式如下:
其中W和bias B都是预先训练好的,即大小是固定的,当然输入X和输出Y也就是固定大小。所以,也就印证了Roi Pooling的必要性。
与检测网络类似的是,依然使用Conv Layers提取feature maps。整个网络使用的Loss如下:
在上述公式中,i表示anchors index,pi表示foreground softmax predict概率,pi代表对应的GT predict概率(即当第i个anchor与GT间IoU>0.7,认为是该anchor是foreground,pi=1;反之IoU<0.3时,认为是该anchor是background,pi=0;至于那些0.3<IoU<0.7的anchor则不参与训练);t代表predict bounding box,t代表对应foreground anchor对应的GT box。可以看到,整个Loss分为2部分:
- cls loss,即rpn_cls_loss层计算的softmax loss,用于分类anchors为forground与background的网络训练
- reg loss,即rpn_loss_bbox层计算的soomth L1 loss,用于bounding box regression网络训练。注意在该loss中乘了pi,相当于只关心foreground anchors的回归。
由于在实际过程中,Ncls和Nreg差距过大,用参数λ平衡二者(如Ncls=256,Nreg=2400时设置λ=10),使总的网络Loss计算过程中能够均匀考虑2种Loss。这里比较重要是Lreg使用的soomth L1 loss,计算公式如下:
- 在RPN训练阶段,rpn-data(python AnchorTargetLayer)层会按照和test阶段Proposal层完全一样的方式生成Anchors用于训练
- 对于rpn_loss_cls,输入的rpn_cls_scors_reshape和rpn_labels分别对应p与p,Ncls参数隐含在p与p的caffe blob的大小中
- 对于rpn_loss_bbox,输入的rpn_bbox_pred和rpn_bbox_targets分别对应t于t,rpn_bbox_inside_weigths对应p*,rpn_bbox_outside_weights对应1/Nreg。
特别需要注意的是,在训练和检测阶段生成和存储anchors的顺序完全一样,这样训练结果才能被用于检测!
2)通过训练好的RPN网络收集proposals
在该步骤中,利用之前的RPN网络,获取proposal rois,同时获取foreground softmax probability,如下图。注意:在前向传播中,将该部分看作是固定的,不对其计算loss。而实际上,本应该对proposal rois的坐标进行回归。所以,这种端到端的训练方式称为Approximate joint training。
如果是分步计算,此处应该产生loss。
- layer {
- name: 'proposal'
- type: 'Python'
- bottom: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
- bottom: 'rpn_bbox_pred'
- bottom: 'im_info'
- top: 'rpn_rois'
- # top: 'rpn_scores'
- python_param {
- module: 'rpn.proposal_layer'
- layer: 'ProposalLayer'
- param_str: "'feat_stride': 16"
- }
- }
layer {
name: 'proposal'
type: 'Python'
bottom: 'rpn_cls_prob_reshape'
bottom: 'rpn_bbox_pred'
bottom: 'im_info'
top: 'rpn_rois'
top: 'rpn_scores'
python_param {
module: 'rpn.proposal_layer'
layer: 'ProposalLayer'
param_str: "'feat_stride': 16"
}
}

3)训练Faster RCNN网络
- layer {
- name: 'roi-data'
- type: 'Python'
- bottom: 'rpn_rois'
- bottom: 'gt_boxes'
- top: 'rois'
- top: 'labels'
- top: 'bbox_targets'
- top: 'bbox_inside_weights'
- top: 'bbox_outside_weights'
- python_param {
- module: 'rpn.proposal_target_layer'
- layer: 'ProposalTargetLayer'
- param_str: "'num_classes': 2"
- }
- }
layer {
name: 'roi-data'
type: 'Python'
bottom: 'rpn_rois'
bottom: 'gt_boxes'
top: 'rois'
top: 'labels'
top: 'bbox_targets'
top: 'bbox_inside_weights'
top: 'bbox_outside_weights'
python_param {
module: 'rpn.proposal_target_layer'
layer: 'ProposalTargetLayer'
param_str: "'num_classes': 2"
}
}



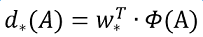
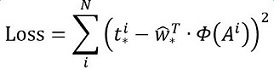
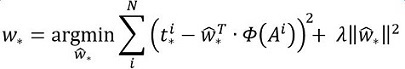

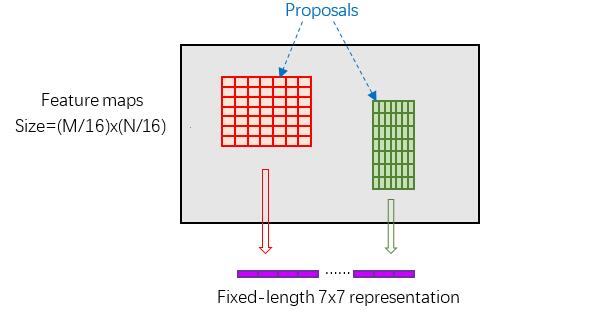
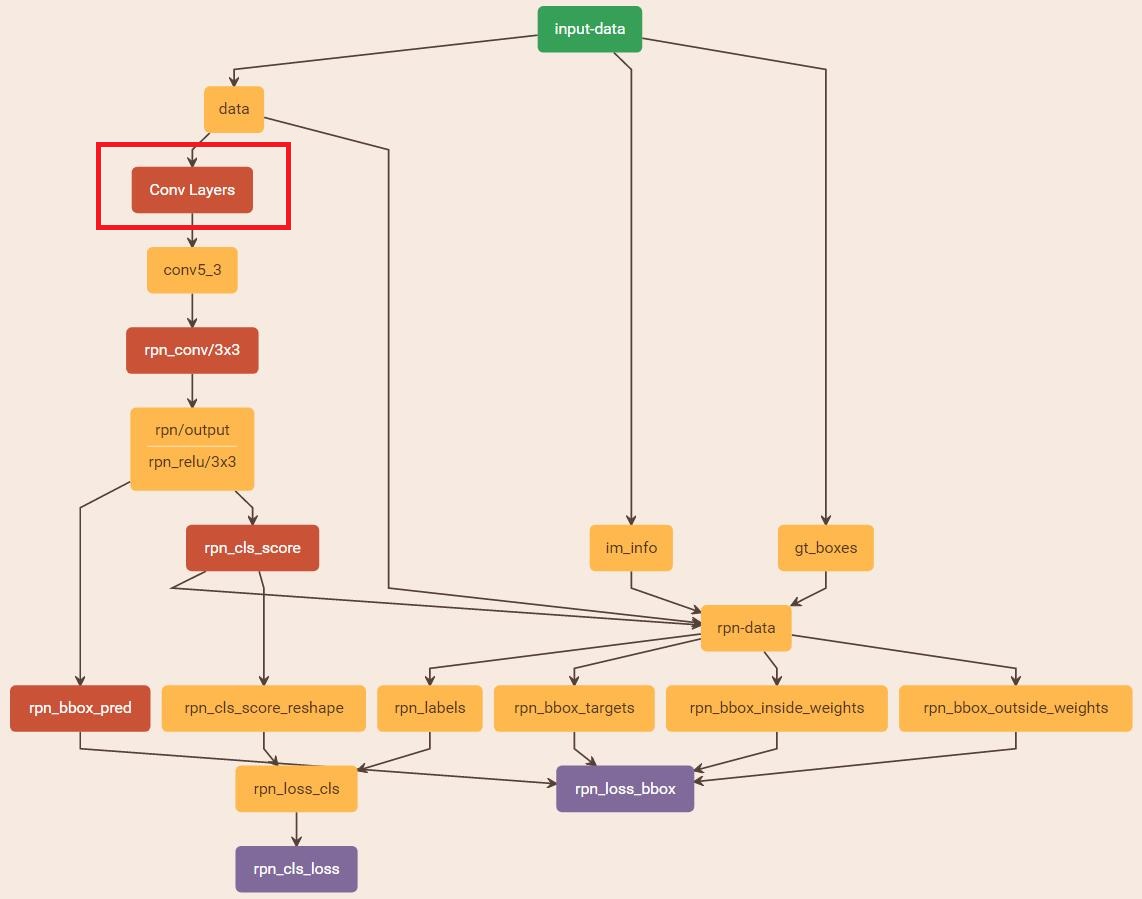
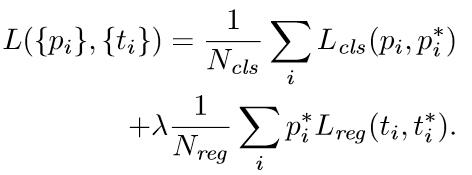
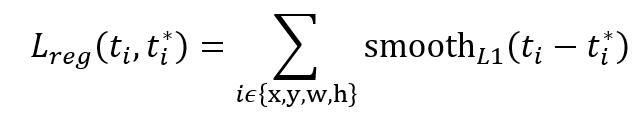

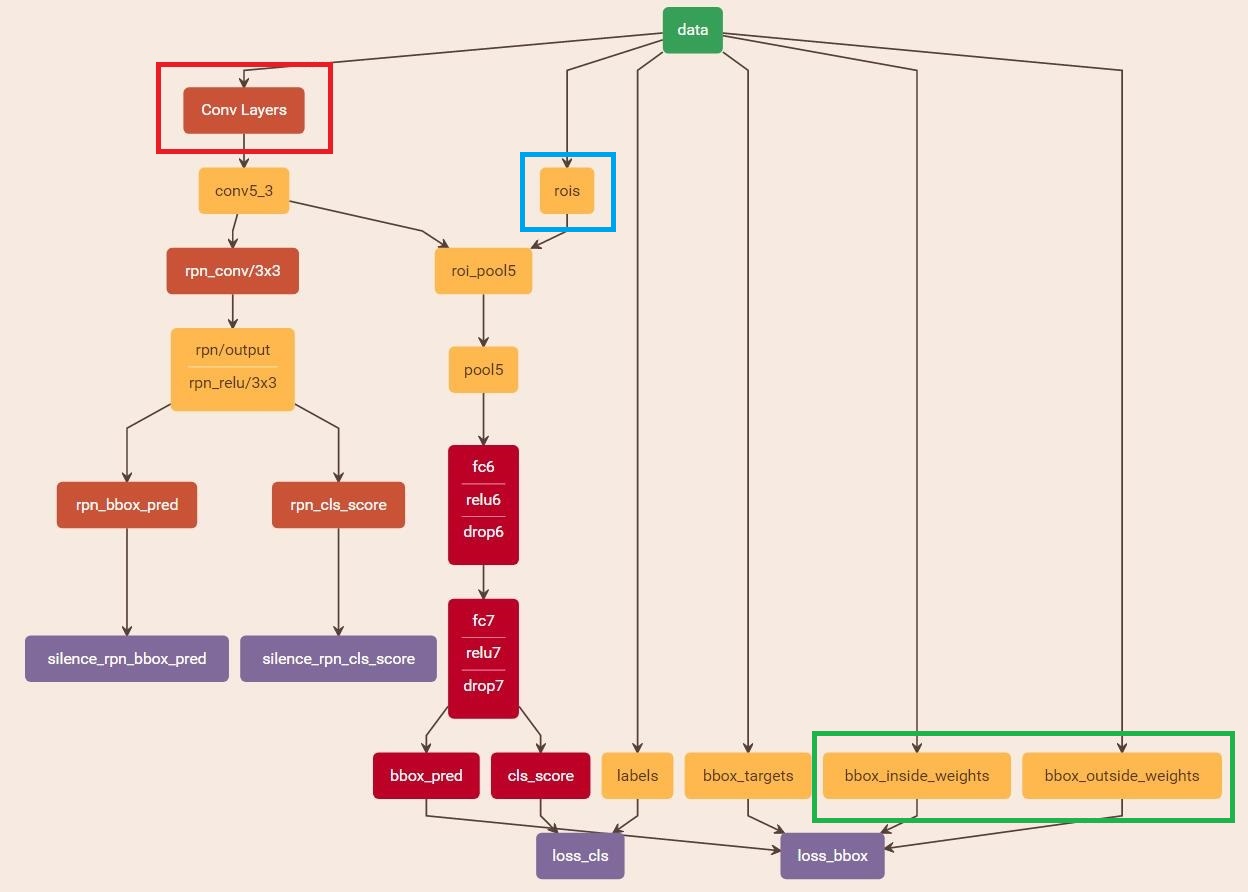

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号