一、初识驱动
(1)Linux驱动 = 软件框架 + 硬件操作
(2)应用程序打开的文件在内核中的表示
2.1
应用程序打开文件时,可以得到一个文件句柄(一般用整数表示),并且对于每一个文件句柄内核中都有一个"struct file"与之对应。
struct file { /* * fu_list becomes invalid after file_free is called and queued via * fu_rcuhead for RCU freeing */ union { struct list_head fu_list; struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead; } f_u; struct path f_path; #define f_dentry f_path.dentry #define f_vfsmnt f_path.mnt const struct file_operations *f_op; atomic_t f_count; unsigned int f_flags; mode_t f_mode; loff_t f_pos; struct fown_struct f_owner; unsigned int f_uid, f_gid; struct file_ra_state f_ra; unsigned long f_version;
使用 open 打开文件时,传入的 flags、mode 等参数会被记录在内核中对应的 "struct file" 结构体里(f_flags、f_mode)。
读写文件时,文件的当前偏移地址也会保存在 "struct file"结构体的 f_pos 成员中。
2.2
打开字符设备节点时,内核中也有对应的 "struct file",驱动程序提供的"struct file_operations *f_op"至关重要,"f_op"根据主设备号找到 "struct file_operations *f_op"。
1 struct file_operations { 2 struct module *owner; 3 loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); 4 ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); 5 ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); 6 ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); 7 ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); 8 int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t); 9 unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); 10 int (*ioctl) (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 11 long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 12 long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); 13 int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); 14 int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); 15 int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id); 16 int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); 17 int (*fsync) (struct file *, struct dentry *, int datasync); 18 int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync); 19 int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int); 20 int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); 21 ssize_t (*sendfile) (struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, read_actor_t, void *); 22 ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int); 23 unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long); 24 int (*check_flags)(int); 25 int (*dir_notify)(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg); 26 int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); 27 ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int); 28 ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int); 29 };
(3)驱动框架
(1)确定主设备号
(2)定义 file_operations 结构
(3)实现对应的 drv_open()/drv_read()/drv_write() 等函数,填入 file_operations 结构体
(4) 把 file_operations 结构体告诉内核:register_chrdev ()
(5) 注册驱动程序,安装驱动程序时,就会去调用这个入口函数 module_init()
(6) 出口函数module_exit(),卸载驱动程序时,出口函数调用 unregister_chrdev ()
(7)其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点:class_create(), device_create()
(4)驱动框架
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
/* 1. 确定主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static char kernel_buf[1024];
static struct class *hello_class; //创建类
#define MIN(a, b) (a < b ? a : b)
/* 3. 实现对应的open/read/write等函数,填入file_operations结构体
file 目标文件结构体指针
buf 要读出文件的信息缓冲区
size 要读出信息的长度
offset 当前的偏移位置,这个值通常是用来判断写文件是否越界
*/
static ssize_t hello_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_to_user(buf, kernel_buf, MIN(1024, size));//驱动程序与应用程序之间数据传递
return MIN(1024, size);
}
static ssize_t hello_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_from_user(kernel_buf, buf, MIN(1024, size));
return MIN(1024, size);
}
/*
node 表示具体的文件
file 文件运行时的状态信息
*/
static int hello_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static int hello_drv_close (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/* 2. 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations hello_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, //驱动装载成功后阻止被卸载
.open = hello_drv_open,
.read = hello_drv_read,
.write = hello_drv_write,
.release = hello_drv_close,
};
/* 4. 把file_operations结构体告诉内核:注册驱动程序 */
/* 5. 入口函数:安装驱动程序时,就会去调用这个入口函数 */
static int __init hello_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_drv); /* 0表示系统分配主设备号/dev/hello */
/*创建类,它会在sys目录下创建hello_class这个类*/
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");
err = PTR_ERR(hello_class);
if (IS_ERR(hello_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
return -1;
}
/*创建类设备,它会在hello_class类下创建hello设备,然后mdev通过这个自动创建/dev/hello这个设备节点*/
device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); /* /dev/hello */
return 0;
}
/* 6. 卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数 */
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
device_destroy(hello_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(hello_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息, */
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
测试程序:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
* ./hello_drv_test -w abc
* ./hello_drv_test -r
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char buf[1024];
int len;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s -w <string>\n", argv[0]);
printf(" %s -r\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open("/dev/hello", O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file /dev/hello\n");
return -1;
}
/* 3. 写文件或读文件 */
if ((0 == strcmp(argv[1], "-w")) && (argc == 3))
{
len = strlen(argv[2]) + 1; //要写入文件的大小
len = len < 1024 ? len : 1024;
write(fd, argv[2], len); //写入文件
}
else
{
len = read(fd, buf, 1024);//读出文件
buf[1023] = '\0';
printf("APP read : %s\n", buf);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
上机测试:
装载驱动
![]()
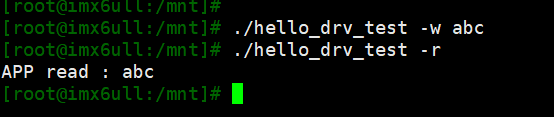
测试驱动:
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号