wk1&2 字符串
【CQ】
自增怎么样都增了,赋值不一定:
int x = 2;
int y = 2;
int i = ++x;
int j = y++;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(j);
3
3
3
2
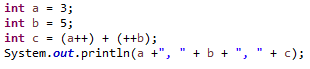
a4 b6 c9

good evening,default也会默认输出:goodbye
highest precision:Wrapper class BigDecimal BigInteger:有多长存多长
【SA】
可移植编程语言:编译一次,然后在Unix,Solaris,Windows,Mac和其他有操作系统的操作系统中运行它。缺点:吃memory 需要垃圾回收。优点:顺序随便,分类处理。
jdk =>jre = jvm + library
java doc/compiler-开发工具-jdk
run time lib - 基本条件-jre
配置:java_?HOME + path
NetBeans IntelliJ都是集成ide
Hello.java-用javac Hello.java来compile(Interpreted 解释意味着应用程序被编译为在运行时解释的格式,而不是直接作为机器代码运行,这就是使应用程序可移植的原因。)-Hello.class文件(bytecode)-用 java Hello来运行
integral整型数据类型:byte/short int/ long int
byte b = 127;
b++; b = -128
Adding one extra bit when the byte is at its highest positive value will push the number to its other extreme, that is the lowest negative value.相反极数。
极数:Byte.MAX_VALUE
数学运算的结果: Widest of the data-type of its operands 取运算结果的最广范围
从高位数到低位数:必须要用explicit casting syntax显式转换/强制转换。不加不行:
int i = 10;
char c = i;
This code won't compile as it needs casting
效果如下。
double d = 5.64267;
int i = (int) d; i = 5
代表取整数,不是四舍五入啊。
可能丢失精度,理由:位数变少了
从低位数到高位数:
低---------------------------------------------------->高
byte1->char 2 short int 2-> int 4 float4 - > long 8 double 8
bsc il fd
此外,位数相等的可能丢失精度
本来就是低精度,加两个小数点就行了
可能丢失精度,理由:变成高精度,数字变少 小数变多,超出范围时可能会有精度的损失。eg int - float
What will be the output of the code shown below?
int i = 5;
int j = 2;
double d = i/j;
System.out.println(d);
整数运算结果是2,加个小数点变?2.0
int x = 10;
int y = x;
x and y are separate memory locations (not reference)holding their own copy of number 10
传值而非传引用
方法内外的变量赋值:Only local variables inside a method need to be initialized before use仅有方法内的实例变量需要赋值,方法外的成员变量可以仅声明 等于默认值。
布尔型变量默认为false。eg
public class Hello {
static boolean b1;
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b2 = !b1;
System.out.println(b2);
}
} b2 = true
==用于判断是不是同一个对象,判断是不是同一个字符串就用equals就行了
What will be the output of following code:
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = s1;
String s3 = new String("Hello");
System.out.println(s1 == s2); //statement 1 对, 同一个对象
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); //statement 2 对,还相等
System.out.println(s1 == s3); //statement 3 错,不是同一个对象
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); //statement 4 对,但相等
switch语句接受的变量:数字/字符/布尔型/字符串/都可以。
语句中必须有default语句。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号