单链表面试题笔记整理
第一题:求如下单链表中有效节点的个数
// 结点信息
class HeroNode{
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode next;
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
}
// 链表类
class SingleLinkedList{
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0,"","");
public HeroNode getHead() {
return head;
}
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode){
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;
while (true){
if (temp.next == null){
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no){
break;
}else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no){
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
System.out.println("准备插入的英雄编号"+heroNode.no+"已经存在");
}else {
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
/**
* 获取到链表的节点的个数(如果带头节点,记得不统计头节点)
* @param head 链表的头结点
* @return 返回的是有效的结点个数
*/
public static int getLength(HeroNode head){
int length = 0;
HeroNode cur = head.next;
while (true){
if (cur == null){
return length;
}
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
}
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨");
HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义", "玉麒麟");
HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3, "吴用", "智多星");
HeroNode hero4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲", "豹子头");
HeroNode hero5 = new HeroNode(6, "林冲2", "豹子头2");
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
System.out.println(SingleLinkedList.getLength(singleLinkedList.getHead()));
}
}
其中getLength(HeroNode head)方法为获取单链表结点有效个数的方法
第二题:查找单链表的倒数第k个结点
代码示范
/**
* 编写该方法,接收head同时接收index
* 1、index表示的是倒数第几个结点
* 2、先把链表从头到尾遍历一遍,得到链表的总长度
* 3、我们再次从第一个结点开始遍历(总结点个数-index)个,就可以得到该想要的结点
* 4、如果找到就返回该结点,否则返回null
* @param head 头结点
* @param index 倒数第几个
* @return
*/
public static HeroNode findLastIndexNode(HeroNode head,int index){
//判断如果链表为空,则返回null
if (head.next == null){
return null;
}
//第一个遍历得到链表的长度(也就是节点的总个数)
int size = getLength(head);
//第二次遍历到size-index的位置,这个就是我们倒数的第k个结点
//我们还需要校验index的合理性
if (index <= 0 || index > size){
return null;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
for (int i = 0; i < (size - index); i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
第三题:单链表的反转
思路分析
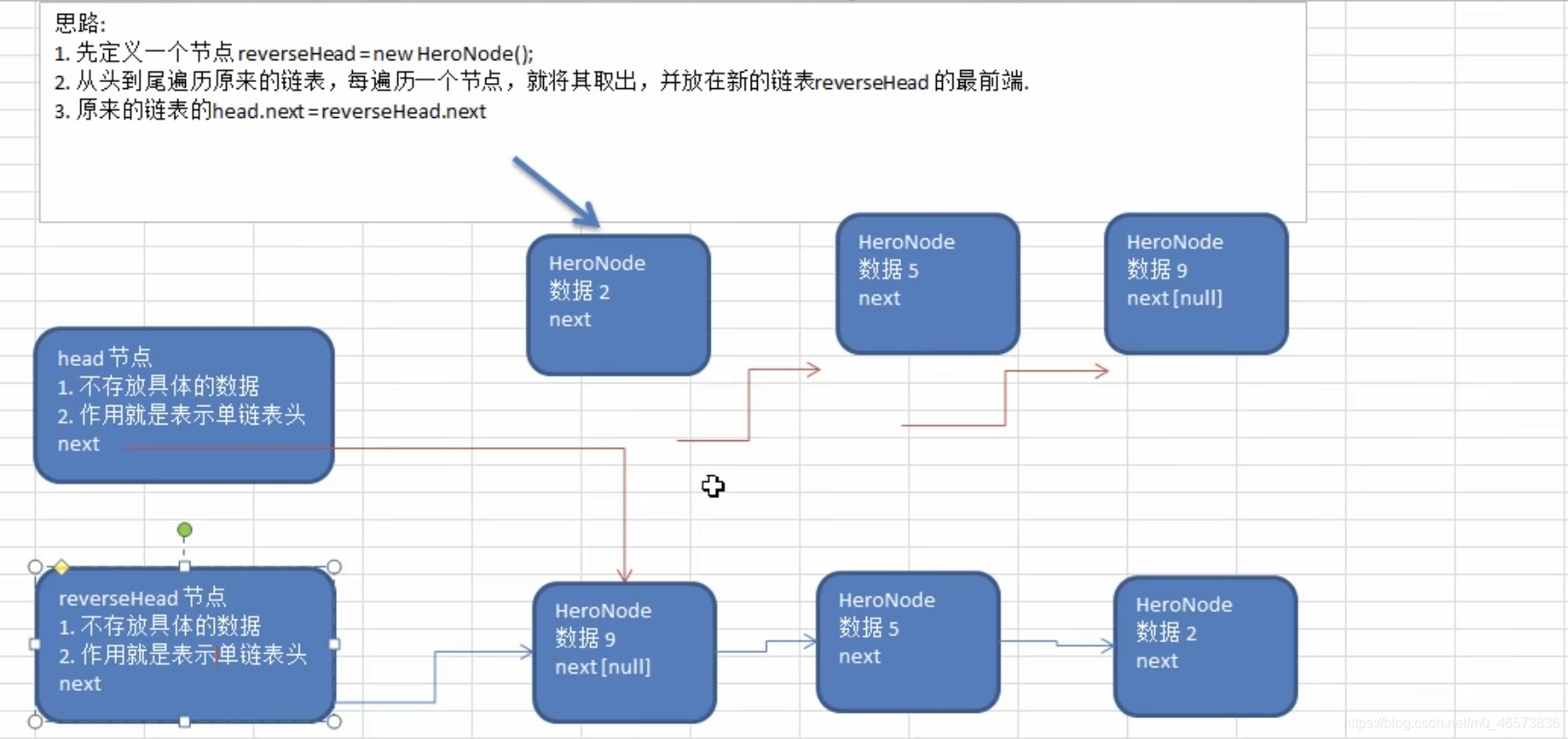
代码实现
public static void reversetList(HeroNode head){
//判断链表中是否含有数据,如果没有数据直接输出为null;并且判断当数据是由一个的时候,直接输出数据
if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
return;
}
//定义一个辅助指针
HeroNode cur = head.next;
//定义一个临时变量,防止后面在取出遍历的节点和另一个头节点拼接过程中该节点的next发生改变,导致原先的链表无法连接
HeroNode next = null;
//定义一个新的头节点,用于拼接新的一根链表
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0,"","");
//循环遍历将原先链表中的节点每一个都拼接到新链表的头节点后面
while (cur != null){
//将cur节点中的next中的节点赋值给next这个临时变量,因为在下边要把cur.next属性赋予新的值
next = cur.next;
//将新的头节点的next赋值给取出的节点的next属性,,就是将取出的节点的next指向新的链表头节点后面的那个节点
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
//将取出来的这个节点拼接到头节点的后面(注意不是拼接到链表的后面,一定是头节点的后面,这很重要
reverseHead.next = cur;
//将指针移动一个位置
cur = next;
}
//将新链表和拼接到旧链表的头结点后面
head.next = reverseHead.next;
}
第四题:从尾到头打印单链表
思路分析
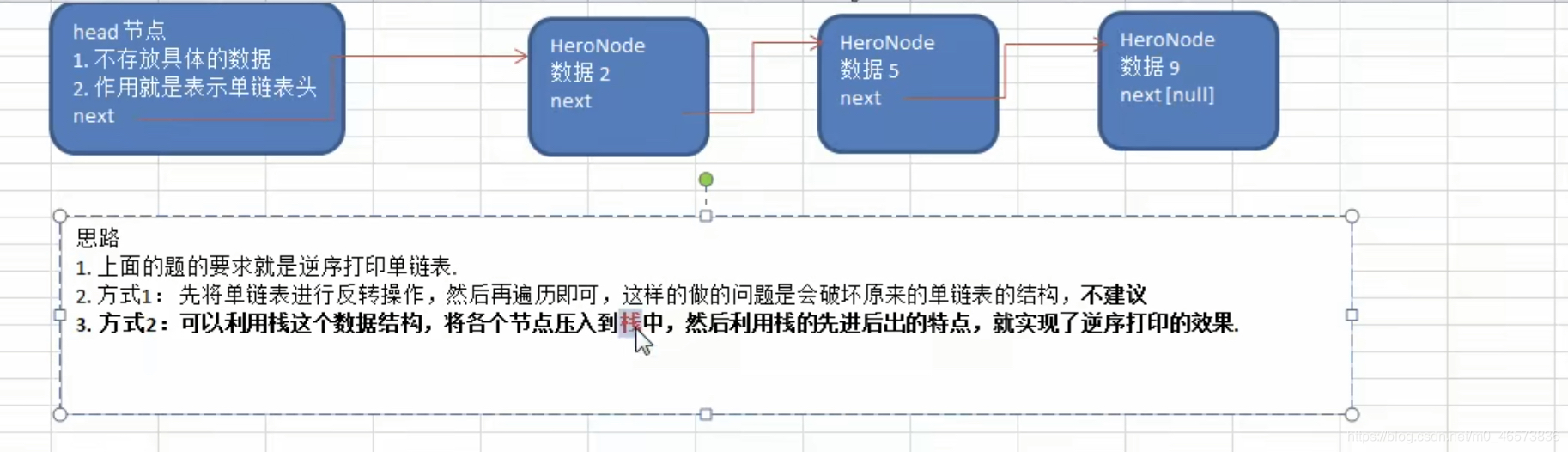
代码实现,这里我们只进行第二种方式的代码实现,因为第一种和上一题类似
public static void reversePrint(HeroNode head){
if (head.next == null){
return;
}
Stack<HeroNode> stack = new Stack<>();
HeroNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
while (stack.size() > 0){
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号