结对编程代码分析
结对编程代码分析
该同学用python语言实现中小学生试卷生成系统。
一、项目结构:
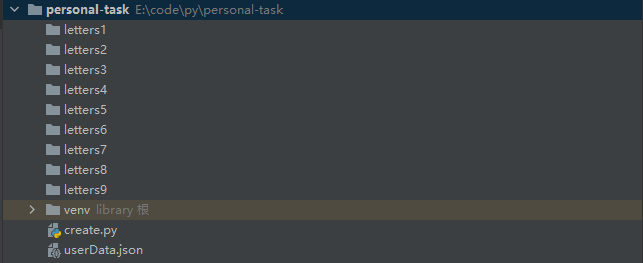
-
letters1~letters9依次存放张三1到王五3的过往试卷,create.py为项目的主程序,userData.json 存放用户数据
-
userData.json内容如图:
![image]()
- 每个用户存有三个属性,account是为用户名,password为密码,grade为用户的预设年级。
二、主程序代码分析:
- 参数及主要函数总览:
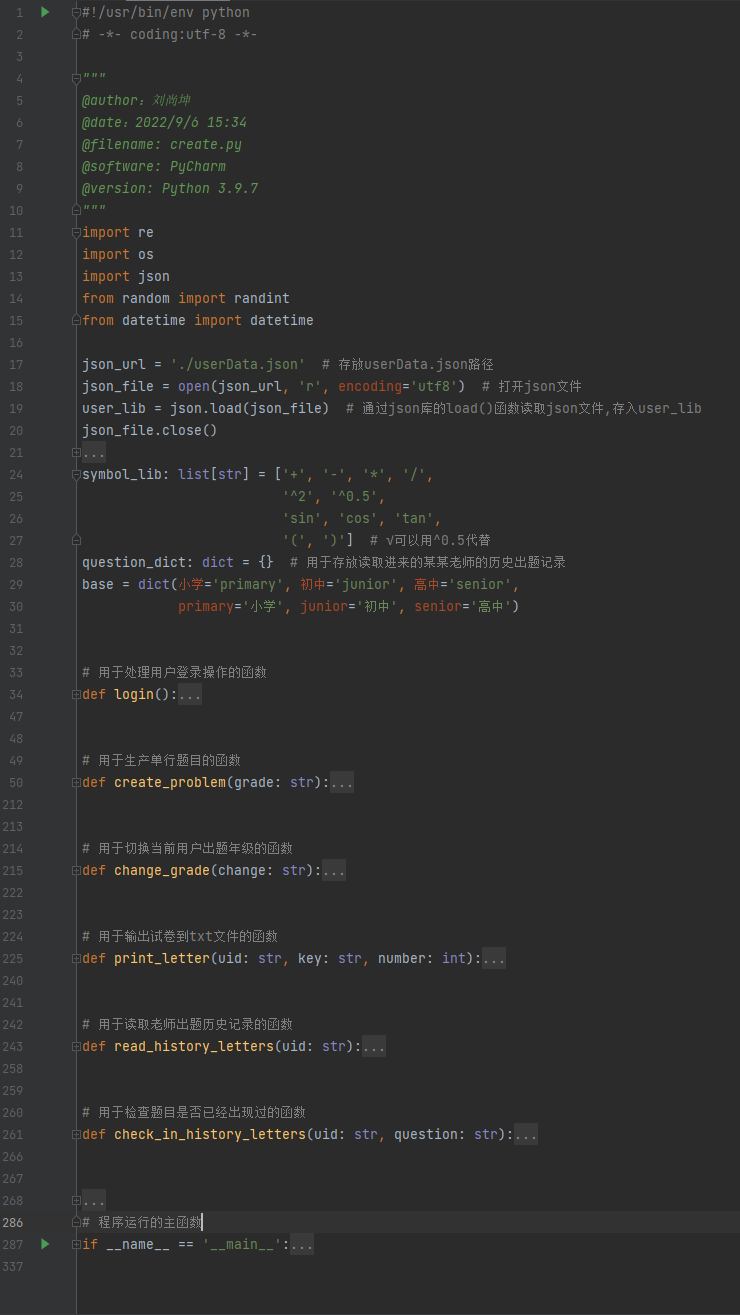
-
login()函数:
# 用于处理用户登录操作的函数 def login(): get: list[str] = [] flag: bool = False # 标识是否登录成功 while 1: if flag: get = input("请输入正确的用户名、密码:").split(' ')#空格分隔 elif not flag: get = input("请输入用户名、密码:").split(' ') flag = True for y in user_lib: if get[0] == user_lib[y]['account'] and get[1] == user_lib[y]['password']: return {'uid': y, 'grade': user_lib[y]['grade']} -
create_problem()函数:
# 用于生产单行题目的函数 def create_problem(grade: str): question: str = '' # 返回值 length: int = randint(2, 5) # 可操作数的个数 考虑到实际情况,不可能只有一个操作数。 # print(f"length:{length}") # 注释掉 num_square = randint(1, length) # 有几个数被赋予特殊符号(开方和平方) num_tangle = randint(1, length) # 有几个数被赋予特殊符号(三角函数) # print(f"num:{num_square}") # 注释掉 data_lib: list[int] = [] # 给操作数编号,为了保证随机时不出现重复数值,使用数组 for i in range(0, length): data_lib.append(i + 1) # print(f"data_lib:{data_lib}") # 注释掉 square_map: dict = {} tangle_map: dict = {} leftbracket: int = 0 # 计数 leftbracket_flag: bool = False # no_double_bracket: bool = False # 防止出现(x)的情况 # 变量定义———————————————————————————————————————————————— if grade == 'primary': # 还未设计添加括号进去 for i in range(0, length): no_double_bracket = False if randint(0, 1) == 1 and length > 2 and i != length - 1: # 随机生成左括号 question += '(' leftbracket += 1 leftbracket_flag = True no_double_bracket = True if i == length - 1: # 只剩一个数了,不用再加符号了 question += f"{randint(1, 100)}" for i in range(0, leftbracket): # 补全括号部分 question += ')' question += '=\n' # if check_string(re_exp, question):# 为了避免等式两端出现括号 # return re.findall(re_exp, question)[0]+'\n' # else: # return question return question question += f"{randint(1, 100)}" for i in range(0, leftbracket): # 随机补全右括号 if randint(0, 1) == 1 and leftbracket_flag and not no_double_bracket: question += ')' leftbracket -= 1 if leftbracket == 0: leftbracket_flag = False question += f"{symbol_lib[randint(0, 3)]}" # 小学题目———————————————————————————————————————————————— elif grade == 'junior': for i in range(0, len(data_lib)): # 给随机几位操作数生成 a = randint(0, len(data_lib) - 1) # 0对应1,1对应2,2对应3,3对应4 symbol_index = randint(4, 5) # print(data_lib[a]) square_map[data_lib[a]] = symbol_lib[symbol_index] data_lib.pop(a) num_square -= 1 if num_square == 0: break # print(square_map) for i in range(0, length): no_double_bracket = False if randint(0, 1) == 1 and length > 2 and i != length - 1: # 随机生成左括号 question += '(' leftbracket += 1 leftbracket_flag = True no_double_bracket = True if i == length - 1: # 只剩一个数了,不用再加符号了 if square_map.__contains__(i + 1): # dict里面有和i对应的键值,说明需要加平方或者开方 question += f"({randint(1, 100)}{square_map[i + 1]})" # 决定暂时给平方、开方加上括号 else: question += f"{randint(1, 100)}" for i in range(0, leftbracket): # 补全括号部分 question += ')' question += '=\n' # if check_string(re_exp, question): # 为了避免等式两端出现括号 # return re.findall(re_exp, question)[0] + '\n' # else: # return question return question r: str = symbol_lib[randint(0, 3)] if square_map.__contains__(i + 1): question += f"({randint(1, 100)}{square_map[i + 1]})" # 决定暂时给平方、开方加上括号 else: question += f"{randint(1, 100)}" for i in range(0, leftbracket): # 随机补全右括号 if randint(0, 1) == 1 and leftbracket_flag and not no_double_bracket: question += ')' leftbracket -= 1 if leftbracket == 0: leftbracket_flag = False question += f"{r}" # 初中题目———————————————————————————————————————————————— elif grade == 'senior': num_square = randint(0, length) for i in range(0, len(data_lib)): # 给随机几位操作数生成 a = randint(0, len(data_lib) - 1) symbol_index = randint(4, 5) # print(data_lib[a]) square_map[data_lib[a]] = symbol_lib[symbol_index] data_lib.pop(a) num_square -= 1 if num_square == 0: break # print(square_map) # 注释掉 data_lib = [] # 为tangle的判定重置data_lib for i in range(0, length): data_lib.append(i + 1) for i in range(0, len(data_lib)): # 给随机几位操作数生成 a = randint(0, len(data_lib) - 1) symbol_index = randint(6, 8) tangle_map[data_lib[a]] = symbol_lib[symbol_index] data_lib.pop(a) num_tangle -= 1 if num_tangle == 0: break # print(tangle_map) # 注释掉 for i in range(0, length): no_double_bracket = False if randint(0, 1) == 1 and length > 2 and i != length - 1: # 随机生成左括号 question += '(' leftbracket += 1 leftbracket_flag = True no_double_bracket = True if i == length - 1: # 只剩一个数了,不用再加符号了 if square_map.__contains__(i + 1) and tangle_map.__contains__(i + 1): # dict里面有和i对应的键值,说明需要加平方或者开方 question += f"{tangle_map[i + 1]}({randint(1, 100)}{square_map[i + 1]})" elif square_map.__contains__(i + 1) and not tangle_map.__contains__(i + 1): question += f"({randint(1, 100)}{square_map[i + 1]})" elif not square_map.__contains__(i + 1) and tangle_map.__contains__(i + 1): question += f"{tangle_map[i + 1]}({randint(1, 100)})" else: question += f"{randint(1, 100)}" for i in range(0, leftbracket): # 补全括号部分 question += ')' question += '=\n' return question r: str = symbol_lib[randint(0, 3)] if square_map.__contains__(i + 1) and tangle_map.__contains__(i + 1): # dict里面有和i对应的键值,说明需要加平方或者开方 question += f"{tangle_map[i + 1]}({randint(1, 100)}{square_map[i + 1]})" elif square_map.__contains__(i + 1) and not tangle_map.__contains__(i + 1): question += f"({randint(1, 100)}{square_map[i + 1]})" elif not square_map.__contains__(i + 1) and tangle_map.__contains__(i + 1): question += f"{tangle_map[i + 1]}({randint(1, 100)})" else: question += f"{randint(1, 100)}" for i in range(0, leftbracket): # 随机补全右括号 if randint(0, 1) == 1 and leftbracket_flag and not no_double_bracket: question += ')' leftbracket -= 1 if leftbracket == 0: leftbracket_flag = False question += f"{r}" # 高中题目———————————————————————————————————————————————— return question -
change_grade()函数:
# 用于切换当前用户出题年级的函数 def change_grade(change: str): if change in {'小学', '初中', '高中'}: return base[change] while 1: change = input("请输入小学、初中和高中三个选项中的一个:").split("切换为")[0] if change in {'小学', '初中', '高中'}: return base[change] -
print_letter()函数:
# 用于输出试卷到txt文件的函数 def print_letter(uid: str, key: str, number: int): file_url = f"./letters{uid}/{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')}.txt" # 使用datatime类的now()函数获取当前时间 # %Y%m%d%H%M%S 格式化选择输出 question: str file = open(file_url, 'w+') for i in range(0, number): while 1: question = create_problem(key) # 调用试题生成函数 if check_in_history_letters(uid, question): break else: pass question += '\n' file.write(question) file.close() return f"********已生成{file_url}********" -
read_history_letters()函数:
# 用于读取老师出题历史记录的函数 def read_history_letters(uid: str): dir_url = f'letters{uid}' question_list: list[str] = [] files: list[str] = [] for root, dirs, files in os.walk(dir_url, topdown=False): # root 根目录、dirs 子目录、files 子目录里的文件 # print(files) # 注释掉 pass for file in files: # 遍历目录里的txt文件 f = open(f'./{dir_url}/{file}', 'r') for line in f: # 遍历文件的每一行 if line != '\n': question_list.append(line.split('\n')[0]) # 去除换行转义字符 question_dict[uid] = question_list # print(question_dict) # 注释掉 -
check_in_history_letters()函数:
# 用于检查题目是否已经出现过的函数 def check_in_history_letters(uid: str, question: str): if question_dict[uid].__contains__(question): return False else: return True -
main函数
# 程序运行的主函数 if __name__ == '__main__': user = login() key = user.get('grade') uid = user.get('uid') # print(datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S'))#注释掉 print(f"当前选择为{base[key]}出题") read_history_letters(uid) # 预先读取当前用户的题库 while 1: change: str = '' number: int = 0 error: bool = False print("********---********") get = input(f"准备生成{base[key]}数学题目,请输入生成题目数量(输入-1将退出当前用户,重新登录):") if len(get.split("切换为")) == 2: change = get.split("切换为")[1] if change == '': error = True else: try: number = int(get) except ValueError: error = True if number <= 30 and number >= 10: # 10-30 正常输出 print(print_letter(uid, key, number)) elif get == '-1': # -1重新登录(-1 的判断优先级必须高于 >30 or <10 的判断) user = login() uid = user.get('uid') key = user.get('grade') read_history_letters(uid) # 同时更新key和uid elif change in {'小学', '初中', '高中'} and key != base[change]: # 切换年级 key = change_grade(change) print(f"当前选择为{base[key]}出题") elif error: print("请输入正确的指令,切换年级请输入\"切换为XX\"") pass elif number > 30 or number < 10: # 超出题数范围,重新输入 while 1: get = input(f"准备生成{base[key]}数学题目,请在允许范围内输入生成题目数量(10-30之间):") try: number = int(get) if number <= 30 and number >= 10 or number == -1: break; except ValueError: pass if number != -1: print(print_letter(uid, key, number)) else: print("请输入正确的指令,切换年级请输入\"切换为XX\"") pass
三、代码优缺点分析:
-
优点:
-
分了多个函数实现功能,每个函数的作用明确,整体的结构清晰
-
可拓展性强
代码结构清晰,对各数据结构、函数进行了明确细致地划分,有利于后期功能拓展与项目扩大。
-
文件路径使用相对路径,清晰明确。
-
-
缺点:
-
功能实现不完全:不能在三角函数、平方和开方的计算中掺杂复杂表达式(例如:tan(10+20)、(1+9)^2等等类似题目),无法生成
-
括号的使用会出现冗余现象,指:
(21-(11/(96+18)))=这种情况,计算式最外层出现的无意义括号。
-
四、生成结果展示:
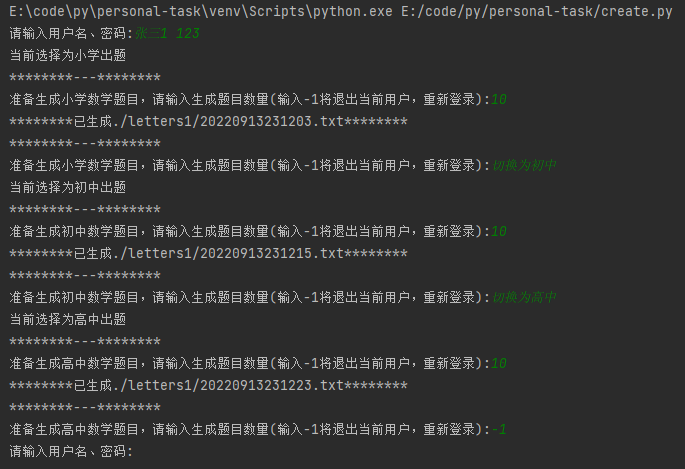
-
小学
33/73-45+72= 44/81= 42-59= (1/30)-72*(26-40)= (44/67)+76*(14-47)= (21-(11/(96+18)))= 65/(85/91*11-2)= 32+(91-61)= 26-(88/15)= 89/13= -
初中
(85-22*((65^0.5)/28))= 51/15*(77^0.5)= (81^0.5)-(25^2)= ((51^0.5)*29*((96^0.5)+((87^2)*31)))= 65-25-(36^2)= ((90^0.5)-(32/((75^0.5)-(66+(65^2)))))= (20/(67^2))-51= (35^2)-((65^0.5)-(60^2))/(68^0.5)+(73^2)= (59^0.5)+2= (54^0.5)*(75^2)= -
高中
(tan(78^0.5)/tan(45^2))+(50^2)= tan(93^0.5)/(sin(27^2)-sin(37^2))= (88^2)/78/(tan(99^0.5)*(23+83))= tan(64^0.5)-(41^2)= (tan(68^0.5)/cos(96))/sin(34)= (sin(87^2)+cos(94^0.5)*(cos(35^2)+tan(30^0.5))+sin(2^0.5))= tan(20^0.5)*cos(23^2)= (92-((46^0.5)-(16+((92^0.5)-cos(91^2)))))= (99^2)-sin(100^2)= (29^2)-cos(3^0.5)/cos(22^0.5)=



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号