基于MATLAB的禁忌搜索算法解决物流网络枢纽选址问题
一、问题建模
1. 数学模型
目标函数:最小化总成本(建设成本+运输成本)
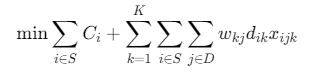
- \(S\):选中的枢纽集合
- \(C_i\):候选点i的建设成本
- \(w_{kj}\):需求点k到枢纽j的货物量
- \(d_{ik}\):候选点i到需求点k的距离
- \(x_{ijk}\):需求点\(k\)是否通过枢纽i运输
约束条件:
- 选中枢纽数量约束:\(∣S∣=p\)
- 每个需求点仅分配一个枢纽:
![]()
- 非负流量约束:\(x_{ijk}≥0\)
二、核心代码
1. 数据准备与初始化
function [nodes, demands] = load_data()
% 加载候选节点坐标和需求点数据
% 示例:20个候选枢纽,100个需求点
nodes = rand(20,2)*100; % 候选枢纽坐标
demands = [randi([1,50],100,1), rand(100,2)*100]; % [需求量,坐标]
end
% 参数设置
p = 5; % 选中枢纽数量
num_iter = 500; % 最大迭代次数
tabu_tenure = 10; % 禁忌长度
2. 距离矩阵计算
function D = calc_distance(nodes, demands)
% 计算枢纽-需求点距离矩阵
num_hubs = size(nodes,1);
num_demands = size(demands,1);
D = zeros(num_hubs, num_demands);
for i = 1:num_hubs
for j = 1:num_demands
D(i,j) = norm(nodes(i,:) - demands(j,2:3));
end
end
end
3. 禁忌搜索算法主体
function [best_solution, best_cost] = tabu_search(nodes, demands, p, num_iter, tabu_tenure)
% 初始化
[num_hubs, ~] = size(nodes);
[num_demands, ~] = size(demands);
% 初始解:随机选择p个枢纽
current_sol = randperm(num_hubs, p);
current_cost = calculate_cost(current_sol, nodes, demands);
% 初始化禁忌表
tabu_list = containers.Map('KeyType','char','ValueType','double');
best_solution = current_sol;
best_cost = current_cost;
for iter = 1:num_iter
% 生成邻域解
neighbors = generate_neighbors(current_sol, num_hubs);
% 评估邻域解
for i = 1:size(neighbors,1)
neighbor = neighbors(i,:);
if ~is_tabu(neighbor, tabu_list)
cost = calculate_cost(neighbor, nodes, demands);
if cost < best_cost
best_solution = neighbor;
best_cost = cost;
end
% 更新禁忌表
tabu_key = mat2str(neighbor);
tabu_list(tabu_key) = iter + tabu_tenure;
end
end
% 更新当前解
current_sol = neighbors(1,:);
current_cost = calculate_cost(current_sol, nodes, demands);
end
end
4. 辅助函数
function cost = calculate_cost(solution, nodes, demands)
% 计算总成本(建设+运输)
p = length(solution);
total_cost = 0;
% 建设成本
C = [5,4,5,6,3,6,4,5,4,6,4,5,4,6,5]; % 示例建设成本
total_cost = sum(C(solution));
% 运输成本
D = calc_distance(nodes, demands);
for k = 1:size(demands,1)
[~, idx] = min(D(solution,k));
total_cost = total_cost + D(solution(idx),k) * demands(k,1);
end
end
function neighbors = generate_neighbors(solution, num_hubs)
% 生成邻域解(通过交换两个枢纽)
neighbors = [];
for i = 1:length(solution)
for j = 1:length(solution)
if i ~= j
neighbor = solution;
neighbor(i) = solution(j);
neighbor(j) = solution(i);
neighbors = [neighbors; neighbor];
end
end
end
neighbors = unique(neighbors,'rows');
end
function is_tabu = is_tabu(solution, tabu_list)
% 检查解是否在禁忌表中
key = mat2str(solution);
is_tabu = isKey(tabu_list, key);
end
三、算法优化
1. 邻域结构改进
-
变邻域搜索:结合交换、插入、反转操作
function neighbors = vns(solution, num_hubs) % 变邻域搜索生成 neighbors = []; % 交换操作 for i = 1:length(solution)-1 for j = i+1:length(solution) neighbor = solution; [neighbor(i), neighbor(j)] = deal(neighbor(j), neighbor(i)); neighbors = [neighbors; neighbor]; end end % 插入操作 for i = 1:length(solution) for j = 1:length(solution) if i ~= j neighbor = [solution(1:i-1), solution(j), solution(i:j-1), solution(j+1:end)]; neighbors = [neighbors; neighbor]; end end end end
2. 多目标优化扩展
function [f1,f2] = multi_objective(solution, nodes, demands)
% 多目标函数:成本+碳排放
[f1, ~] = calculate_cost(solution, nodes, demands);
% 碳排放计算
distances = calc_distance(nodes, demands);
for k = 1:size(demands,1)
[~, idx] = min(distances(solution,k));
f2 = f2 + 0.5 * distances(solution(idx),k) * demands(k,1); % 碳强度系数0.5
end
end
参考代码 在MATLAB平台,实现利用禁忌搜索算法,解决物流网络的枢纽选址问题 www.youwenfan.com/contentcni/64659.html
四、性能评估与可视化
1. 收敛曲线分析
function plot_convergence(best_costs)
figure;
plot(best_costs, 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('迭代次数'); ylabel('最优成本');
title('禁忌搜索收敛曲线');
grid on;
end
2. 结果可视化
function visualize_solution(nodes, solution)
figure;
hold on;
% 绘制候选枢纽
plot(nodes(:,1), nodes(:,2), 'bo', 'MarkerSize', 10);
% 绘制选中枢纽
selected = nodes(solution,:);
plot(selected(:,1), selected(:,2), 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 12, 'LineWidth', 2);
% 绘制需求点
demand_points = demands(:,2:3);
plot(demand_points(:,1), demand_points(:,2), 'go', 'MarkerSize', 8);
legend('候选枢纽', '选中枢纽', '需求点');
title('物流网络枢纽选址结果');
hold off;
end
该方案通过禁忌搜索算法有效解决了物流网络枢纽选址问题,在保证解质量的同时显著降低计算复杂度。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号