数据处理类
这里主要介绍DecimalFormat类、Math类、Random类、BigInteger类和BigDecimal类。
1.DecimalFormat类(用于格式化数据)
在Java中没有格式化的数据遵循以下原则:
- 如果数据绝对值在0.001~107,Java将以常规小数形式表示。
- 绝对值小于0.001或大于107,使用科学计数法表示。
DecimalFormat类时NumberFormat的一个之类,用于格式化十进制数字,它可以将一些数字格式化为整数、浮点数、百分数等。
表1 DemicalFormat类中特殊字符说明
| 字符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 代表阿拉伯数字,如果该位不存在数字,则显示0 |
| # | 代表阿拉伯数字,如果改为上不存在数字,则不显示 |
| . | 小数分隔符 |
| - | 负号 |
| , | 分组分隔符 |
| E | 分隔科学计数法中的尾数和指数 |
| % | 放置在数字的前缀或后缀,将数字乘以100显示为百分数 |
| \u2030 | 放置在数字的前缀或后缀,将数字乘以1000显示为千分数 |
| \u00A4 | 前缀或后缀,作为货币记号 |
| ' | 当上述特殊字符出现在数字中,应为特殊字符添加单引号,系统会将此符号当作普通符号处理 |
应用实例:
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class DecimalFormatSimpleDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
simgleFormat("###,###.###",123456.789); //调用simgleFormat方法
simgleFormat("0000000.###kg",4654890.124); //调用simgleFormat方法
simgleFormat("00.000",1234.12); //调用simgleFormat方法
UsedapplyPattern("#.###%",0.789); //调用UsedapplyPattern()方法
UsedapplyPattern("###.##",23345.132); //调用UsedapplyPattern()方法
UsedapplyPattern("0.00\u2030",0.789); //调用UsedapplyPattern()方法
}
static public void simgleFormat(String pattern, double value)
{
DecimalFormat myformat =new DecimalFormat(pattern); //创建DecimalFormat对象 myformat,并设置格式化模式
String output = myformat.format(value); //使用格式化模式格式化value
System.out.println(value+"__"+pattern+"__"+output);
}
static public void UsedapplyPattern(String pattern, double value)
{
DecimalFormat myFormat= new DecimalFormat(); //创建DecimalFormat对象,但不设置格式化模式
myFormat.applyPattern(pattern); //使用applyFormat()设置格式化模式
String output=myFormat.format(value);
System.out.println(value+"__"+pattern+"__"+output);
}
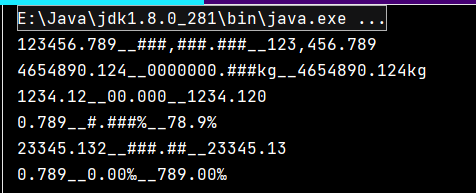
/*
123456.789__###,###.###__123,456.789
4654890.124__0000000.###kg__4654890.124kg
1234.12__00.000__1234.120
0.789__#.###%__78.9%
23345.132__###.##__23345.13
0.789__0.00‰__789.00‰
*/
}
2. Math 类
使用方法:
Math.数学方法
例:
Math.PI
Math.E
常用数学运算方法:
三角函数:
Math.sin(double a): 返回正弦值;
Math.cos(double a): 返回余弦值;
Math.tan(double a): 返回正切值;
Math.asin(double a): 返回反正弦;
Math.acos(double a): 返回反余弦;
Math.atan(double a): 返回反正切;
Math.toRadians(double a): 角度转弧度;
Math.toDegrees(double a): 弧度转角度。
指数函数:
exp(double a): ea
log(double a): ln a
log10(double a): log10a
sqrt(double a): a的平方根
cbrt(double a): a的立方根
pow(double a, double b): ab
取整函数:
ceil(double a): 返回大于等于参数的最小整数
floor(double a):返回小于等于参数的最大整数
rint(double a): 返回与参数最接近的整数,两整数同样接近,则结果取偶数
round(float a): 将参数+0.5后向下取整
round(double a): 将参数+0.5后,四舍五入
3. Random类
Random类提供产生各种类型随机数的方法。
1.Math.random()方法
Math.random()可以产生随机数,默认产生0.0~1.0的double型随机数,即0<=Math.random()<1.0。
2.Rondom类
使用java.util.Random类,可以通过实例化一个Random对象创建一个随机数生成器。
语法如下:
Random r=new Random();
以这种方式实例化对象时,Java编译器以系统当前时间作为随机数生成器的种子,因为每时每刻时间不可能相同,所以产生的随机数将不同,但是如果运行速度太快,也会产生两次结果相同的随机数。
同时,也可以在实例化Random类对象时,设置随机数生成器的种子。语法如下:
Random r= new Random(seedValue)
在Random类中提供了获取各种数据类型的随机数方法,常用的如下:
nextInt():返回一个随机整数;nextInt(int n):返回一个大于等于0小于n的整数;nextLong():返回一个随机长整形数;nexyBoolean():返回一个随机的布尔型值;nextFloat():返回一个随机浮点型值;nextDouble():返回一个随机双精度型值;nextGaussian():返回一个概率密度为高斯分布的双精度值。
程序实例:
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r=new Random();
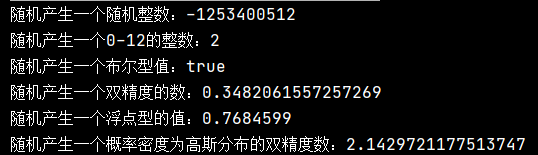
System.out.println("随机产生一个随机整数:"+r.nextInt());
System.out.println("随机产生一个0-12的整数:"+r.nextInt(13));
System.out.println("随机产生一个布尔型值:"+r.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("随机产生一个双精度的数:"+r.nextDouble());
System.out.println("随机产生一个浮点型的值:"+r.nextFloat());
System.out.println("随机产生一个概率密度为高斯分布的双精度数:"+r.nextGaussian());
}
}
运行结果为:
4. BigInteger类和BigDecimal类
这两个类主要用于高精度计算,BigInteger类是针对大整数的处理类,Bigdecimal时针对大小数的处理类。
4.1 Biginteger类
Biginteger类支持任意精度的整数,也就是说在运算中BigInteger类型可以准确地表示任何大小的整数值而不会丢失任何信息。
可以通过实例化一个BigInteger对象,来使用BigInteger类。语法如下:
public BigInteger(String val),其中val为十进制字符串
例子:
BigInteger twoInstance =new BigInteger("2"); //将十进制2转换为BigInteger形式
BigInteger类的一些常用方法:
- add(BigInteger val): 加法
- subtract(BigInteger val): 减法
- multiply(BigInteger val): 乘法
- divide(BigInteger val): 除法
- remainder(BigInteger val):取余
- divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val):用数组返回余数和商,结果数组中,第一个值为商,第二个值为余数。
- pow(int exponent): 参数的exponent次方操作
- negate():取相反数
- shiftLeft(int n):将数字左移n位,如果n为负数,做右移操作;
- shiftRight(int n):将数字右移n位,如果n为负数,做左移操作
- and(BigInteger val):与操作
- or(BigInteger val):或操作
- compareTo(BigInteger val):做数字比较操作
- equals(Object x):当参数x是BigInteger类型的数字并且数值相等时,返回true
- min(BigInteger val):返回较小的值;
- max(BigInteger val):返回较大的值
实例:
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class BigIntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigInteger bigInstance =new BigInteger("4");
//bigInstance+2操作
System.out.println("加法操作: "+ bigInstance.add(new BigInteger("2")));
//减法
System.out.println("减法操作: "+ bigInstance.subtract(new BigInteger("2")));
//乘法
System.out.println("乘法操作: "+ bigInstance.multiply(new BigInteger("2")));
//除法
System.out.println("除法操作: "+ bigInstance.divide(new BigInteger("2")));
//取商和取余
System.out.println("取商: "+bigInstance.divideAndRemainder(new BigInteger("3"))[0]);
System.out.println("取余: "+bigInstance.divideAndRemainder(new BigInteger("3"))[1]);
//平方
System.out.println("平方: "+bigInstance.pow(2));
//相反数
System.out.println("相反数: "+bigInstance.negate());
}
/*
*加法操作: 6
减法操作: 2
乘法操作: 8
除法操作: 2
取商: 1
取余: 1
平方: 16
相反数: -4
*/
}
4.2 BigDecimal类
BigDecimal类与BigInteger类大致相同,不同的时BigDecimal加入了小数的概念。
方法使用也与BigInteger使用大致相同,不同点在于除法。
public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale ,int roundingMode),3个参数依次为除数,商的小数点后的位数,近似处理模式。
| 模式 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| BigDecimal.ROUND_UP | 商的最后一位如果大于0,则向前进位,正负都是如此 |
| BigDecimal.ROUND_DOWN | 商的最后一位无论是什么数字都省略 |
| BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING | 商如果时正数,按照ROUND_UP;负数,按照ROUND_DOWN。 |
| BigDecimal.ROUND_FLOOR | 与ROUND_CEILING相反 |
| BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_DOWN | 四舍五入,最后一位<=5,舍弃;>5,进位操作 |
| BigDecimal.ROUND_HAIF_UP | 四舍五入,最后一位<5,舍弃;>=5,进位操作 |
| BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_EVEN | 商的倒数第二位为奇数,ROUNF_HALF_UP,为偶数,按照ROUND_HALF_DOWN |
实例:
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class BigDecimalDemo {
static final int location=10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimalDemo b=new BigDecimalDemo();
System.out.println("加法:"+b.add(-7.5,8.9));
System.out.println("减法:"+b.sub(-7.5,8.9));
System.out.println("乘法:"+b.mul(-7.5,8.9));
System.out.println("除法(10位小数)"+ b.div(10,2));
System.out.println("除法(5位小数)" +b.div(-7.5,8.9,5));
}
//定义加法
public BigDecimal add(double val1, double val2)
{
BigDecimal b1=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val1));
BigDecimal b2=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val2));
return b1.add(b2);
}
//定义减法
public BigDecimal sub(double val1,double val2)
{
BigDecimal b1=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val1));
BigDecimal b2=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val2));
return b1.subtract(b2);
}
//定义乘法
public BigDecimal mul(double val1, double val2)
{
BigDecimal b1=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val1));
BigDecimal b2=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val2));
return b1.multiply(b2);
}
//定义除法
public BigDecimal div(double val1,double val2)
{
return div(val1,val2,location);
}
public BigDecimal div(double val1,double val2,int b)
{
if(b<0)
{
System.out.println("b的值必须大于等于0");
}
BigDecimal b1=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val1));
BigDecimal b2=new BigDecimal(Double.toString(val2));
return b1.divide(b2,b,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号