173. Binary Search Tree Iterator
173. Binary Search Tree Iterator
Implement an iterator over a binary search tree (BST). Your iterator will be initialized with the root node of a BST.
Calling next() will return the next smallest number in the BST.
Example
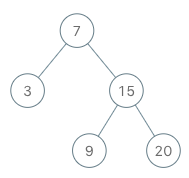
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // return 3
iterator.next(); // return 7
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 9
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 15
iterator.hasNext(); // return true
iterator.next(); // return 20
iterator.hasNext(); // return false
Note
next()andhasNext()should run in average $O(1)$ time and uses $O(h)$ memory, where h is the height of the tree.- You may assume that next() call will always be valid, that is, there will be at least a next smallest number in the BST when
next()is called.
Solution
-
☝️
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class BSTIterator {
private Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
inOrder(root);
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
public int next() {
return this.queue.poll();
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
public boolean hasNext() {
return !this.queue.isEmpty();
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root != null) {
inOrder(root.left);
this.queue.offer(root.val);
inOrder(root.right);
}
}
}
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj.next();
* boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext();
*/
该方法使用队列和中序遍历把BST遍历一边,得到的队列就是从小到大排序好了的,接下来只要运用Java队列的offer、poll、isEmpty函数即可解决该问题。该方法的空间复杂度为$O(N)$,时间复杂度为$O(N)$,对于突发性的大量数据,会OOM,但对于该题,由于友好的测试样例,该方法才得意通过。
-
✌️
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class BSTIterator {
TreeNode node;
Stack<TreeNode> stack;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {
this.node = root;
this.stack = new Stack<>();
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
public int next() {
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
}
node = stack.pop();
int retval = node.val;
node = node.right;
return retval;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
public boolean hasNext() {
return node != null || !stack.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root);
* int param_1 = obj.next();
* boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext();
*/
该方法借助堆栈实现的中序遍历BST完美的解决了问题,且堆栈的数据大小一般不会是节点的大小(除非是左斜树),空间复杂度$O(N)$,时间复杂度$O(N)$。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号