MyBatis学习记录
MyBatis
1 简介
1.1 什么是MyBatis
- MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架。
- 它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。
- MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。
- MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
1.2 什么是持久化
数据持久化
- 持久化就是将程序的数据在持久状态和瞬时状态转化的过程
- 持久层,可以理解成数据 保存在 数据库或者 硬盘一类可以保存很长时间的设备里面,不像放在内存中那样断电就消失了,也就是把数据存在持久化设备上,mybatis就是持久层。
- 数据库(Jdbc),io文件持久化。
1.3 什么是持久层
Dao层、Service层、Controller层、...
- 完成持久化工作的代码块
- 层界限十分明显
1.4 MyBatis特点
- 简单易学:本身就很小且简单。没有任何第三方依赖,最简单安装只要两个jar文件+配置几个sql映射文件易于学习,易于使用,通过文档和源代码,可以比较完全的掌握它的设计思路和实现。
- 灵活:mybatis不会对应用程序或者数据库的现有设计强加任何影响。 sql写在xml里,便于统一管理和优化。通过sql语句可以满足操作数据库的所有需求。
- 解除sql与程序代码的耦合:通过提供DAO层,将业务逻辑和数据访问逻辑分离,使系统的设计更清晰,更易维护,更易单元测试。sql和代码的分离,提高了可维护性。
- 提供映射标签,支持对象与数据库的orm字段关系映射。
- 提供对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系组建维护。
- 提供xml标签,支持编写动态sql。
2 第一个MyBatis程序
2.1 创建mybatis的核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306?mybatis?userSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
2.2 编写mybatis工具类
//sqlSessionFactory -> sqlSession
public class MyBatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static {
try {
// 使用MyBatis第一步:获取sqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static SqlSession getSqlSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
2.3 编写代码
-
实体类
package com.pojo; public class User { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; public User(int id, String name, String pwd) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; } public int getId() { return id; } public String getName() { return name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } } -
Dao接口
package com.dao; import com.pojo.User; import java.util.List; public interface UserDao { List<User> getUserList(); } -
接口实现类:由原来的UserDaoImpl转为UserMapper
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--namespace=绑定一个对应的Dao/Mapper接口--> <mapper namespace="com.dao.UserDao"> <select id="getUserList" resultType="com.pojo.User"> select * from mybatis.user </select> </mapper> -
测试
// UserDaoTest.java package com.dao; import com.pojo.User; import com.utils.MyBatisUtils; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.List; public class UserDaoTest { @Test public void Test1() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { // 1 获得SqlSession对象 // 2 方式一:getMapper 更推荐 UserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class); List<User> userList= mapper.getUserList(); // 2 方式二:selectList //List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("com.dao.UserDao.getUserList"); for (User user : userList) { System.out.println(user); } } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 3 关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); } } }
2.4 可能出现的问题
-
org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Type interface com.dao.UserDao is not known to theMapperRegistry.
解决方法:在MyBatis的核心配置文件中注册Mapper
-
java . ang.ExceptionInInitializerError异常
原因:maven由于它的约定大于配置,可能遇到写的配置文件无法被到处或者生效问题
解决方法:
<build> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.xml</include> <include>**/*.properties</include> </includes> <!--<filtering>true</filtering>--> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.xml</include> <include>**/*.properties</include> </includes> <!--<filtering>true</filtering>--> </resource> </resources> </build> -
绑定接口错误
-
方法名不对
-
返回类型不对
3 增删改查(CRUD)
3.1 namespace
namespace中的包名要和接口的包名一致!
3.2 select
查询语句
- id: 就是对应的 namespace 中的方法名
- resultTypr: SQL语句执行的返回值
- parameterType: 参数类型
-
编写接口方法
// 查询全部用户 List<User> getUserList(); //根据id查询用户 User getUserById(int id); -
编写对应的mapper中的SQL语句
<select id="getUserList" resultType="com.pojo.User"> select * from mybatis.user </select> <select id="getUserById" resultType="com.pojo.User" parameterType="int"> select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}; </select> -
测试
@Test public void Test1() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { UserDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class); List<User> userList= mapper.getUserList(); for (User user : userList) { System.out.println(user); } } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 3 关闭SqlSession sqlSession.close(); } } @Test public void Test2() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); System.out.println(mapper.getUserById(1)); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
3.2 insert
-
编写接口方法
//插入数据 int addUser(User user); -
编写对应的mapper中的SQL语句
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.pojo.User"> insert into mybatis.user (id, name, pwd) values (#{id}, #{name}, #{pwd}); </insert> -
测试,注意增删改需要提交事务
@Test //增删改需要提交事务 //增 public void Test3() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); int res = mapper.addUser(new User(4, "赵六", "1593857")); if(res > 0) { System.out.println("插入成功"); } //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
3.3 update
-
编写接口方法
//修改用户 int updateUser(User user); -
编写对应的mapper中的SQL语句
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.pojo.User"> update mybatis.user set name=#{name}, pwd=#{pwd} where id=#{id}; </update> -
测试,注意增删改需要提交事务
@Test //增删改需要提交事务 //改 public void Test4() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); int res = mapper.updateUser(new User(4, "赵六", "15321564")); if(res > 0) { System.out.println("修改成功"); } //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
3.4 delete
-
编写接口方法
//删除用户 int deleteUser(int id); -
编写对应的mapper中的SQL语句
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int"> delete from mybatis.user where id=#{id}; </delete> -
测试,注意增删改需要提交事务
@Test //增删改需要提交事务 //删 public void Test5() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); int res = mapper.deleteUser(4); if(res > 0) { System.out.println("删除成功"); } //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
3.5 Map使用
若实体类或者数据库中的表、字段或者参数过多时,可以考虑使用Map,列名与属性名不一致的时候使用Map。
-
编写接口方法
// 使用Map插入数据 int addUserByMap(Map<String, Object> map); -
编写对应的mapper中的SQL语句
<insert id="addUserByMap" parameterType="map"> insert into mybatis.user (id, name, pwd) values (#{userId}, #{userName}, #{userPwd}); </insert> -
测试
@Test public void Test31() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("userId", 5); map.put("userName", "July"); map.put("userPwd", "12312312"); int res = mapper.addUserByMap(map); if(res > 0) { System.out.println("插入成功"); } //提交事务 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
3.6 模糊查询
-
Java代码执行的时候,传递通配符(% %)
List<User> userList = mapper.getUserLike("%李%"); -
在SQL拼接中使用通配符
select * from mybatis.user where name like "%"#{value}"%"
4 配置
MyBatis 的配置文件包含了会深深影响 MyBatis 行为的设置和属性信息。 配置文档的顶层结构如下:
- configuration(配置)
- properties(属性)
- settings(设置)
- typeAliases(类型别名)
- typeHandlers(类型处理器)
- objectFactory(对象工厂)
- plugins(插件)
- environments(环境配置)
- environment(环境变量)
- transactionManager(事务管理器)
- dataSource(数据源)
- environment(环境变量)
- databaseIdProvider(数据库厂商标识)
- mappers(映射器)
4.1 属性(properties)
这些属性可以在外部进行配置,并可以进行动态替换。你既可以在典型的 Java 属性文件中配置这些属性,也可以在 properties 元素的子元素中设置。(可以通过properties属性来实现引用配置文件。)
-
编写properties文件
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?userSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 username=root password=root -
引入外部配置文件
<!--引入外部配置文件--> <properties resource="db.properties"> <!--同一字段优先使用外部配置文件--> <property name="username" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="root"></property> </properties> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
4.2 环境配置(environments)
- MyBatis 可以配置成适应多种环境,这种机制有助于将 SQL 映射应用于多种数据库之中, 现实情况下有多种理由需要这么做。例如,开发、测试和生产环境需要有不同的配置;或者想在具有相同 Schema 的多个生产数据库中使用相同的 SQL 映射。还有许多类似的使用场景。
- 不过要记住:尽管可以配置多个环境,但每个 SqlSessionFactory 实例只能选择一种环境。
environments 元素定义了如何配置环境。
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="..." value="..."/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
注意:
- 默认使用的环境 ID(比如:default="development")。
- 每个 environment 元素定义的环境 ID(比如:id="development")。
- 事务管理器的配置(比如:type="JDBC")。
- 数据源的配置(比如:type="POOLED")。
4.2.1 事务管理器
在 MyBatis 中有两种类型的事务管理器(也就是 type="[JDBC|MANAGED]"):
- JDBC – 这个配置直接使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设施,它依赖从数据源获得的连接来管理事务作用域。(默认)
- MANAGED – 这个配置几乎没做什么。它从不提交或回滚一个连接,而是让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 默认情况下它会关闭连接。然而一些容器并不希望连接被关闭,因此需要将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false 来阻止默认的关闭行为。(了解)
- 如果你正在使用 Spring + MyBatis,则没有必要配置事务管理器,因为 Spring 模块会使用自带的管理器来覆盖前面的配置。
4.2.2 数据源
dataSource 元素使用标准的 JDBC 数据源接口来配置 JDBC 连接对象的资源。有三种内建的数据源类型(也就是 type="[UNPOOLED|POOLED|JNDI]"):
-
UNPOOLED– 这个数据源的实现会每次请求时打开和关闭连接。虽然有点慢,但对那些数据库连接可用性要求不高的简单应用程序来说,是一个很好的选择。 性能表现则依赖于使用的数据库,对某些数据库来说,使用连接池并不重要,这个配置就很适合这种情形。UNPOOLED 类型的数据源仅仅需要配置以下 5 种属性:
driver– 这是 JDBC 驱动的 Java 类全限定名(并不是 JDBC 驱动中可能包含的数据源类)。url– 这是数据库的 JDBC URL 地址。username– 登录数据库的用户名。password– 登录数据库的密码。defaultTransactionIsolationLevel– 默认的连接事务隔离级别。defaultNetworkTimeout– 等待数据库操作完成的默认网络超时时间(单位:毫秒)。
-
POOLED – 这种数据源的实现利用“池”的概念将 JDBC 连接对象组织起来,避免了创建新的连接实例时所必需的初始化和认证时间。 这种处理方式很流行,能使并发 Web 应用快速响应请求。(默认使用)除了上述提到 UNPOOLED 下的属性外,还有更多属性用来配置 POOLED 的数据源:
poolMaximumActiveConnections– 在任意时间可存在的活动(正在使用)连接数量,默认值:10poolMaximumIdleConnections– 任意时间可能存在的空闲连接数。poolMaximumCheckoutTime– 在被强制返回之前,池中连接被检出(checked out)时间,默认值:20000 毫秒(即 20 秒)poolTimeToWait– 这是一个底层设置,如果获取连接花费了相当长的时间,连接池会打印状态日志并重新尝试获取一个连接(避免在误配置的情况下一直失败且不打印日志),默认值:20000 毫秒(即 20 秒)。poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance– 这是一个关于坏连接容忍度的底层设置, 作用于每一个尝试从缓存池获取连接的线程。 如果这个线程获取到的是一个坏的连接,那么这个数据源允许这个线程尝试重新获取一个新的连接,但是这个重新尝试的次数不应该超过poolMaximumIdleConnections与poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance之和。 默认值:3(新增于 3.4.5)poolPingQuery– 发送到数据库的侦测查询,用来检验连接是否正常工作并准备接受请求。默认是“NO PING QUERY SET”,这会导致多数数据库驱动出错时返回恰当的错误消息。poolPingEnabled– 是否启用侦测查询。若开启,需要设置poolPingQuery属性为一个可执行的 SQL 语句(最好是一个速度非常快的 SQL 语句),默认值:false。poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor– 配置 poolPingQuery 的频率。可以被设置为和数据库连接超时时间一样,来避免不必要的侦测,默认值:0(即所有连接每一时刻都被侦测 — 当然仅当 poolPingEnabled 为 true 时适用)。
-
JNDI – 这个数据源实现是为了能在如 EJB 或应用服务器这类容器中使用,容器可以集中或在外部配置数据源,然后放置一个 JNDI 上下文的数据源引用。这种数据源配置只需要两个属性:
initial_context– 这个属性用来在 InitialContext 中寻找上下文(即,initialContext.lookup(initial_context))。这是个可选属性,如果忽略,那么将会直接从 InitialContext 中寻找 data_source 属性。data_source– 这是引用数据源实例位置的上下文路径。提供了 initial_context 配置时会在其返回的上下文中进行查找,没有提供时则直接在 InitialContext 中查找。
和其他数据源配置类似,可以通过添加前缀“env.”直接把属性传递给 InitialContext。比如:
env.encoding=UTF8
这就会在 InitialContext 实例化时往它的构造方法传递值为
UTF8的encoding属性。
4.3 设置(settings)
这是 MyBatis 中极为重要的调整设置,它们会改变 MyBatis 的运行时行为。 下表描述了设置中各项设置的含义、默认值等。
| 设置名 | 描述 | 有效值 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cacheEnabled | 全局性地开启或关闭所有映射器配置文件中已配置的任何缓存。 | true | false | true |
| lazyLoadingEnabled | 延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。 特定关联关系中可通过设置 fetchType 属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。 |
true | false | false |
| aggressiveLazyLoading | 开启时,任一方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有延迟加载属性。 否则,每个延迟加载属性会按需加载(参考 lazyLoadTriggerMethods)。 |
true | false | false (在 3.4.1 及之前的版本中默认为 true) |
| multipleResultSetsEnabled | 是否允许单个语句返回多结果集(需要数据库驱动支持)。 | true | false | true |
| useColumnLabel | 使用列标签代替列名。实际表现依赖于数据库驱动,具体可参考数据库驱动的相关文档,或通过对比测试来观察。 | true | false | true |
| useGeneratedKeys | 允许 JDBC 支持自动生成主键,需要数据库驱动支持。如果设置为 true,将强制使用自动生成主键。尽管一些数据库驱动不支持此特性,但仍可正常工作(如 Derby)。 | true | false | False |
| autoMappingBehavior | 指定 MyBatis 应如何自动映射列到字段或属性。 NONE 表示关闭自动映射;PARTIAL 只会自动映射没有定义嵌套结果映射的字段。 FULL 会自动映射任何复杂的结果集(无论是否嵌套)。 | NONE, PARTIAL, FULL | PARTIAL |
| autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior | 指定发现自动映射目标未知列(或未知属性类型)的行为。NONE: 不做任何反应。WARNING: 输出警告日志('org.apache.ibatis.session.AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior' 的日志等级必须设置为 WARN)。FAILING: 映射失败 (抛出 SqlSessionException)。 |
NONE, WARNING, FAILING | NONE |
| defaultExecutorType | 配置默认的执行器。SIMPLE 就是普通的执行器;REUSE 执行器会重用预处理语句(PreparedStatement); BATCH 执行器不仅重用语句还会执行批量更新。 | SIMPLE REUSE BATCH | SIMPLE |
| defaultStatementTimeout | 设置超时时间,它决定数据库驱动等待数据库响应的秒数。 | 任意正整数 | 未设置 (null) |
| defaultFetchSize | 为驱动的结果集获取数量(fetchSize)设置一个建议值。此参数只可以在查询设置中被覆盖。 | 任意正整数 | 未设置 (null) |
| defaultResultSetType | 指定语句默认的滚动策略。(新增于 3.5.2) | FORWARD_ONLY | SCROLL_SENSITIVE | SCROLL_INSENSITIVE | DEFAULT(等同于未设置) | 未设置 (null) |
| safeRowBoundsEnabled | 是否允许在嵌套语句中使用分页(RowBounds)。如果允许使用则设置为 false。 | true | false | False |
| safeResultHandlerEnabled | 是否允许在嵌套语句中使用结果处理器(ResultHandler)。如果允许使用则设置为 false。 | true | false | True |
| mapUnderscoreToCamelCase | 是否开启驼峰命名自动映射,即从经典数据库列名 A_COLUMN 映射到经典 Java 属性名 aColumn。 | true | false | False |
| localCacheScope | MyBatis 利用本地缓存机制(Local Cache)防止循环引用和加速重复的嵌套查询。 默认值为 SESSION,会缓存一个会话中执行的所有查询。 若设置值为 STATEMENT,本地缓存将仅用于执行语句,对相同 SqlSession 的不同查询将不会进行缓存。 | SESSION | STATEMENT | SESSION |
| jdbcTypeForNull | 当没有为参数指定特定的 JDBC 类型时,空值的默认 JDBC 类型。 某些数据库驱动需要指定列的 JDBC 类型,多数情况直接用一般类型即可,比如 NULL、VARCHAR 或 OTHER。 | JdbcType 常量,常用值:NULL、VARCHAR 或 OTHER。 | OTHER |
| lazyLoadTriggerMethods | 指定对象的哪些方法触发一次延迟加载。 | 用逗号分隔的方法列表。 | equals,clone,hashCode,toString |
| defaultScriptingLanguage | 指定动态 SQL 生成使用的默认脚本语言。 | 一个类型别名或全限定类名。 | org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.XMLLanguageDriver |
| defaultEnumTypeHandler | 指定 Enum 使用的默认 TypeHandler 。(新增于 3.4.5) |
一个类型别名或全限定类名。 | org.apache.ibatis.type.EnumTypeHandler |
| callSettersOnNulls | 指定当结果集中值为 null 的时候是否调用映射对象的 setter(map 对象时为 put)方法,这在依赖于 Map.keySet() 或 null 值进行初始化时比较有用。注意基本类型(int、boolean 等)是不能设置成 null 的。 | true | false | false |
| returnInstanceForEmptyRow | 当返回行的所有列都是空时,MyBatis默认返回 null。 当开启这个设置时,MyBatis会返回一个空实例。 请注意,它也适用于嵌套的结果集(如集合或关联)。(新增于 3.4.2) |
true | false | false |
| logPrefix | 指定 MyBatis 增加到日志名称的前缀。 | 任何字符串 | 未设置 |
| logImpl | 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找。 | SLF4J | LOG4J | LOG4J2 | JDK_LOGGING | COMMONS_LOGGING | STDOUT_LOGGING | NO_LOGGING | 未设置 |
| proxyFactory | 指定 Mybatis 创建可延迟加载对象所用到的代理工具。 | CGLIB | JAVASSIST | JAVASSIST (MyBatis 3.3 以上) |
| vfsImpl | 指定 VFS 的实现 | 自定义 VFS 的实现的类全限定名,以逗号分隔。 | 未设置 |
| useActualParamName | 允许使用方法签名中的名称作为语句参数名称。 为了使用该特性,你的项目必须采用 Java 8 编译,并且加上 -parameters 选项。(新增于 3.4.1) |
true | false | true |
| configurationFactory | 指定一个提供 Configuration 实例的类。 这个被返回的 Configuration 实例用来加载被反序列化对象的延迟加载属性值。 这个类必须包含一个签名为static Configuration getConfiguration() 的方法。(新增于 3.2.3) |
一个类型别名或完全限定类名。 | 未设置 |
| shrinkWhitespacesInSql | 从SQL中删除多余的空格字符。请注意,这也会影响SQL中的文字字符串。 (新增于 3.5.5) | true | false | false |
| defaultSqlProviderType | Specifies an sql provider class that holds provider method (Since 3.5.6). This class apply to the type(or value) attribute on sql provider annotation(e.g. @SelectProvider), when these attribute was omitted. |
A type alias or fully qualified class name | Not set |
4.4 别名(typeAliases)
-
类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。 它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。例如:
<typeAliases> <typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/> <typeAlias alias="Blog" type="domain.blog.Blog"/> <typeAlias alias="Comment" type="domain.blog.Comment"/> <typeAlias alias="Post" type="domain.blog.Post"/> <typeAlias alias="Section" type="domain.blog.Section"/> <typeAlias alias="Tag" type="domain.blog.Tag"/> </typeAliases> -
也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean(扫描这个包的实体类,它的默认别名就是类名首字母小写),比如:
<typeAliases> <package name="domain.blog"/> </typeAliases> -
每一个在包
domain.blog中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。 比如domain.blog.Author的别名为author;若有注解,则别名为其注解值。见下面的例子:@Alias("author") public class Author { ... } -
注意
- 实体类比较少时,建议使用第一种;实体类比较多时,建议使用第二种。
- 别名优先级:typeAlias > 注解 > package
-
一些为常见的 Java 类型内建的类型别名。它们都是不区分大小写的,注意,为了应对原始类型的命名重复,采取了特殊的命名风格。
| 别名 | 映射的类型 |
| ---------- | ---------- |
| _byte | byte |
| _long | long |
| _short | short |
| _int | int |
| _integer | int |
| _double | double |
| _float | float |
| _boolean | boolean |
| string | String |
| byte | Byte |
| long | Long |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| integer | Integer |
| double | Double |
| float | Float |
| boolean | Boolean |
| date | Date |
| decimal | BigDecimal |
| bigdecimal | BigDecimal |
| object | Object |
| map | Map |
| hashmap | HashMap |
| list | List |
| arraylist | ArrayList |
| collection | Collection |
| iterator | Iterator |
4.5 其余配置
- 类型处理器(typeHandlers)
- 对象工厂(objectFactory)
- 插件(plugins)
- mybatis-generator-core
- mybatis-plus
- 通用mapper
4.6 映射器(mappers)
既然 MyBatis 的行为已经由上述元素配置完了,我们现在就要来定义 SQL 映射语句了。 但首先,我们需要告诉 MyBatis 到哪里去找到这些语句。 在自动查找资源方面,Java 并没有提供一个很好的解决方案,所以最好的办法是直接告诉 MyBatis 到哪里去找映射文件。 你可以使用相对于类路径的资源引用,或完全限定资源定位符(包括 file:/// 形式的 URL),或类名和包名等。
-
方式一:推荐使用
<mappers> <mapper resource="com/dao/UserMapper.xml"/> </mappers> -
方式二:使用class文件绑定注册
<mappers> <mapper class="com.dao.UserMapper"/> </mappers>注意点:
- 接口和它的Mapper配置文件必须同名
- 接口和它的Mapper配置文件必须在同一个包下
-
方式三:使用扫描包绑定注册
<mappers> <mapper package="com.dao"/> </mappers>注意点:
- 接口和它的Mapper配置文件必须同名
- 接口和它的Mapper配置文件必须在同一个包下
5 作用域和生命周期
作用域和生命周期类别是至关重要的,因为错误的使用会导致非常严重的并发问题。
5.1 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
- 这个类可以被实例化、使用和丢弃,一旦创建了 SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了。
- 因此 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 实例的最佳作用域是方法作用域(也就是局部方法变量)。
- 你可以重用 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 来创建多个 SqlSessionFactory 实例,但最好还是不要一直保留着它,以保证所有的 XML 解析资源可以被释放给更重要的事情。
5.2 SqlSessionFactory
- SqlSessionFactory 一旦被创建就应该在应用的运行期间一直存在,没有任何理由丢弃它或重新创建另一个实例。
- 使用 SqlSessionFactory 的最佳实践是在应用运行期间不要重复创建多次,多次重建 SqlSessionFactory 被视为一种代码“坏习惯”。
- 因此 SqlSessionFactory 的最佳作用域是应用作用域。 有很多方法可以做到,最简单的就是使用单例模式或者静态单例模式。
- 可以理解成数据库连接池。
5.3 SqlSession
-
每个线程都应该有它自己的 SqlSession 实例。
-
相当于连接池的一个连接请求,需要开启和关闭。
-
SqlSession 的实例不是线程安全的,因此是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳的作用域是请求或方法作用域。
-
绝对不能将 SqlSession 实例的引用放在一个类的静态域,甚至一个类的实例变量也不行。
-
也绝不能将 SqlSession 实例的引用放在任何类型的托管作用域中,比如 Servlet 框架中的 HttpSession。
-
如果你现在正在使用一种 Web 框架,考虑将 SqlSession 放在一个和 HTTP 请求相似的作用域中。 换句话说,每次收到 HTTP 请求,就可以打开一个 SqlSession,返回一个响应后,就关闭它。 这个关闭操作很重要,为了确保每次都能执行关闭操作,你应该把这个关闭操作放到 finally 块中。 下面的示例就是一个确保 SqlSession 关闭的标准模式:
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) { // 你的应用逻辑代码 }
6 结果映射
6.1 当属性名与字段名不一致时,查询结果会出现异常
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
}
//查询结果
//User{id=1, name='张三', pwd='null'}
解决方法:
-
起别名(不建议)
<!--UserMapper.xml--> <select id="getUserById" resultType="com.pojo.User" parameterType="int"> <!--select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id};--> select id, name, pwd as password from mybatis.user where id = #{id}; </select>
6.2 ResultMap结果映射集
-
resultMap元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素。它可以让你从 90% 的 JDBCResultSets数据提取代码中解放出来,并在一些情形下允许你进行一些 JDBC 不支持的操作。 -
实际上,在为一些比如连接的复杂语句编写映射代码的时候,一份
resultMap能够代替实现同等功能的数千行代码。 -
ResultMap 的设计思想是,对简单的语句做到零配置,对于复杂一点的语句,只需要描述语句之间的关系就行了。
-
下面的语句只是简单地将所有的列映射到
HashMap的键上,这由resultType属性指定。虽然在大部分情况下都够用,但是 HashMap 并不是一个很好的领域模型。你的程序更可能会使用 JavaBean 或 POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)作为领域模型。<select id="selectUsers" resultType="map"> select id, username, hashedPassword from some_table where id = #{id} </select> -
ResultMap的优秀之处——你完全可以不用显式地配置它们。对于6.1中的问题,采用ResultMap进行解决:<!-- 进行映射,将列映射到相应的属性上 type : 自定义规则的Java类型 id : 唯一id方便引用 --> <resultMap id="userMap" type="com.pojo.User"> <!-- 封装规则——只要写resultMap就建议把全部的映射规则都写上 id : 定义主键会底层有优化 column : 指定哪一列 property : 指定对应的javaBean属性 result : 普通列封装规则 --> <result column="pwd" property="password"></result> </resultMap> <select id="getUserById" resultMap="userMap"> select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}; </select>
6.3 resultMap相关参数
-
constructor: 用于在实例化类时,注入结果到构造方法中idArg: ID 参数;标记出作为 ID 的结果可以帮助提高整体性能arg: 将被注入到构造方法的一个普通结果
-
id: 一个 ID 结果;标记出作为 ID 的结果可以帮助提高整体性能 -
result: 注入到字段或 JavaBean 属性的普通结果 -
association: 一个复杂类型的关联;许多结果将包装成这种类型- 嵌套结果映射: 关联可以是
resultMap元素,或是对其它结果映射的引用
- 嵌套结果映射: 关联可以是
-
collection: 一个复杂类型的集合- 嵌套结果映射: 集合可以是
resultMap元素,或是对其它结果映射的引用
- 嵌套结果映射: 集合可以是
-
discriminator: 使用结果值来决定使用哪个resultMapcase: 基于某些值的结果映射- 嵌套结果映射 :
case也是一个结果映射,因此具有相同的结构和元素;或者引用其它的结果映射
- 嵌套结果映射 :
6.4 关联查询
6.4.1 级联属性封装
<!--
场景一:
查询Employee的同时查询员工对应的部门
一个员工有与之对应的部门信息
id last_name gender d_id dept_name
-->
<resultMap type="com.pojo.Employee" id="EmpMap1">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="did" property="dept.id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="dept.deptName"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Employee getEmpAndDept(int id)-->
<select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="EmpMap1">
select e.id id, e.name name, e.gender gender, e.d_id d_id,
d.id did, d.dept_name dept_name
from employee e, dept d
where e.d_id = d.id and e.id=#{id}
</select>
6.4.2 association定义关联对象封装规则
基于6.4.1中查询,更改resultMap
<!-- 使用association定义关联的单个对线的封装规则-->
<resultMap id="EmpMap2" type="com.pojo.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<!-- association可以指定联合的javaBean对象
property : 指定哪个属性是联合的对象
javaType : 指定这个属性对象的类型[不能省略]
-->
<association property="dept" javaType="com.pojo.Dept">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
使用associtaion进行分布查询
<!-- 使用associtaion进行分布查询
1. 先按照员工id查询员工信息
2. 根据查询员工信息中的d_id值去部门表查出部门信息
3. 部门设置到员工中
-->
<!--EmpMapper.xml-->
<resultMap id="EmpMapByStep" type="com.pojo.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<!-- association定义关联对象的封装规则
select : 表明当前属性是调用select指定方法查出的结果
column : 指定将哪一列的值传给这个方法
-->
<association property="dept" select="com.dao.DeptMapper.getDeptById" column="d_id"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getEmpDeptByStep" resultMap="EmpMapByStep">
select * from Employee where id=#{id}
</select>
<!--DeptMapper.xml-->
<resultMap id="deptMap" type="com.pojo.Dept">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName" />
</resultMap>
<select id="getDeptById" resultMap="deptMap">
select *
from Dept
where id=#{id}
</select>
分布查询&延迟加载
查询Employee对象的是想,都将一起查询出来。部门信息在我们使用的时候再去查询;分段查询的基础上加上两个配置。
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true" />
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false" />
</settings>
6.4.3 collection嵌套结果集的方式,定义关联的集合类型元素的封装规则
<!--场景二:
查询部门的时候将部门对应的所有员工信息也查询出来
-->
<!--
collection嵌套结果集的方式,定义关联的集合类型元素的封装规则
-->
<resultMap id="deptMap1" type="com.pojo.Dept">
<id column="did" property="id"/>
<result column="dept_name" property="deptName" />
<!--
collection : 定义关联集合类型的属性封装规则
ofType : 指定集合里面元素的类型
-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="com.pojo.Employee">
<id column="eid" property="id" />
<result column="name" property="name" />
<result column="gender" property="gender" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getDeptByIdPlus" resultMap="deptMap1">
select d.id did, d.dept_name dept_name, e.id eid, e.name name, e.gender gender
from dept d
left join employee e on d.id=e.d_id
where d.id=#{id};
</select>
分布查询&延迟加载
跟6.4.2 association的分布查询&延迟加载一样,设置lazyLoadingEnabled和aggressiveLazyLoading
<!-- DeptMapper.xml -->
<resultMap id="deptMap2" type="com.pojo.Dept">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="dept" property="deptName" />
<collection property="emps" select="com.dao.EmpMapper.getEmpByDeptId" column="id"></collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getDeptByStep" resultMap="deptMap2">
select * from dept where id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- EmpMapper.xml -->
<select id="getEmpByDeptId" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee where d_id=#{id}
</select>
分布查询传递多列值和fetchType
将多列的值封装map传递
<!--
将多列的值封装map传递:
column="{key1=column1, key2=column2}"
fetchType='lazy' : 表示使用延迟加载;
- laze : 延迟
- eager : 立即
-->
6.5 discriminator鉴别器(了解)
<discriminator javaType="">
<case value=""></case>
</discriminator>
<!--
鉴别器 mybatis可以使用discriminator判断某列的值
以封装Employee为例:
如果查出的是女生 : 将部门信息查询出来,否则不查询;
-->
<resultMap id="EmpDis" type="com.pojo.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<!--
column : 指定判定的列名
javaType : 列值对应的java类型
-->
<discriminator javaType="string" column="gender">
<!-- resultType 不能缺少。或者用resultMap-->
<case value="女" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
<association property="dept" select="com.dao.DeptMapper.getDeptById" column="d_id"></association>
</case>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
7 日志
7.1 日志工厂
如果一个数据库操作,出现了异常,我们需要排错,日志就是最好的助手。
以往使用sout、debug,现在则使用日志工厂
-
logImpl
常用设置:
- SLF4J
- LOG4J(掌握)
- LOG4J2
- JDK_LOGGING
- COMMONS_LOGGING
- STDOUT_LOGGING(掌握)
- NO_LOGGING
-
使用STDOUT_LOGGING标准日志输出
在mybatis核心配置文件中,配置文件
<settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> </settings>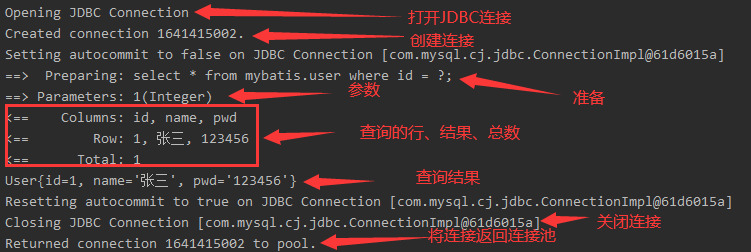
7.2 LOG4J
什么是LOG4J
- Log4j是Apache的一个开源项目,通过使用Log4j,我们可以控制日志信息输送的目的地是控制台、文件、GUI组件,甚至是套接口服务器、NT的事件记录器、UNIX Syslog守护进程等;
- 我们也可以控制每一条日志的输出格式;
- 通过定义每一条日志信息的级别,我们能够更加细致地控制日志的生成过程。
- 这些可以通过一个配置文件来灵活地进行配置,而不需要修改应用的代码。
-
导入依赖包
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j --> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> -
配置 log4j.properties 文件
# log4j.rootLogger日志输出类别和级别:只输出不低于该级别的日志信息DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < FATAL # WARN:日志级别 CONSOLE:输出位置自己定义的一个名字 logfile:输出位置自己定义的一个名字 log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,console,logfile ############# # 输出到控制台 ############# # 配置CONSOLE输出到控制台 log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.console.Target = System.out log4j.appender.console.Threshold = DEBUG # 配置CONSOLE设置为自定义布局模式 log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout # 配置CONSOLE日志的输出格式 [frame] 2019-08-22 22:52:12,000 %r耗费毫秒数 %p日志的优先级 %t线程名 %C所属类名通常为全类名 %L代码中的行号 %x线程相关联的NDC %m日志 %n换行 log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[frame] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} - %-4r %-5p [%t] [%C]:%L %m%n ################ # 输出到日志文件中 ################ # 配置logfile输出到文件中 文件大小到达指定尺寸的时候产生新的日志文件 log4j.appender.logfile=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender # 保存编码格式 log4j.appender.logfile.Encoding=UTF-8 # 输出文件位置此为项目根目录下的logs文件夹中 log4j.appender.logfile.File=./logs/root.log # 后缀可以是KB,MB,GB达到该大小后创建新的日志文件 log4j.appender.logfile.MaxFileSize=10MB # 设置滚定文件的最大值3 指可以产生root.log.1、root.log.2、root.log.3和root.log四个日志文件 log4j.appender.logfile.MaxBackupIndex=3 log4j.appender.D.Threshold=DEBUG # 配置logfile为自定义布局模式 log4j.appender.logfile.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.logfile.layout.ConversionPattern=[%-5p]-[%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss}] [%c] %m%n ################ # 日志输出级别 ################ log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG -
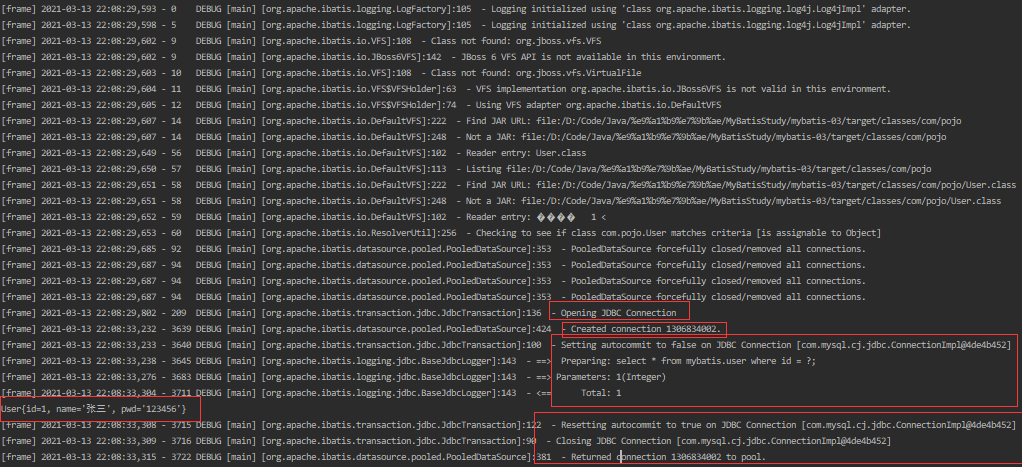
配置LOG4J为日志的实现
<settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"></setting> </settings> -
LOG4J的使用
-
简单使用
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; public class UserTest { static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(UserDaoTest.class); @Test public void testLog4j() { logger.info("info:运行了testLog4j"); logger.debug("debug:运行了testLog4j"); logger.error("error:运行了testLog4j"); } }
8 分页
为什么要分页
- 减少数据的处理量
8.1 使用limit分页
#语法: select * from user limit startIndex, pageSize (or pageSize);只使用一个参数时,默认范围为[0, pageSize)
select * from user limit 0, 2;
8.2 使用Mybatis分页
-
编写接口方法
List<User> getUserLimit(Map<String, Object> map); -
编写对应的SQL语句
<select id="getUserLimit" parameterType="map" resultType="User"> select * from mybatis.user limit #{startIndex}, #{pageSize}; </select> -
测试
@Test public void testLimit() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("startIndex", 0); map.put("pageSize", 2); List<User> userList = mapper.getUserLimit(map); for(User user : userList) { System.out.println(user); } } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
8.3 RowBounds分页(了解)
-
编写接口方法
List<User> getUserRowBounds(); -
编写对应的SQL语句
<select id="getUserRowBounds" resultType="User"> select * from mybatis.user; </select> -
测试
@Test public void getUserByRowBounds() { SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(0,2); List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("com.dao.UserMapper.getUserRowBounds", null, rowBounds); for(User user:userList) { System.out.println(user); } } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
8.3 MyBatis分页插件——PageHelper(了解)
9 注解开发
使用注解来映射简单语句会使代码显得更加简洁,但对于稍微复杂一点的语句,Java 注解不仅力不从心,还会让你本就复杂的 SQL 语句更加混乱不堪。 因此,如果你需要做一些很复杂的操作,最好用 XML 来映射语句。
- 本质:反射机制实现
- 原理:动态代理模式
- 编写接口方法
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> getUser();
- 核心配置文件绑定接口
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.dao.UserMapper"/>
</mappers>
- 测试
10 mybatis运行原理
- 通过加载mybatis全局配置文件以及mapper映射文件初始化configuration对象
和Executor对象(通过全局配置文件中的defaultExecutorType初始化); - 创建一个defaultSqlSession对象,将configuration对象和Executor对象注入给
defaulSqlSession对象中; - defaulSqlSession通过getMapper()获取mapper接口的代理对象mapperProxy
(mapperProxy中包含defaultSQLSession对象) - 执行增删改查:
1)通过defaulSqlSession中的属性Executor创建statementHandler对象;
2)创建statementHandler对象的同时也创建parameterHandler和
resultSetHandler;
3) 通过parameterHandler设置预编译参数及参数值;
4)调用statementHandler执行增删改查;
5)通过resultsetHandler封装查询结果
11 动态SQL
11.1 什么是动态SQL
-
动态 SQL 是 MyBatis 的强大特性之一。
-
如果你使用过 JDBC 或其它类似的框架,你应该能理解根据不同条件拼接 SQL 语句有多痛苦,例如拼接时要确保不能忘记添加必要的空格,还要注意去掉列表最后一个列名的逗号。
-
利用动态 SQL,可以彻底摆脱这种痛苦。
-
使用动态 SQL 并非一件易事,但借助可用于任何 SQL 映射语句中的强大的动态 SQL 语言,MyBatis 显著地提升了这一特性的易用性。
-
四种标签:
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
11.2 if标签
使用动态 SQL 最常见情景是根据条件包含 where 子句的一部分。
<!-- 查询员工 要求 : 携带了哪个字段查询条件就带上这个字段的值
test : 判断表达式 (OGNL表达式)
-->
<select id="getEmpByConditionIf" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee
where
<if test="id != 0">
id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != """>
and name like #{name}
</if>
</select>
判断表达式使用了OGNL
OGNL ( Object Graph Navigation Language ) 对象图导航语言,这是一种强大的表达式语言,通过它可以非常方便的来操作对象属性。类似于我们的EL , SpEL等。
-
访问对象属性: person.name
-
调用方法: person.getName()
-
调用静态属性/方法:
- @java.lang.Math@PI
- @java.uil.UUlD@randomUUID()
-
调用构造方法: new com.pojo.Employee('admin').name
-
运算符: +, -, *, /, %
-
逻辑运算符: in, not in, >, >=, <, <=, ==, !=
-
注意: xmI中特殊符号如",>,<等这些都需要使用转义字符
11.2 trim(where, set)标签
如果查询的时候未携带某些条件可能SQL拼装会有问题,例如11.1中的查询不携带id。
解决方法:
- 给where 后面加上1=1,以后的条件都and xxx.
- MyBatis是用where标签来将所有的查询条件包括在内。MyBatis就会将where标签中拼装的SQL多出来的and或者or去掉,只会去掉开头的and或or
- 若and和or连接在末尾,则使用trim标签
<!-- 使用where标签-->
<select id="getEmpByConditionIf" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee
<where>
<if test="id != 0">
id=#{id} and
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != """>
name like #{name} and
</if>
<if test="gender == "男" or gender == "女"">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<!-- 使用trim标签
prefix="" :
前缀,trim标签中是整个字符串拼串后的结果。
prefix给拼串后的整个字符加一个前缀
prefixOverrides="" :
前缀覆盖:去掉整个字符串前面多余的字符
suffix="" :
后缀,给拼串后的整个字符加一个后缀
suffixOverrides="" :
后缀覆盖去掉整个字符串后面多余的字符
-->
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and | or">
<if test="id != 0">
id=#{id} and
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != """>
name like #{name} and
</if>
<if test="gender == "男" or gender == "女"">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
动态更新语句——set标签
<update id="updateEmpBySet">
update employee
<set>
<if test="name != null">
name=#{name},
</if>
<if test="gender != null">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
<!-- 使用trim标签 -->
<update id="updateEmpBySet">
update employee
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">
name=#{name},
</if>
<if test="gender != null">
gender=#{gender},
</if>
</trim>
where id=#{id}
</update>
简单总结:where标签封装查询语句,set标签封装更新语句
11.3 choose (when, otherwise)标签——分支选择
有时候,我们不想使用所有的条件,而只是想从多个条件中选择一个使用。针对这种情况,MyBatis 提供了 choose 元素,它有点像 Java 中的 switch 语句。
以11.1查询为例,将查询的条件改为“如果携带了id就用id查,如果携带了name,就用name查,如果携带了gender,就用gender查”
<!-- choose标签
类似于Switch-case-default语句
when就相当于case语句
otherwise相当于default语句
-->
<select id="getEmpByConditionChoose" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee
<where>
<choose>
<when test="id != 0">
id=#{id}
</when>
<when test="name != null">
name like #{name}
</when>
<otherwise>
gender = "男"
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
11.4 foreach标签
动态 SQL 的另一个常见使用场景是对集合进行遍历(尤其是在构建 IN 条件语句的时候)
<!--
foreach:
collection : 指定要遍历的集合
list类型的参数会特殊处理封装在map中
item : 将当前遍历出的元素赋值给指定变量
separator : 每个元素之间的分隔符
open : 遍历出所有结果拼接一个开始的字符
close : 遍历出所有结果拼接一个结束的字符
index : 索引。
遍历list的时候index是索引,item就是当前值
遍历map的时候index表示的是map的key,item就是key对应的值
#{变量名} 就能取出变量的值也就是当前遍历出的元素
-->
<select id="getEmpByForeach" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee where id in
<foreach collection="list" item="item_id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{item_id}
</foreach>
</select>
批量保存
<!-- int addEmps(@Param("list")List<Employee> empList);
@Param注解 : 给变量取别名
-->
<insert id="addEmps">
insert into employee (id, name, gender, d_id)
values
<foreach collection="list" separator="," item="emp">
(#{emp.id}, #{emp.name}, #{emp.gender}, #{emp.dept.id})
</foreach>
</insert>
11.5 其他标签或参数
-
_parameter(参数): 代表整个参数
- 单个参数: -parameter就是这个参数
- 参数会被封装为一个map,_parameter就是代表这个map
-
_databaseId(参数): 用于多数据库支持,如果配置了databaseIdProvider标签。
- _databaseId: 就代表当前数据库的别名
<select id="getEmp" resultType="Employee"> <if test="_databaseId == 'mysql'"> select * from employee </if> <if test="_databaseId == 'oracle'"> select * from employee </if> </select>
-
bind(标签)
bind元素允许你在 OGNL 表达式以外创建一个变量,并将其绑定到当前的上下文<select id="getEmp" resultType="Employee"> <bind name="_name" value="'%' + _parameter.name + '%'" /> select * from employee where name like #{_name} </select> -
sql(标签)
抽取可重用的sql片段。方便后面引用
<sql id="insertColumn"> id, name, gender, d_id </sql> <insert id="addEmp"> insert into employee(<include refid="insertColumn"></include>) values (...) </insert>
12 缓存机制
MyBatis包含一个非常强大的查询缓存特性,它可以非常方便地配置和定制。缓存可以极大的提升查询效率。
MyBatis系统中默认定义了两级缓存:一级缓存和二级缓存。
- 默认情况下﹐只有一级缓存(SqlSession级别的缓存,也称为本地缓存)开启。
- 二级缓存需要手动开启和配置,他是基于namespace级别的缓存。
- 为了提高扩展性。MyBatis定义了缓存接口Cache。我们可以通过实现Cache接口来自定义二级缓存
12.1 一级缓存
与数据库同一次回话期间查询到的数据会放在本地缓存中。以后如果需要获取相同的数据,直接从缓存中拿,不需要再去数据库查询。
EmpMapper.xml
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee
where id=#{id}
</select>
EmpMapperTest.java
@Test
public void testGetEmpByConditionIf() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();
try {
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
Employee emp1 = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(emp1);
Employee emp2 = mapper.getEmpById(1);
System.out.println(emp2);
System.out.println(emp1 == emp2);
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
运行结果:
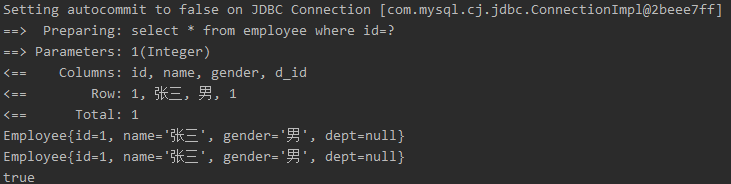
sqlSession级别的缓存。一级缓存是一直开启的。也就是说一个sqlSession有一个一级缓存,不同之间的一级缓存不能共享
一级缓存失效情况(没有使用到当前一级缓存的情况,还需要向数据库发送查询):
- sqlSession不同。
- sqlSession相同,查询条件不同。(当前一级缓存中还没有这个数据)
- sqlSession相同,两次查询之间执行了增删改。(这次增删改可能对当前数据有影响)
- sqlSession相同,手动清除了一级缓存。(缓存清空)
12.2 二级缓存(全局缓存)
基于namespace级别缓存,一个namespace对应一个缓存。
工作机制:
- 一个会话,查询一条数据,这个数据就会被放在当前会话的一级缓存中
- 如果会话关闭,一级缓存中的数据会被保存到二级缓存中。新的会话查询信息,就可以参照二级缓存。
- 不同namespace查出的数据会放在自己对应的缓存中
使用:
-
开启全局二级缓存配置:
-
去mapeer.xml中配置使用二级缓存。
<!-- eviction: 缓存的回收策略 LRU - 最近最少使用的: 移除最长时间不被使用的对象。 FIFO - 先进先出: 按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。 SOFT - 软引用: 移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。 WEAK - 弱引用: 更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。 默认的是LRU。 flushInterval: 缓存刷新间隔 缓存多长时间清空一次,默认不清空,设置一个毫秒值 readOnly: 是否只读 true: 只读,mybatis认为所有从缓存中获取数据的操作都是只读操作,不会修改数据。 mybatis为了加快获取速度,直接就会将数据在缓存中的引用交给用户。不安全,速度快 false: 非只读,mybatis觉得获取的数据可能会被修改 mybatis会用序列化&反序列的技术克隆一份新的数据给你。安全,速度慢 size: 缓存存放多少元素 type: 指定自定义缓存的全类名。实现Cache接口即可 --> <cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="false"></cache> -
我们的POJO中的实体类需要实现序列化Serializable接口(若cache标签中的readOnly设置为true则不需要)。
//Employee.java实体类 public class Employee implements Serializable { private int id; private String name; private String gender; } //测试类 @Test public void testSecendCache() { SqlSession sqlSession1 = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession(); try { EmpMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); EmpMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(EmpMapper.class); Employee emp1 = mapper1.getEmpById(1); System.out.println(emp1 + "******1******"); sqlSession1.close(); Employee emp2 = mapper2.getEmpById(1); System.out.println(emp2 + "******2******"); System.out.println(emp1 == emp2); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { sqlSession2.close(); } } }运行结果
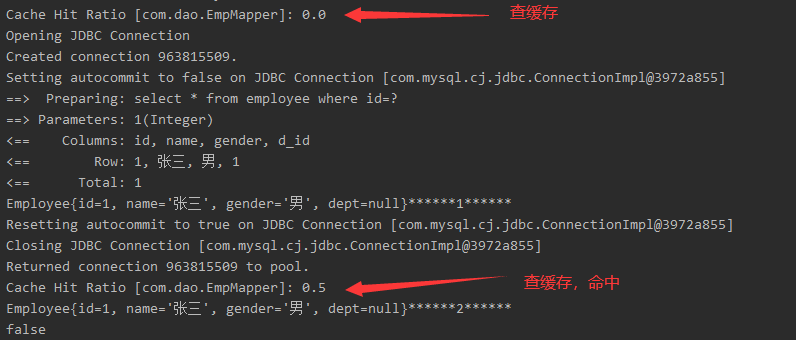
效果:数据会从二级缓存中获取
- 查出的数据都会被默认先放在一级缓存中
- 只有会话提交或者关闭以后,一级缓存中的数据才会转移到二级缓存


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号