#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int main() {
// typedef struct Node{
// int data;
// struct Node* p;
// }Node, *pNode;
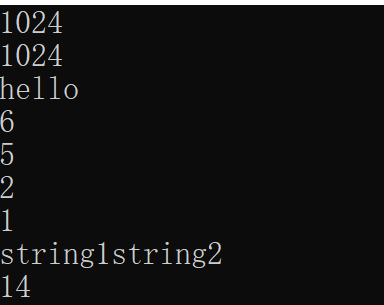
int array_i[1024];
printf("%d\n", sizeof(array_i) / sizeof(int));
char array_c[1024];
printf("%d\n", sizeof(array_c));
//字符指针
char* p = "hello";
printf("%s\n", p);
char p2[] = "world";
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p2)); //自带'0'
printf("%d\n", strlen(p2)); //不带'0',strlen不管有没有'0',只计算长度,不包括0
char p3[] = { '1','2' };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p3)); //不带'0'
//strlen 在计算长度的时候不会把结束符 '\x00' 计算在内,strcpy 在拷贝的时候会把 '\x00' 也算上,所以就会造成 off by one
char p4[1024];
memset(p4, 1, sizeof(p4));
printf("%d\n", p4[0]);
char p5[1024] = "string1";
char p6[] = "string2";
strcat(p5, p6);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
printf("%c", p5[i]);
printf("\n%d", strlen(p5));
//strcpy
return 0;
}
![]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号