图-最短路-dijkstra-0/1BFS-1368. 使网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价
2020-03-01 22:59:59
问题描述:
给你一个 m x n 的网格图 grid 。 grid 中每个格子都有一个数字,对应着从该格子出发下一步走的方向。 grid[i][j] 中的数字可能为以下几种情况:
- 1 ,下一步往右走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i][j + 1] - 2 ,下一步往左走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i][j - 1] - 3 ,下一步往下走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i + 1][j] - 4 ,下一步往上走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i - 1][j]
注意网格图中可能会有 无效数字 ,因为它们可能指向 grid 以外的区域。
一开始,你会从最左上角的格子 (0,0) 出发。我们定义一条 有效路径 为从格子 (0,0) 出发,每一步都顺着数字对应方向走,最终在最右下角的格子 (m - 1, n - 1) 结束的路径。有效路径 不需要是最短路径 。
你可以花费 cost = 1 的代价修改一个格子中的数字,但每个格子中的数字 只能修改一次 。
请你返回让网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价。
示例 1:
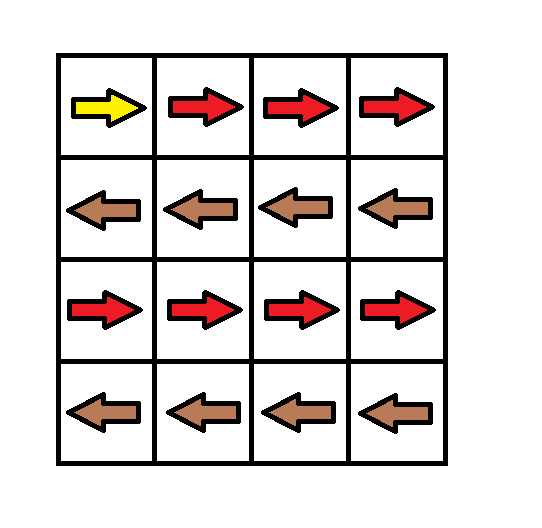
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]] 输出:3 解释:你将从点 (0, 0) 出发。 到达 (3, 3) 的路径为: (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (3, 3) 总花费为 cost = 3.
示例 2:

输入:grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]] 输出:0 解释:不修改任何数字你就可以从 (0, 0) 到达 (2, 2) 。
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100
问题求解:
最重要的是reduce,如何将问题转成已知的知识非常重要。
本题中看似是需要求改变方向个数最少,其实是在最短路径。
如果我们将通过标示到达w = 0,那么通过修改到达的w = 1。
解法一:dijkstra
朴素的dijkstra算法的时间复杂度为O(V ^ 2);如果使用优先队列和邻接表可以将时间复杂度优化为O((E + V)logV)。
时间复杂度:O(mnlog(mn))
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int minCost(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[] dist = new int[m * n];
Arrays.fill(dist, (int)(1e9));
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((int[] o1, int[] o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1]);
int[] used = new int[m * n];
pq.add(new int[]{0, 0});
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] node = pq.poll();
int from = node[0];
int d = node[1];
if (used[from] == 1) continue;
used[from] = 1;
dist[from] = d;
int x = from / n;
int y = from % n;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dirs[i - 1][0];
int ny = y + dirs[i - 1][1];
if (nx >= m || nx < 0 || ny >= n || ny < 0) continue;
int w = grid[x][y] == i ? 0 : 1;
int to = nx * n + ny;
if (dist[to] > dist[from] + w) {
dist[to] = dist[from] + w;
pq.add(new int[]{to, dist[to]});
}
}
}
return dist[m * n - 1];
}
解法二:0-1BFS
本题有个特殊的地方就是边权重只为0 / 1,在这样的图上求解最短路径的最优解是使用0-1 BFS。
0-1BFS使用了BFS的性质,当前层和下一层的节点的距离最大不超过1,因此当我们碰到w = 0的节点的时候可将其加入队首,如果碰到w = 1的节点的时候将其加入队尾,这样就巧妙的进行了排序工作,因此时间复杂度要更优。
时间复杂度:O(mn)
int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int minCost(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
if (m == 1 && n == 1) return res;
Deque<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> used = new HashSet<>();
q.add(new int[]{0, 0});
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] curr = q.pollFirst();
if (used.contains(curr[0])) continue;
used.add(curr[0]);
int x = curr[0] / n;
int y = curr[0] % n;
int cost = curr[1];
if (x == m - 1 && y == n - 1) return cost;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dirs[i - 1][0];
int ny = y + dirs[i - 1][1];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n || used.contains(nx * n + ny)) continue;
if (grid[x][y] == i)
q.addFirst(new int[]{nx * n + ny, cost});
else
q.addLast(new int[]{nx * n + ny, cost + 1});
}
}
return -1;
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号