实验3 类和对象Ⅱ
实验四

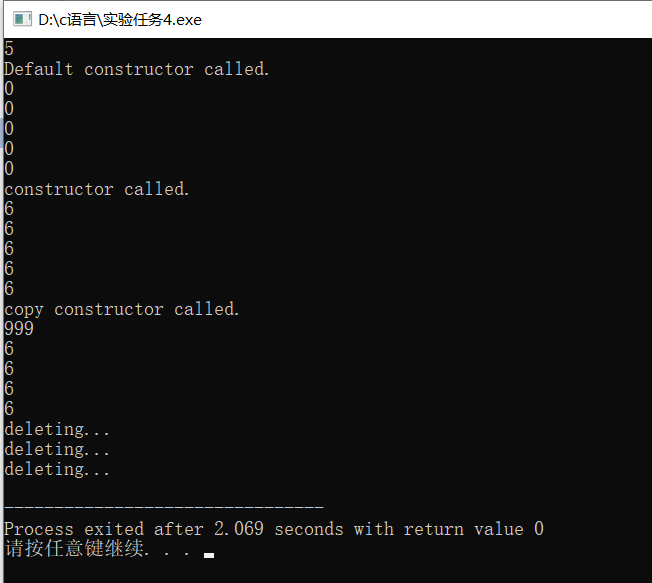
#ifndef VECTOR_INT #define VECTOR_INT #include<iostream> #include<cassert> using namespace std; class Vector_int { public: Vector_int(int n); Vector_int(int m,int n); Vector_int(const Vector_int &x); ~Vector_int(); int &at(int n) ; void show() const; private: int size; int *p; }; Vector_int::Vector_int(int n): size(n) { cout << "Default constructor called." << endl; p=new int[n](); } Vector_int::Vector_int(int m,int n): size(m) { cout << "constructor called." << endl; p=new int[m]; for(int i=0; i<m; i++) { *(p+i)=n; //通过指针给数组赋值 } } Vector_int::Vector_int(const Vector_int &x): size(x.size) { cout << "copy constructor called." << endl; p=new int[size]; for(auto i=0; i<size; ++i) // 通过for循环实现对p指向的内存空间的数据复制 p[i] = x.p[i]; } int& Vector_int::at(int n) { assert(n>=0&&n<size); return p[n]; } void Vector_int::show() const { for(auto i=0; i<size; ++i) {// 通过for循环实现对p指向的内存空间的数据复制 cout<<*(p+i)<<endl; } } Vector_int::~Vector_int() { cout << "deleting..." << endl; delete[] p; } #endif

#include <iostream> #include "vector_int.hpp" int main() { int n; cin>>n; Vector_int x1(n); x1.show(); // 创建一个动态大小的int型数组对象x,向系统申请n个int型数据项空间 Vector_int x2(n, 6); x2.show(); // 创建一个动态大小的int型数组对象x,向系统申请n个int型数据项空间, 初始值均为6 Vector_int y(x2); // 用已经存在的对象x构造新的对象y y.at(0)=999; y.show(); }
实验五

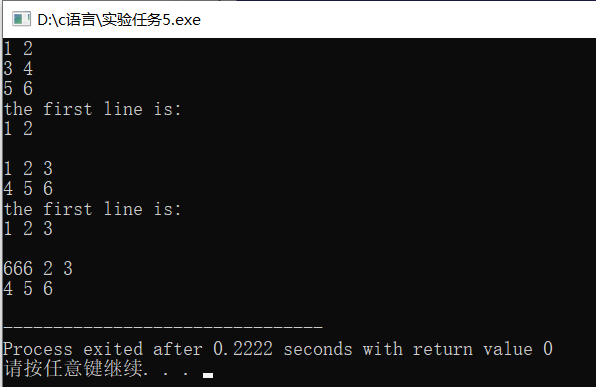
#ifndef MATRIX_H #define MATRIX_H #include <iostream> #include <cassert> using namespace std; class Matrix { public: Matrix(int n); // 构造函数,构造一个n*n的矩阵 Matrix(int n, int m); // 构造函数,构造一个n*m的矩阵 Matrix(const Matrix &X); // 复制构造函数,使用已有的矩阵X构造 ~Matrix(); //析构函数 void set(const double *pvalue); // 用pvalue指向的连续内存块数据为矩阵赋值 void set(int i, int j, int value); //设置矩阵第i行第j列元素值为value double &at(int i, int j); //返回矩阵第i行第j列元素的引用 double at(int i, int j) const; // 返回矩阵第i行第j列元素的值 int get_lines() const; //返回矩阵行数 int get_cols() const; //返回矩列数 void print() const; // 按行打印输出矩阵 private: int lines; // 矩阵行数 int cols; // 矩阵列数 double *p; // 指向存放矩阵数据的内存块的首地址 }; Matrix::Matrix(int n) :lines(n),cols(n) { p=new double[n*n]; } Matrix::Matrix(int n,int m) :lines(n),cols(m) { p=new double[n*m]; } Matrix::Matrix(const Matrix &X):lines(X.lines),cols(X.cols) { p=new double[lines*cols]; for(int i=0; i<lines*cols; i++) { p[i]=X.p[i]; } } Matrix::~Matrix() { delete[] p; } void Matrix::set(const double *pvalue) { for(int i=0; i<lines*cols; i++) p[i]=*(pvalue+i); } void Matrix::set(int i, int j, int value) { p[i*cols+j]=value; } double Matrix::at(int i, int j) const { return p[i*cols+j]; } double & Matrix::at(int i, int j) { return p[i*cols+j]; } int Matrix::get_lines() const { return lines; } int Matrix::get_cols() const { return cols; } void Matrix::print() const { for(int i=0; i<lines; i++) { for(int j=0; j<cols; j++) { cout<<p[i*cols+j]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } } #endif

#include <iostream> #include "matrix.hpp" int main() { using namespace std; double x[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; Matrix m1(3, 2); // 创建一个3×2的矩阵 m1.set(x); // 用一维数组x的值按行为矩阵m1赋值 m1.print(); // 打印矩阵m1的值 cout << "the first line is: " << endl; cout << m1.at(0, 0) << " " << m1.at(0,1) << endl; cout << endl; Matrix m2(2, 3); m2.set(x); m2.print(); cout << "the first line is: " << endl; cout << m2.at(0, 0) << " " << m2.at(0, 1) << " " << m2.at(0, 2) << endl; cout << endl; Matrix m3(m2); m3.set(0, 0, 666); m3.print(); }
实验总结
1.在实验二中,删去复制构造函数会导致把x浅复制给y,并在运行结束时报错,所以在设计类时最好自己定义好复制构造函数
2.实验四中,at() 的返回值应该是引用类型,否则无法实现对数组中对应元素的修改
3.实验五实际上还是用一维数组去表示和存储二维数组




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号