创建第一个Django app-part2
数据库设置
open mysite/settings.py
点击查看代码
'''
这里的数据需要提前创建,否则就回报错:(1049, "Unknown database 'polls'")
'''
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
DATABASES = {
'default': {
# 'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
# 'NAME': BASE_DIR / 'db.sqlite3',
"ENGINE": "django.db.backends.mysql",
"NAME": "polls",
"USER": "root",
"PASSWORD": "#######",
"HOST": "127.0.0.1",
"PORT": "3306",
}
}
创建models
编辑polls/models.py
点击查看代码
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
class Question(models.Model):
question_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
pub_date = models.DateTimeField("date published")
class Choice(models.Model):
question = models.ForeignKey(Question, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
choice_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
votes = models.IntegerField(default=0)
编辑mysite/settings.py激活models
点击查看代码
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'polls.apps.PollsConfig',
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
]
执行命令
python3 manage.py makemigrations polls
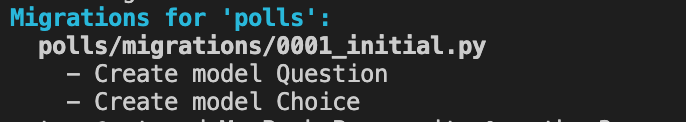
查看models的修改对应的数据库的迁移
python3 manage.py sqlmigrate polls 0001
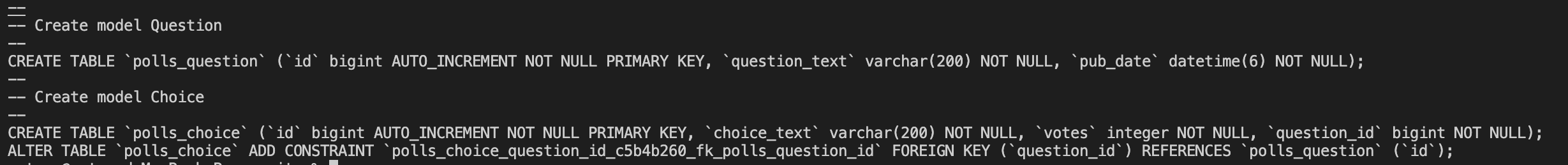
迁移到数据库
python3 manage.py migrate
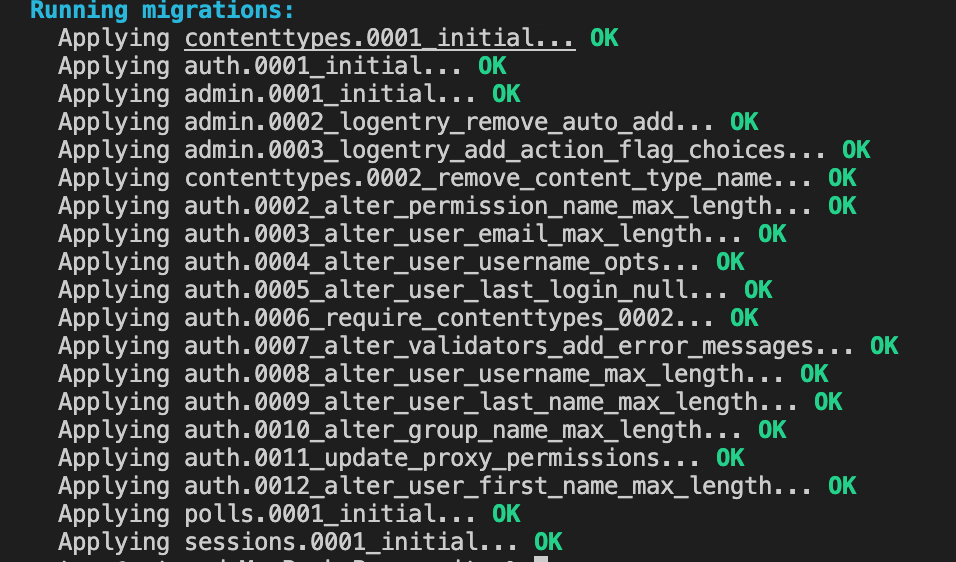
API的使用
进入python shell
python3 manage.py shell
使用shell
点击查看代码
>>> from polls.models import Choice, Question # Import the model classes we just wrote.
# No questions are in the system yet.
>>> Question.objects.all()
<QuerySet []>
# Create a new Question.
# Support for time zones is enabled in the default settings file, so
# Django expects a datetime with tzinfo for pub_date. Use timezone.now()
# instead of datetime.datetime.now() and it will do the right thing.
>>> from django.utils import timezone
>>> q = Question(question_text="What's new?", pub_date=timezone.now())
# Save the object into the database. You have to call save() explicitly.
>>> q.save()
# Now it has an ID.
>>> q.id
1
# Access model field values via Python attributes.
>>> q.question_text
"What's new?"
>>> q.pub_date
datetime.datetime(2012, 2, 26, 13, 0, 0, 775217, tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc)
# Change values by changing the attributes, then calling save().
>>> q.question_text = "What's up?"
>>> q.save()
# objects.all() displays all the questions in the database.
>>> Question.objects.all()
<QuerySet [<Question: Question object (1)>]>
修改对象的返回值并添加客户化方法,编辑polls/models.py
点击查看代码
from django.db import models
from django.utils import timezone
import datetime
# Create your models here.
class Question(models.Model):
question_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
pub_date = models.DateTimeField("date published")
def __str__(self):
return self.question_text
'''
客户化方法
'''
def was_published_recently(self):
return self.pub_date >= timezone.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=1)
class Choice(models.Model):
question = models.ForeignKey(Question, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
choice_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
votes = models.IntegerField(default=0)
def __str__(self):
return self.choice_text
重新进入shell
python3 manage.py shell
点击查看代码
>>> from polls.models import Choice, Question
# Make sure our __str__() addition worked.
>>> Question.objects.all()
<QuerySet [<Question: What's up?>]>
# Django provides a rich database lookup API that's entirely driven by
# keyword arguments.
>>> Question.objects.filter(id=1)
<QuerySet [<Question: What's up?>]>
>>> Question.objects.filter(question_text__startswith="What")
<QuerySet [<Question: What's up?>]>
# Get the question that was published this year.
>>> from django.utils import timezone
>>> current_year = timezone.now().year
>>> Question.objects.get(pub_date__year=current_year)
<Question: What's up?>
# Request an ID that doesn't exist, this will raise an exception.
>>> Question.objects.get(id=2)
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
DoesNotExist: Question matching query does not exist.
# Lookup by a primary key is the most common case, so Django provides a
# shortcut for primary-key exact lookups.
# The following is identical to Question.objects.get(id=1).
>>> Question.objects.get(pk=1)
<Question: What's up?>
# Make sure our custom method worked.
>>> q = Question.objects.get(pk=1)
>>> q.was_published_recently()
True
# Give the Question a couple of Choices. The create call constructs a new
# Choice object, does the INSERT statement, adds the choice to the set
# of available choices and returns the new Choice object. Django creates
# a set to hold the "other side" of a ForeignKey relation
# (e.g. a question's choice) which can be accessed via the API.
>>> q = Question.objects.get(pk=1)
# Display any choices from the related object set -- none so far.
>>> q.choice_set.all()
<QuerySet []>
# Create three choices.
>>> q.choice_set.create(choice_text="Not much", votes=0)
<Choice: Not much>
>>> q.choice_set.create(choice_text="The sky", votes=0)
<Choice: The sky>
>>> c = q.choice_set.create(choice_text="Just hacking again", votes=0)
# Choice objects have API access to their related Question objects.
>>> c.question
<Question: What's up?>
# And vice versa: Question objects get access to Choice objects.
>>> q.choice_set.all()
<QuerySet [<Choice: Not much>, <Choice: The sky>, <Choice: Just hacking again>]>
>>> q.choice_set.count()
3
# The API automatically follows relationships as far as you need.
# Use double underscores to separate relationships.
# This works as many levels deep as you want; there's no limit.
# Find all Choices for any question whose pub_date is in this year
# (reusing the 'current_year' variable we created above).
>>> Choice.objects.filter(question__pub_date__year=current_year)
<QuerySet [<Choice: Not much>, <Choice: The sky>, <Choice: Just hacking again>]>
# Let's delete one of the choices. Use delete() for that.
>>> c = q.choice_set.filter(choice_text__startswith="Just hacking")
>>> c.delete()
Django Admin
创建admin user
python3 manage.py createsuperuser
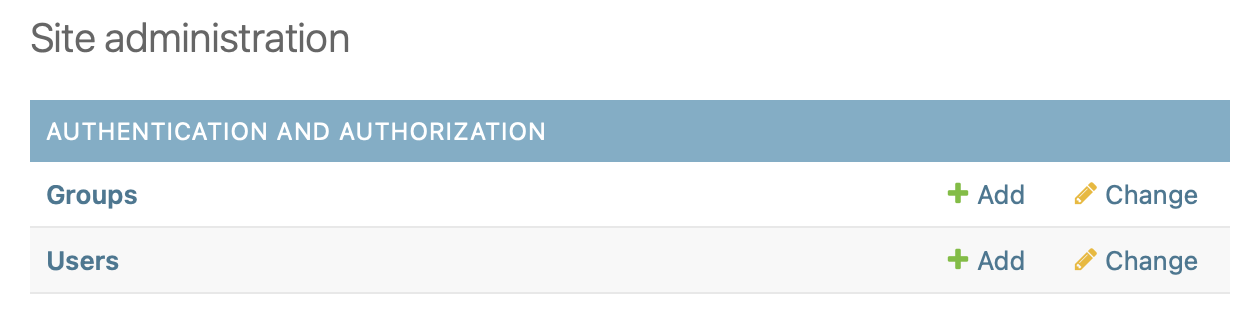
修改LANGUAGE_CODE为中文,编辑mysite/settings.py
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'zh-CN'
重新刷新网址
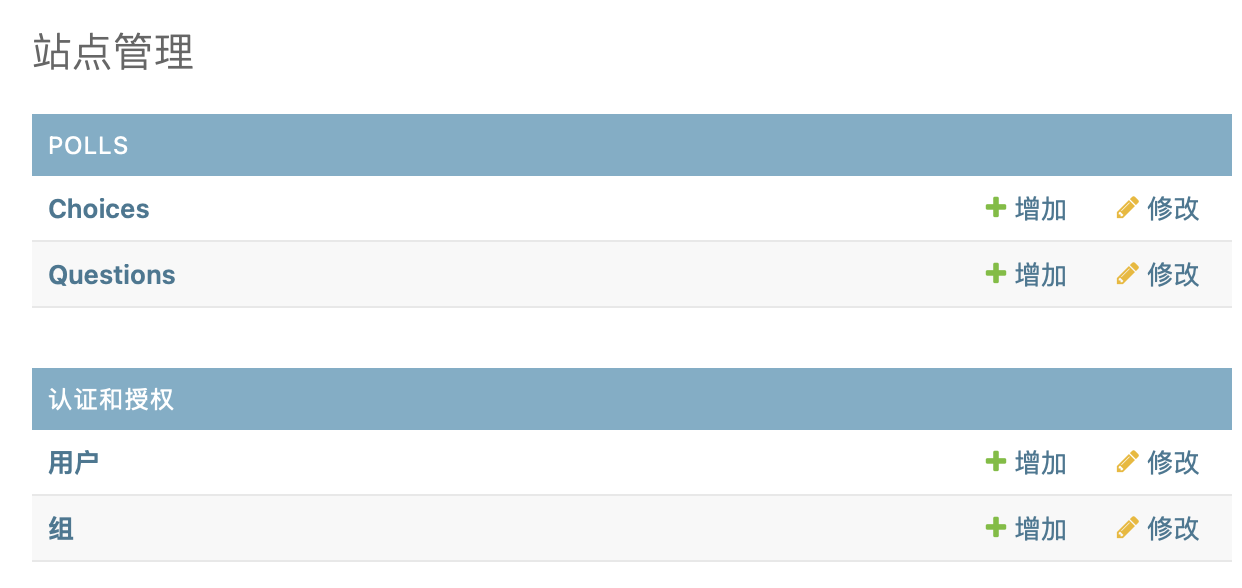
添加model至admin,修改polls/admin.py
点击查看代码
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Question, Choice
# Register your models here.
admin.site.register(Question)
admin.site.register(Choice)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号