稀疏八叉树算法(SVO)示例
稀疏八叉树算法示例:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class OctreeNode:
def __init__(self, bounds, depth=0):
self.bounds = bounds # 体素的空间边界
self.children = [] # 存储子节点
self.depth = depth # 当前节点的深度
self.is_leaf = True # 标记是否为叶节点
self.points = [] # 存储在该节点内的点云数据
# 判断是否需要细分节点
def needs_subdivision(self, max_points):
# 当节点中的点数超过最大限制且深度未超过最大深度时细分
return len(self.points) > max_points and self.depth < OctreeNode.MAX_DEPTH
# 细分节点,将其分成8个子节点
def subdivide(self):
x_min, y_min, z_min = self.bounds['min']
x_max, y_max, z_max = self.bounds['max']
mid_x = (x_min + x_max) / 2
mid_y = (y_min + y_max) / 2
mid_z = (z_min + z_max) / 2
sub_bounds = [
{'min': [x_min, y_min, z_min], 'max': [mid_x, mid_y, mid_z]},
{'min': [mid_x, y_min, z_min], 'max': [x_max, mid_y, mid_z]},
{'min': [x_min, mid_y, z_min], 'max': [mid_x, y_max, mid_z]},
{'min': [mid_x, mid_y, z_min], 'max': [x_max, y_max, mid_z]},
{'min': [x_min, y_min, mid_z], 'max': [mid_x, mid_y, z_max]},
{'min': [mid_x, y_min, mid_z], 'max': [x_max, mid_y, z_max]},
{'min': [x_min, mid_y, mid_z], 'max': [mid_x, y_max, z_max]},
{'min': [mid_x, mid_y, mid_z], 'max': [x_max, y_max, z_max]},
]
for i in range(8):
self.children.append(OctreeNode(sub_bounds[i], self.depth + 1))
self.is_leaf = False # 不再是叶节点
# 分配点云到子节点
def distribute_points(self):
if self.is_leaf:
return
for point in self.points:
for child in self.children:
if child.contains_point(point):
child.points.append(point)
break
self.points = [] # 清空当前节点的点,所有点已分配到子节点
# 检查点是否在节点的边界内
def contains_point(self, point):
x, y, z = point
x_min, y_min, z_min = self.bounds['min']
x_max, y_max, z_max = self.bounds['max']
return x_min <= x <= x_max and y_min <= y <= y_max and z_min <= z <= z_max
# 定义 Octree 的最大深度
OctreeNode.MAX_DEPTH = 6
class SVO:
def __init__(self, points, bounds):
self.root = OctreeNode(bounds) # 根节点
self.points = points # 输入的点云数据
def build_tree(self, max_points_per_node):
self.root.points = self.points
self._subdivide(self.root, max_points_per_node)
def _subdivide(self, node, max_points_per_node):
if node.needs_subdivision(max_points_per_node):
node.subdivide()
node.distribute_points()
for child in node.children:
self._subdivide(child, max_points_per_node)
def traverse(self, callback):
self._traverse_node(self.root, callback)
def _traverse_node(self, node, callback):
if node.is_leaf:
callback(node)
else:
for child in node.children:
self._traverse_node(child, callback)
# 绘制框图
def draw_box(ax, min_corner, max_corner):
# 绘制一个框图,min_corner和max_corner分别是框图的最小和最大点
min_corner = np.array(min_corner)
max_corner = np.array(max_corner)
# 定义框图的8个顶点
vertices = [
min_corner, # 0
(min_corner[0], max_corner[1], min_corner[2]), # 1
(min_corner[0], min_corner[1], max_corner[2]), # 2
(min_corner[0], max_corner[1], max_corner[2]), # 3
(max_corner[0], min_corner[1], min_corner[2]), # 4
(max_corner[0], max_corner[1], min_corner[2]), # 5
(max_corner[0], min_corner[1], max_corner[2]), # 6
(max_corner[0], max_corner[1], max_corner[2]), # 7
]
# 定义框图的12条边
edges = [
(0, 1), (1, 5), (5, 4), (4, 0), # 底面
(2, 3), (3, 7), (7, 6), (6, 2), # 顶面
(0, 2), (1, 3), (4, 6), (5, 7), # 侧面
]
# 绘制框图的边
for edge in edges:
start_point = vertices[edge[0]]
end_point = vertices[edge[1]]
ax.plot([start_point[0], end_point[0]], [start_point[1], end_point[1]], [start_point[2], end_point[2]], 'k-')
def callback(node):
print(node.bounds)
# 绘制边界框图
draw_box(ax, node.bounds['min'], node.bounds['max'])
print(node.points)
# 绘制点
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
if __name__ == '__main__':
points = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12],[13, 14, 15]]
bounds = {'min': [-50, -50, -50], 'max': [50, 50, 50]}
svo = SVO(points, bounds)
svo.build_tree(2)
svo.traverse(callback)
ax.scatter(*zip(*points))
# 绘制整个边界框图
draw_box(ax, bounds['min'], bounds['max'])
# 设置坐标轴的显示范围
ax.set_xlim(-60, 60)
ax.set_ylim(-60, 60)
ax.set_zlim(-60, 60)
# 显示图形
plt.show()
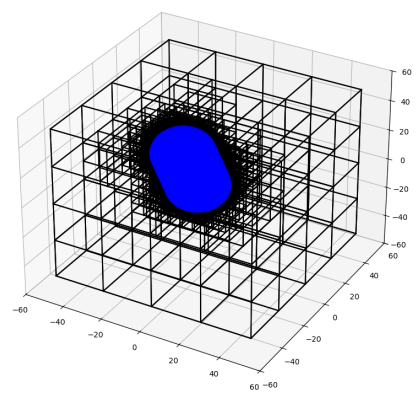
效果如下:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号