ArrayList详解
ArrayList类和它的常见方法
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{// 继承AbstractList类,实现List接口和Serializable序列话接口
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //初始大小,也就是集合的容量
transient Object[] elementData; // 元素的存放数组
private int size; // 实际存放元素的数量
// 直接获取ArrayList的元素数量
public int size() {
return size;
}
// 判断集合内元素是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 集合中是否存在该元素 indexOf方法中循环数组用equals比较元素是否相同相同则返回改元素的下标
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
// 将集合转为数组
public Object[] toArray() {
return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
// 检查下标是否超出数组界限
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
// 通过下标获取元素
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
// 修改指定下标的值为element算做替换,返回之前的元素值
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
// 添加新元素
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// 插入添加,把元素添加到指定的下标,之后的下标开始后的元素向后移一位
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
// 通过下标移除元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
// 移除集合o元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 移除集合第一个元素
// 清空集合
// 合并集合
...
}
实例ArrayList
ArrayList<String> arr = new ArrayList<>();// 只能放String类型对象,在添加第一个值的时候初始容量为10
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();// 可以放任意类型Object
ArrayList<String> arr = new ArrayList<>(5);// 限制集合的类型,并设置集合的初始容量5通过反射获取集合内存放元素的数组
Class<? extends List> aClass = arr.getClass();
Field elementData = aClass.getDeclaredField("elementData");
elementData.setAccessible(true);
Object[] o = (Object[]) elementData.get(arr);
System.out.println(o.length);// 数组的长度也就是集合的容量第一种方式创建的集合输出为0(说明在没有设置集合长度和添加元素的时候集合的长度为零)
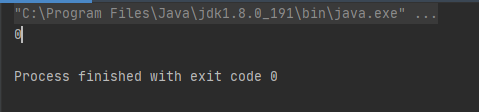
当给集合添加第一个值后(数组的长度变成了10)
arr.add("arr");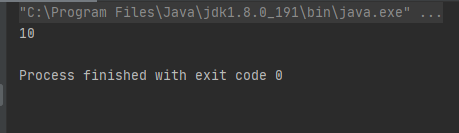
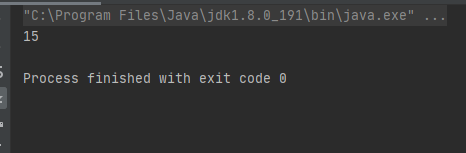
当元素增加到11为时数组的长度再次发生变化
当元素增加到16时数组长度又发生了变化
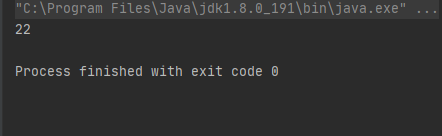
三次变化可以得到一个结论:在元素超过当前数组的长度时,会有一个新的数组替换原来的数组。而新数组的长度为原数组长度加原数组长度的1/2.
那么这么判断是新的数组呢?
通过获取这个数组的hashcode值来判断集合中数组长度变化前和变化后的是否一致


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号