SpringBoot大致启动流程
以main方法为入口进入:
↓

↓
↓
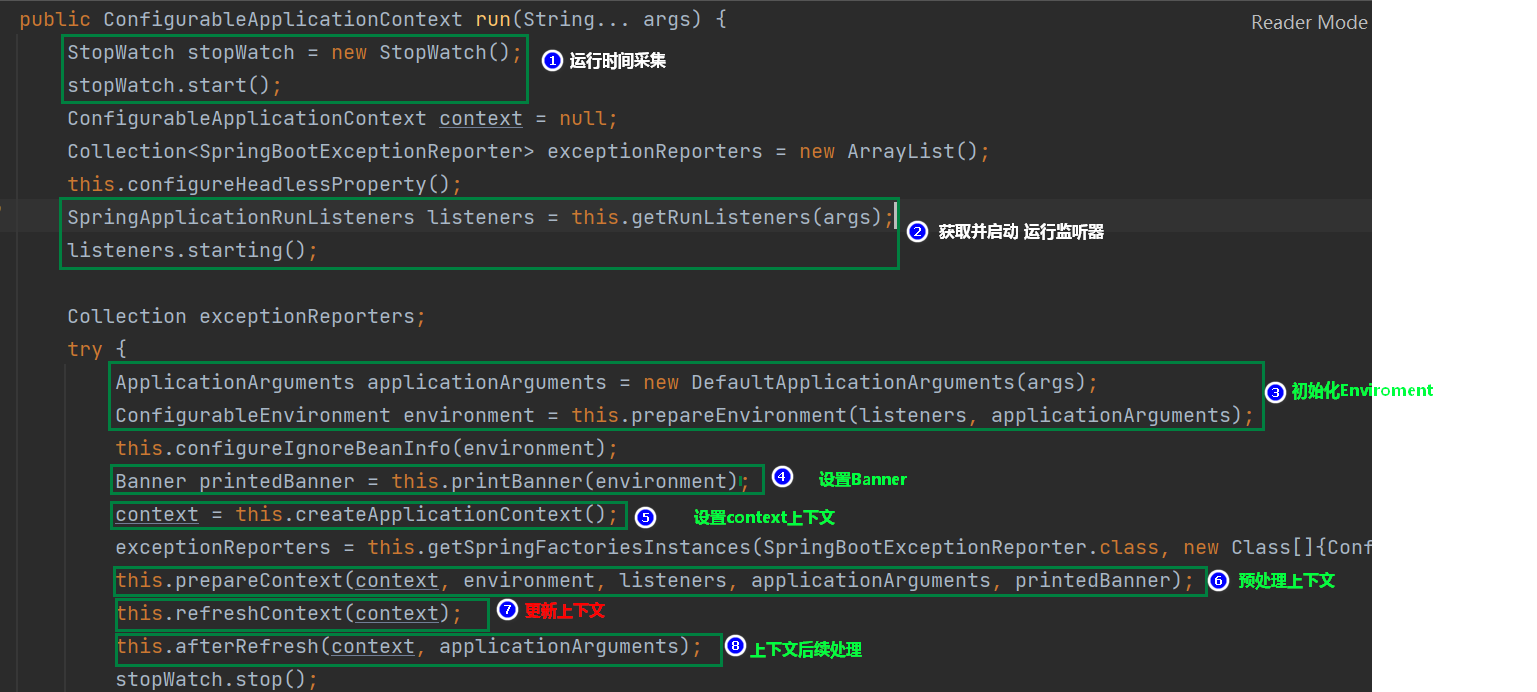
主线流程到此结束,接下来重点看 6,7,8这三个方法中详细的代码流程,首先是prepareContext进行上下文预处理:
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { context.setEnvironment(environment);//为上下文设置Environment this.postProcessApplicationContext(context); this.applyInitializers(context); listeners.contextPrepared(context); if (this.logStartupInfo) { this.logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); this.logStartupProfileInfo(context); } ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); if (printedBanner != null) { beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);//注册banner单例 } if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) { ((DefaultListableBeanFactory)beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); } if (this.lazyInitialization) { context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor()); } Set<Object> sources = this.getAllSources(); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");//断言 this.load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); listeners.contextLoaded(context); }
之后是refreshContext进行上下文更新:
1 private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { 2 this.refresh((ApplicationContext)context); 3 if (this.registerShutdownHook) { 4 try { 5 context.registerShutdownHook(); 6 } catch (AccessControlException var3) { 7 } 8 } 9 10 }
↓
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {//使用synchronized对象锁锁住整个方法,strtupShutdownMonitor为Object实例对象
this.prepareRefresh();//更新前的数据准备,startupDate设置为当前时间,closed设为false,active设为true
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//进行大量赋值,最终以执行resetCommonCaches结束
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
refresh()方法运行是有规律的,总体流程是prepareRefresh()->onRefresh()->finishRefresh(),接下来分别看看这三个方法的具体代码实现:
protected void prepareRefresh() {
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();//记录开始时间
this.closed.set(false);//打开更新
this.active.set(true);//设置为可更新状态
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
} else {
this.logger.debug("Refreshing " + this.getDisplayName());
}
}
this.initPropertySources();
this.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet(this.applicationListeners);
} else {
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet();
}
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {//空壳方法,看似是一个空方法,但是对于提高系统扩展性有很重要的地位,如它的实现类中有一个createWebServer()方法,这个方法提供了tomcat/netty等的实现源码
}
protected void finishRefresh() {
this.clearResourceCaches();//清空资源缓存
this.initLifecycleProcessor();//重置lifecycle执行器
this.getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
this.publishEvent((ApplicationEvent)(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this)));//发布上下文更新成功事件
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
最後是afterRefresh方法:
1 protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) { 2 }
afterRefresh方法结束,只有一个空壳方法在这里,应该可以进行自定义拓展;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号