1、实验目的
深入理解决策树、预剪枝和后剪枝的算法原理,能够使用Python语言实现带有预剪枝
和后剪枝的决策树算法C4.5算法的训练与测试,并且使用五折交叉验证算法进行模型训练
与评估。
2、实验内容
(1)从scikit-learn 库中加载 iris 数据集或本地读取,进行数据分析;
(2)采用五折交叉验证划分训练集和测试集,使用训练集对C4.5分类算法进行训练;
(3)使用五折交叉验证对模型性能(准确度、精度、召回率和F1值)进行测试;
(4)通过对测试结果进行比较分析,评估模型性能;
实验代码:
"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, confusion_matrix
from collections import Counter
import math
class TreeNode:
"""决策树节点类"""
def __init__(self, feature_idx=None, threshold=None, label=None, children=None):
"""初始化决策树节点"""
self.feature_idx = feature_idx
self.threshold = threshold
self.label = label
self.children = children
class C45DecisionTree:
"""C4.5决策树分类器(带预剪枝和后剪枝),使用信息增益比选择特征"""
def __init__(self, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, max_depth=None,
pre_pruning=True, post_pruning=False, pruning_threshold=0.0):
"""初始化C4.5决策树参数"""
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
self.min_samples_leaf = min_samples_leaf
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.pre_pruning = pre_pruning
self.post_pruning = post_pruning
self.pruning_threshold = pruning_threshold
self.root = None
self.feature_names = None
def _entropy(self, y):
"""计算信息熵"""
if len(y) == 0:
return 0
counter = Counter(y)
entropy = 0
total = len(y)
for count in counter.values():
p = count / total
if p > 0:
entropy -= p * math.log2(p)
return entropy
def _split_continuous_feature(self, X, y, feature_idx):
"""对连续特征进行最优阈值划分,返回(最优阈值, 最大信息增益比)"""
values = X[:, feature_idx]
unique_values = np.unique(values)
if len(unique_values) <= 1:
return None, -1
thresholds = []
sorted_values = np.sort(unique_values)
for i in range(len(sorted_values) - 1):
thresholds.append((sorted_values[i] + sorted_values[i + 1]) / 2)
best_threshold = None
best_gain_ratio = -1
for threshold in thresholds:
left_mask = X[:, feature_idx] <= threshold
right_mask = ~left_mask
if np.sum(left_mask) == 0 or np.sum(right_mask) == 0:
continue
gain_ratio = self._calculate_gain_ratio(X, y, feature_idx, threshold, is_continuous=True)
if gain_ratio > best_gain_ratio:
best_gain_ratio = gain_ratio
best_threshold = threshold
return best_threshold, best_gain_ratio
def _calculate_gain_ratio(self, X, y, feature_idx, threshold=None, is_continuous=False):
"""计算信息增益比(C4.5算法的核心)"""
base_entropy = self._entropy(y)
if is_continuous:
left_mask = X[:, feature_idx] <= threshold
right_mask = ~left_mask
if np.sum(left_mask) == 0 or np.sum(right_mask) == 0:
return 0
left_y = y[left_mask]
right_y = y[right_mask]
left_weight = len(left_y) / len(y)
right_weight = len(right_y) / len(y)
conditional_entropy = left_weight * self._entropy(left_y) + right_weight * self._entropy(right_y)
information_gain = base_entropy - conditional_entropy
intrinsic_value = -left_weight * math.log2(left_weight) - right_weight * math.log2(right_weight)
else:
unique_values = np.unique(X[:, feature_idx])
if len(unique_values) == 1:
return 0
conditional_entropy = 0
intrinsic_value = 0
for value in unique_values:
mask = X[:, feature_idx] == value
subset_y = y[mask]
if len(subset_y) == 0:
continue
weight = len(subset_y) / len(y)
conditional_entropy += weight * self._entropy(subset_y)
intrinsic_value -= weight * math.log2(weight)
information_gain = base_entropy - conditional_entropy
if intrinsic_value == 0:
return 0
gain_ratio = information_gain / intrinsic_value
return gain_ratio
def _find_best_split(self, X, y):
"""找到最优划分特征和阈值,返回(最优特征索引, 阈值, 是否为连续特征, 信息增益比)"""
best_feature = None
best_threshold = None
best_is_continuous = False
best_gain_ratio = -1
n_features = X.shape[1]
for feature_idx in range(n_features):
unique_values = np.unique(X[:, feature_idx])
if len(unique_values) > 10:
threshold, gain_ratio = self._split_continuous_feature(X, y, feature_idx)
if threshold is not None and gain_ratio > best_gain_ratio:
best_gain_ratio = gain_ratio
best_feature = feature_idx
best_threshold = threshold
best_is_continuous = True
else:
gain_ratio = self._calculate_gain_ratio(X, y, feature_idx, is_continuous=False)
if gain_ratio > best_gain_ratio:
best_gain_ratio = gain_ratio
best_feature = feature_idx
best_threshold = None
best_is_continuous = False
return best_feature, best_threshold, best_is_continuous, best_gain_ratio
def _build_tree(self, X, y, depth=0):
"""递归构建决策树"""
if len(np.unique(y)) == 1:
return TreeNode(label=y[0])
if len(y) < self.min_samples_split:
return TreeNode(label=Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0])
if self.max_depth is not None and depth >= self.max_depth:
return TreeNode(label=Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0])
best_feature, best_threshold, is_continuous, gain_ratio = self._find_best_split(X, y)
if self.pre_pruning and gain_ratio < self.pruning_threshold:
return TreeNode(label=Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0])
if best_feature is None:
return TreeNode(label=Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0])
node = TreeNode(feature_idx=best_feature, threshold=best_threshold)
node.children = {}
if is_continuous:
left_mask = X[:, best_feature] <= best_threshold
right_mask = ~left_mask
if np.sum(left_mask) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
node.children['<='] = self._build_tree(X[left_mask], y[left_mask], depth + 1)
else:
node.children['<='] = TreeNode(label=Counter(y[left_mask]).most_common(1)[0][0] if len(y[left_mask]) > 0 else Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0])
if np.sum(right_mask) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
node.children['>'] = self._build_tree(X[right_mask], y[right_mask], depth + 1)
else:
node.children['>'] = TreeNode(label=Counter(y[right_mask]).most_common(1)[0][0] if len(y[right_mask]) > 0 else Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0])
else:
unique_values = np.unique(X[:, best_feature])
for value in unique_values:
mask = X[:, best_feature] == value
subset_X = X[mask]
subset_y = y[mask]
if len(subset_y) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
node.children[value] = self._build_tree(subset_X, subset_y, depth + 1)
else:
node.children[value] = TreeNode(label=Counter(subset_y).most_common(1)[0][0] if len(subset_y) > 0 else Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0])
return node
def _prune_tree(self, node, X, y):
"""后剪枝:使用验证集对树进行剪枝"""
if node.label is not None:
return node
if len(X) == 0:
return TreeNode(label=Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0] if len(y) > 0 else 0)
if node.children:
for key, child in node.children.items():
if node.threshold is not None:
if key == '<=':
mask = X[:, node.feature_idx] <= node.threshold
else:
mask = X[:, node.feature_idx] > node.threshold
else:
mask = X[:, node.feature_idx] == key
node.children[key] = self._prune_tree(child, X[mask], y[mask])
errors_before = 0
for i in range(len(X)):
pred = self._predict_single(X[i], node)
if pred != y[i]:
errors_before += 1
majority_label = Counter(y).most_common(1)[0][0]
errors_after = np.sum(y != majority_label)
if errors_after <= errors_before:
return TreeNode(label=majority_label)
return node
def _predict_single(self, x, node):
"""对单个样本进行预测"""
if node.label is not None:
return node.label
if node.threshold is not None:
if x[node.feature_idx] <= node.threshold:
key = '<='
else:
key = '>'
else:
key = x[node.feature_idx]
if key in node.children:
return self._predict_single(x, node.children[key])
else:
return 0
def fit(self, X, y):
"""训练决策树"""
X = np.array(X)
y = np.array(y)
self.root = self._build_tree(X, y)
if self.post_pruning:
n_samples = len(X)
val_size = int(n_samples * 0.2)
val_indices = np.random.choice(n_samples, val_size, replace=False)
train_indices = np.setdiff1d(np.arange(n_samples), val_indices)
X_val = X[val_indices]
y_val = y[val_indices]
self.root = self._prune_tree(self.root, X_val, y_val)
def predict(self, X):
"""预测,返回预测标签数组"""
X = np.array(X)
predictions = []
for x in X:
predictions.append(self._predict_single(x, self.root))
return np.array(predictions)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=" * 80)
print("C4.5决策树算法实验(带预剪枝和后剪枝)")
print("=" * 80)
print()
print("=" * 80)
print("步骤1:从scikit-learn库中加载iris数据集,进行数据分析")
print("=" * 80)
print()
# load_iris(): 加载iris数据集,返回Bunch对象包含data、target、target_names、feature_names等属性
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
feature_names = iris.feature_names
target_names = iris.target_names
print(f"数据集形状: {X.shape}")
print(f"特征数量: {X.shape[1]}")
print(f"样本数量: {X.shape[0]}")
print(f"类别数量: {len(np.unique(y))}")
print()
print(f"特征名称: {feature_names}")
print(f"类别名称: {target_names}")
print()
print("数据统计信息:")
iris_df = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=feature_names)
iris_df['species'] = [target_names[i] for i in y]
print(iris_df.describe())
print()
print("类别分布:")
for i, name in enumerate(target_names):
count = np.sum(y == i)
print(f" {name}: {count} 个样本 ({count/len(y)*100:.1f}%)")
print()
print("=" * 80)
print("步骤2:采用五折交叉验证划分训练集和测试集,使用训练集对C4.5分类算法进行训练")
print("=" * 80)
print()
# KFold(): 将数据集划分为k折用于交叉验证,n_splits为折数,shuffle是否打乱,random_state随机种子
kfold = KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
print("创建C4.5决策树模型(带预剪枝)...")
print()
fold_results = {
'fold': [],
'accuracy': [],
'precision': [],
'recall': [],
'f1': []
}
all_y_true = []
all_y_pred = []
print("开始五折交叉验证...")
print("-" * 80)
fold_num = 1
for train_idx, test_idx in kfold.split(X, y):
print(f"\n第 {fold_num} 折:")
print(f" 训练集大小: {len(train_idx)} ({len(train_idx)/len(X)*100:.1f}%)")
print(f" 测试集大小: {len(test_idx)} ({len(test_idx)/len(X)*100:.1f}%)")
X_train, X_test = X[train_idx], X[test_idx]
y_train, y_test = y[train_idx], y[test_idx]
model = C45DecisionTree(
min_samples_split=2,
min_samples_leaf=1,
max_depth=10,
pre_pruning=True,
post_pruning=False,
pruning_threshold=0.0
)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
all_y_true.extend(y_test)
all_y_pred.extend(y_pred)
# accuracy_score(): 计算分类准确度;precision_score(): 计算精度,average='weighted'表示加权平均
# recall_score(): 计算召回率;f1_score(): 计算F1分数(精度和召回率的调和平均数)
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
prec = precision_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted', zero_division=0)
rec = recall_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted', zero_division=0)
f1 = f1_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted', zero_division=0)
fold_results['fold'].append(fold_num)
fold_results['accuracy'].append(acc)
fold_results['precision'].append(prec)
fold_results['recall'].append(rec)
fold_results['f1'].append(f1)
print(f" 准确度 (Accuracy): {acc:.4f}")
print(f" 精度 (Precision): {prec:.4f}")
print(f" 召回率 (Recall): {rec:.4f}")
print(f" F1值 (F1-Score): {f1:.4f}")
fold_num += 1
print("\n" + "=" * 80)
print("五折交叉验证完成!")
print("=" * 80)
print()
print("=" * 80)
print("步骤4:通过对测试结果进行比较分析,评估模型性能")
print("=" * 80)
print()
overall_accuracy = accuracy_score(all_y_true, all_y_pred)
overall_precision = precision_score(all_y_true, all_y_pred, average='weighted', zero_division=0)
overall_recall = recall_score(all_y_true, all_y_pred, average='weighted', zero_division=0)
overall_f1 = f1_score(all_y_true, all_y_pred, average='weighted', zero_division=0)
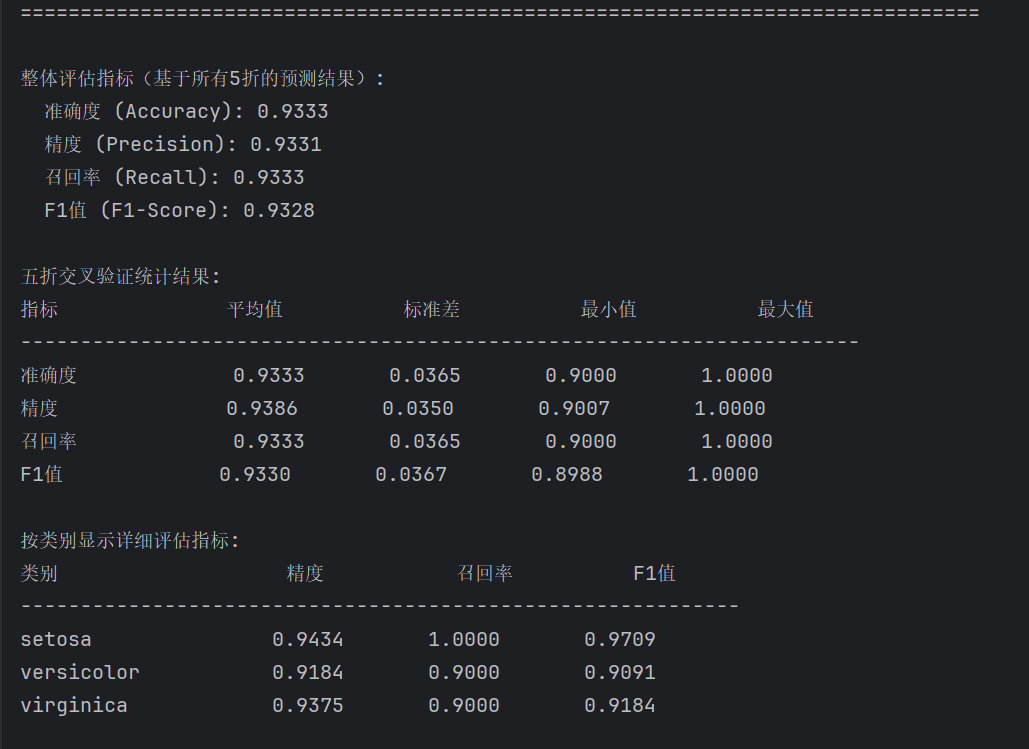
print("整体评估指标(基于所有5折的预测结果):")
print(f" 准确度 (Accuracy): {overall_accuracy:.4f}")
print(f" 精度 (Precision): {overall_precision:.4f}")
print(f" 召回率 (Recall): {overall_recall:.4f}")
print(f" F1值 (F1-Score): {overall_f1:.4f}")
print()
print("五折交叉验证统计结果:")
print(f"{'指标':<15} {'平均值':<12} {'标准差':<12} {'最小值':<12} {'最大值':<12}")
print("-" * 70)
print(f"{'准确度':<15} {np.mean(fold_results['accuracy']):<12.4f} {np.std(fold_results['accuracy']):<12.4f} {np.min(fold_results['accuracy']):<12.4f} {np.max(fold_results['accuracy']):<12.4f}")
print(f"{'精度':<15} {np.mean(fold_results['precision']):<12.4f} {np.std(fold_results['precision']):<12.4f} {np.min(fold_results['precision']):<12.4f} {np.max(fold_results['precision']):<12.4f}")
print(f"{'召回率':<15} {np.mean(fold_results['recall']):<12.4f} {np.std(fold_results['recall']):<12.4f} {np.min(fold_results['recall']):<12.4f} {np.max(fold_results['recall']):<12.4f}")
print(f"{'F1值':<15} {np.mean(fold_results['f1']):<12.4f} {np.std(fold_results['f1']):<12.4f} {np.min(fold_results['f1']):<12.4f} {np.max(fold_results['f1']):<12.4f}")
print()
print("按类别显示详细评估指标:")
precision_per_class = precision_score(all_y_true, all_y_pred, average=None, zero_division=0)
recall_per_class = recall_score(all_y_true, all_y_pred, average=None, zero_division=0)
f1_per_class = f1_score(all_y_true, all_y_pred, average=None, zero_division=0)
print(f"{'类别':<20} {'精度':<12} {'召回率':<12} {'F1值':<12}")
print("-" * 60)
for i, class_name in enumerate(target_names):
print(f"{class_name:<20} {precision_per_class[i]:<12.4f} {recall_per_class[i]:<12.4f} {f1_per_class[i]:<12.4f}")
print()
print("混淆矩阵(Confusion Matrix):")
# confusion_matrix(): 计算混淆矩阵,行表示真实类别,列表示预测类别
cm = confusion_matrix(all_y_true, all_y_pred)
print("\n真实类别(行) vs 预测类别(列):")
print(f"{'':<15}", end="")
for name in target_names:
print(f"{name:<15}", end="")
print()
for i, name in enumerate(target_names):
print(f"{name:<15}", end="")
for j in range(len(target_names)):
print(f"{cm[i, j]:<15}", end="")
print()
print()
print("=" * 80)
print("模型性能分析")
print("=" * 80)
print()
print("1. 准确度分析:")
print(f" 整体准确度为 {overall_accuracy:.4f},说明模型在测试集上的预测正确率为 {overall_accuracy*100:.2f}%")
print(f" 五折交叉验证的平均准确度为 {np.mean(fold_results['accuracy']):.4f},标准差为 {np.std(fold_results['accuracy']):.4f}")
if np.std(fold_results['accuracy']) < 0.05:
print(" 标准差较小,说明模型性能稳定")
else:
print(" 标准差较大,说明模型性能在不同折之间存在一定波动")
print()
print("2. 精度分析:")
print(f" 整体精度为 {overall_precision:.4f},说明模型预测为正类的样本中,实际为正类的比例为 {overall_precision*100:.2f}%")
print()
print("3. 召回率分析:")
print(f" 整体召回率为 {overall_recall:.4f},说明实际为正类的样本中,被正确预测的比例为 {overall_recall*100:.2f}%")
print()
print("4. F1值分析:")
print(f" 整体F1值为 {overall_f1:.4f},综合反映了模型的精度和召回率")
print(f" 由于F1值是精度和召回率的调和平均数,当两者都较高时,F1值也会较高")
print()
print("5. 类别分析:")
for i, class_name in enumerate(target_names):
print(f" {class_name}:")
print(f" 精度: {precision_per_class[i]:.4f}, 召回率: {recall_per_class[i]:.4f}, F1值: {f1_per_class[i]:.4f}")
print()
print("6. 模型特点:")
print(" - C4.5算法使用信息增益比选择特征,相比ID3算法更优")
print(" - 支持连续特征处理(通过阈值划分)")
print(" - 预剪枝可以有效防止过拟合")
print(" - 五折交叉验证提供了更可靠的性能评估")
print()
print("实验完成!")
实验结果:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号