Blog2
一:前言
对于题目集4~6,我做出以下总结:
(1)题目集4:主要运用的知识点是继承。三道题目,分别是:水文数据校验及处理,日期问题面向对象设计,图形继承 。题量不大,但是难度不小,总体来说,得分不多。
(2)题目集5:主要运用的知识点是字符串的处理以及运用。一共五道题目,分别是:找出最长的单词-hebust, 合并两个有序数组为新的有序数组 ,对整型数据排序,统计Java程序中关键词的出现次数 ,日期问题面向对象设计。题目数量相比上一次来说是增大了,但是难度却降低了,前面三道题可以很轻易的做出来,但是所给的分数不多,几乎所有的分数都集中正在后面的两道题。得分相比上一次的题目集有了明显的提升。
(3)题目集6:主要运用的知识点是正则表达式的运用,字符串的分割,接口的运用。一共六道题目,分别是:正则表达式训练-QQ号校验,字符串训练-字符排序 ,正则表达式训练-验证码校验,正则表达式训练-学号校验,图形继承与多态, 实现图形接口及多态性。在这三次的题目集中,这次的题目是最多的,但是也是最简单的,几乎所有的题目都可以比较轻易的做出来,因此,这次的题目集的得分是这三次题目集中最高的。
二:设计与分析
对于这几次题目集中的一些题我做一些分析
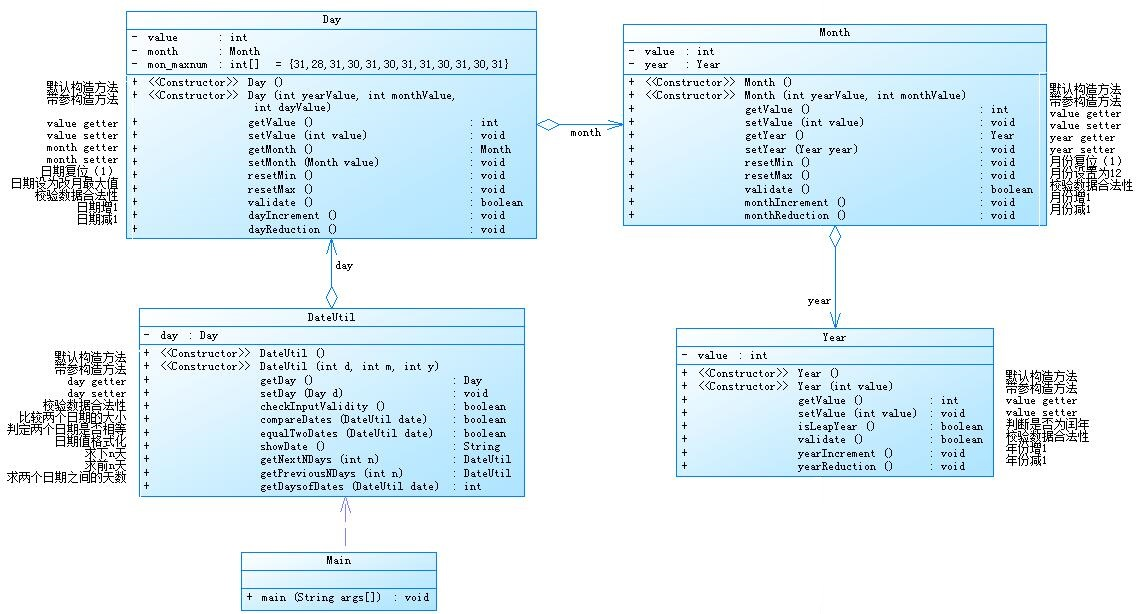
(1)题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
题目集4(7-2):
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()
+ "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue() + "-" + date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()
+ "-" + date.getDay().getValue() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { // test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
Day day;
public DateUtil(){
}
public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y){
this.day = new Day(d,m,y);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day d) {
this.day = d;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
if(this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().validate()&&this.getDay().getMonth().validate()&&day.validate())
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue())
return false;
else if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()
&&date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<this.getDay().getMonth().getValue())
return false;
if (date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()
&&date.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()
&&date.getDay().getValue()<this.getDay().getValue())
return false;
return true;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){//判断两个日期是否相等
if (this.getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()
&& this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()
&& this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==date.getDay().getMonth().getValue())
return true;
return false;
}
public String showDate(){//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
return this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue();
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int year=0, month=0, day=0;
int rest = restday(this);
if (rest>n) {//本年
year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int mday = arr[this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()];
if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==2) {
mday++;
}
mday-=this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期
if (mday>=n) { //本月
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
day = n+this.getDay().getValue();
}
else{ //其他月
n-=mday;
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;
int k = month;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k<=12){
n -= arr[k];
month++;
k++;
}
day = n;
}
}
else {
n-=rest;
year = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1;
int y = 365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) {
y++;
}
while(n-y>0){
n-=y;
year++;
y=365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear())
y++;
}
int k = 1;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k<=12){
n -= arr[k];
k++;
}
month = k;
day = n;
}
// System.out.println(this.showDate()+" next "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public int restday(DateUtil d) {
int n = 0;
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for (int i = d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1; i <=12; i++) {
n+=arr[i];
}
n+=arr[d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-d.getDay().getValue();
if(d.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&d.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)
n++;
return n;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int year=0, month=0, day=0;
int rest = 365-restday(this);
if (this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()) {
rest++;
}
if (rest>n) {//本年
year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();
int mday=this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期
if (mday>n) { //本月
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue();
day = mday-n;
}
else{ //其他月
n-=mday;
month = this.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1;
if (month==0) {
month = 12;
year=this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()-1;
}
int k = month;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){
n -= arr[k];
month--;
k--;
}
day = arr[k]-n;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) {
day++;
}
}
}
else {
n-=rest;
year = this.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()-1;
int y = 365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) {
y++;
}
while(n-y>0){
n-=y;
year--;
y=365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear())
y++;
}
int k = 12;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){
n -= arr[k];
k--;
}
month = k;
day = arr[k]-n;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) {
day++;
}
}
// System.out.println(this.showDate()+" previous "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
DateUtil pred = this;
DateUtil nextd = date;
if (this.equalTwoDates(date)) {
return 0;
}
else if (!this.compareDates(date)) {
pred = date;
nextd = this;
}
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int i,j,d = 0;
for(i=pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1;i<nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue();i++) {
d=d+365;
if(new Year(i).isLeapYear())
d++;
}
if (pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()!=nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
for(j=pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=12;j++)
d=d+arr[j];
d+=arr[pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue();
for(j=1;j<nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue();j++)
d+=arr[j];
d+=nextd.getDay().getValue();
if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)
d++;
if (nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()>2) {
d++;
}
}
else if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()!=nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
for(j=pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()-1;j++)
d+=arr[j];
d+=arr[pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue();
d+=nextd.getDay().getValue();
if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()<=2)
d++;
}
else if(pred.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()==nextd.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&pred.getDay().getMonth().getValue()==nextd.getDay().getMonth().getValue()){
d=nextd.getDay().getValue()-pred.getDay().getValue();
}
return d;
}
}
class Day{
int value;
Month month;
int mon_maxnum[]= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public Day() {
}
public Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue) {
this.month = new Month(yearValue,monthValue);
this.value = dayValue;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month value) {
this.month = value;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1];
}
public boolean validate() {
if(this.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear())
mon_maxnum[1]++;
if(1<=value&&mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]>=value)
return true;
return false;
}
public void dayIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Month{
int value;
Year year;
public Month() {
}
public Month(int yearValue,int monthValue) {
this.year = new Year(yearValue);
this.value = monthValue;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(1<=value&&12>=value)
return true;
return false;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void monthReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Year{
int value;
public Year() {
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(){//判断year是否为闰年
boolean y1 = value%4 == 0;
boolean y2 = value%100 != 0;
boolean y3 = value%400 == 0;
if((y1&&y2)||y3)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value<=2020&&value>=1820)
return true;
return false;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value--;
}
}
题目集5(7-4)

import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.showDate() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.showDate() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { // test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
Year year;
Month month;
Day day;
int mon_maxnum[] = {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public DateUtil(){
}
public DateUtil(int y, int m, int d){
this.day = new Day(d);
this.month = new Month(m);
this.year = new Year(y);
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public void setDayMin() {
this.day.value=1;
}
public void setDatMax() {
if(this.year.isLeapYear())
mon_maxnum[1]++;
this.day.value=mon_maxnum[this.month.value-1];
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
if(this.year.isLeapYear())
mon_maxnum[1]++;
if(this.year.validate()&&this.month.validate()&&this.day.value>=1&&this.day.value<=mon_maxnum[this.month.value-1])
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
if (date.year.value<this.year.value)
return false;
else if (date.year.value==this.year.value
&&date.month.value<this.month.value)
return false;
if (date.year.value==this.year.value
&&date.month.value==this.month.value
&&date.day.value<this.day.value)
return false;
return true;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){//判断两个日期是否相等
if (this.getDay().getValue()==date.getDay().getValue()
&& this.getYear().getValue()==date.getYear().getValue()
&& this.getMonth().getValue()==date.getMonth().getValue())
return true;
return false;
}
public String showDate(){//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
return this.getYear().getValue()+"-"+this.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+this.getDay().getValue();
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int year=0, month=0, day=0;
int rest = restday(this);
if (rest>n) {//本年
year=this.getYear().getValue();
int mday = arr[this.getMonth().getValue()];
if (this.getYear().isLeapYear()&&this.getMonth().getValue()==2) {
mday++;
}
mday-=this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期
if (mday>=n) { //本月
month = this.getMonth().getValue();
day = n+this.getDay().getValue();
}
else{ //其他月
n-=mday;
month = this.getMonth().getValue()+1;
int k = month;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k<=12){
n -= arr[k];
month++;
k++;
}
day = n;
}
}
else {
n-=rest;
year = this.getYear().getValue()+1;
int y = 365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) {
y++;
}
while(n-y>0){
n-=y;
year++;
y=365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear())
y++;
}
int k = 1;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k<=12){
n -= arr[k];
k++;
}
month = k;
day = n;
}
// System.out.println(this.showDate()+" next "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public int restday(DateUtil d) {
int n = 0;
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for (int i = d.getMonth().getValue()+1; i <=12; i++) {
n+=arr[i];
}
n+=arr[d.getMonth().getValue()]-d.getDay().getValue();
if(d.getYear().isLeapYear()&&d.getMonth().getValue()<=2)
n++;
return n;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int year=0, month=0, day=0;
int rest = 365-restday(this);
if (this.getYear().isLeapYear()) {
rest++;
}
if (rest>n) {//本年
year=this.getYear().getValue();
int mday=this.getDay().getValue();//本月剩余的日期
if (mday>n) { //本月
month = this.getMonth().getValue();
day = mday-n;
}
else{ //其他月
n-=mday;
month = this.getMonth().getValue()-1;
if (month==0) {
month = 12;
year=this.getYear().getValue()-1;
}
int k = month;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){
n -= arr[k];
month--;
k--;
}
day = arr[k]-n;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) {
day++;
}
}
}
else {
n-=rest;
year = this.getYear().getValue()-1;
int y = 365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()) {
y++;
}
while(n-y>0){
n-=y;
year--;
y=365;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear())
y++;
}
int k = 12;
while(n-arr[k]>0&&k>=0){
n -= arr[k];
k--;
}
month = k;
day = arr[k]-n;
if (new Year(year).isLeapYear()&&month==2) {
day++;
}
}
// System.out.println(this.showDate()+" previous "+n+" days is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
DateUtil pred = this;
DateUtil nextd = date;
if (this.equalTwoDates(date)) {
return 0;
}
else if (!this.compareDates(date)) {
pred = date;
nextd = this;
}
int arr[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int i,j,d = 0;
for(i=pred.getYear().getValue()+1;i<nextd.getYear().getValue();i++) {
d=d+365;
if(new Year(i).isLeapYear())
d++;
}
if (pred.getYear().getValue()!=nextd.getYear().getValue()) {
for(j=pred.getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=12;j++)
d=d+arr[j];
d+=arr[pred.getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue();
for(j=1;j<nextd.getMonth().getValue();j++)
d+=arr[j];
d+=nextd.getDay().getValue();
if(pred.getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()<=2)
d++;
if (nextd.getYear().isLeapYear()&&nextd.getMonth().getValue()>2) {
d++;
}
}
else if(pred.getYear().getValue()==nextd.getYear().getValue()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()!=nextd.getMonth().getValue()){
for(j=pred.getMonth().getValue()+1;j<=nextd.getMonth().getValue()-1;j++)
d+=arr[j];
d+=arr[pred.getMonth().getValue()]-pred.getDay().getValue();
d+=nextd.getDay().getValue();
if(pred.getYear().isLeapYear()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()<=2)
d++;
}
else if(pred.getYear().getValue()==nextd.getYear().getValue()&&pred.getMonth().getValue()==nextd.getMonth().getValue()){
d=nextd.getDay().getValue()-pred.getDay().getValue();
}
return d;
}
}
class Day{
int value;
public Day() {
}
public Day(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void dayIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void dayReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Month{
int value;
public Month() {
}
public Month(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(1<=this.value&&12>=this.value)
return true;
return false;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void monthReduction() {
value--;
}
}
class Year{
int value;
public Year() {
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(){//判断year是否为闰年
boolean y1 = value%4 == 0;
boolean y2 = value%100 != 0;
boolean y3 = value%400 == 0;
if((y1&&y2)||y3)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(this.value<=2020&&this.value>=1820)
return true;
return false;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value++;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value--;
}
}
对于这两个题目,第一个题目主要考察的是类与类之间的关系,第二个题目主要考察对字符串的输入和输出,相比较来说,第二次的设计风格更好。
(2)题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
题目集4(7-3)
编写程序,实现图形类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。
- 类Shape,无属性,有一个返回0.0的求图形面积的公有方法
public double getArea();//求图形面积 - 类Circle,继承自Shape,有一个私有实型的属性radius(半径),重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求圆的面积
- 类Rectangle,继承自Shape,有两个私有实型属性width和length,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求矩形的面积
- 类Ball,继承自Circle,其属性从父类继承,重写父类求面积方法,求球表面积,此外,定义一求球体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求球体积 - 类Box,继承自Rectangle,除从父类继承的属性外,再定义一个属性height,重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求立方体表面积,此外,定义一求立方体体积的方法
public double getVolume();//求立方体体积 - 注意:
- 每个类均有构造方法,且构造方法内必须输出如下内容:
Constructing 类名 - 每个类属性均为私有,且必须有getter和setter方法(可用Eclipse自动生成)
- 输出的数值均保留两位小数
主方法内,主要实现四个功能(1-4): 从键盘输入1,则定义圆类,从键盘输入圆的半径后,主要输出圆的面积; 从键盘输入2,则定义矩形类,从键盘输入矩形的宽和长后,主要输出矩形的面积; 从键盘输入3,则定义球类,从键盘输入球的半径后,主要输出球的表面积和体积; 从键盘输入4,则定义立方体类,从键盘输入立方体的宽、长和高度后,主要输出立方体的表面积和体积;
假如数据输入非法(包括圆、矩形、球及立方体对象的属性不大于0和输入选择值非1-4),系统输出Wrong Format
import java.util.Scanner;
//3题
class Shape{
public double getArea() {
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape{
private double radius;
double circlearea;
Circle(){
}
public double getradius() {
return radius;
}
public void setradius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getArea(double radius) {
circlearea = radius*radius*Math.PI;
return circlearea;
}
}
class Rectange extends Shape{
private double width;
private double length;
double rectangearea;
Rectange(){
}
public double getwidth() {
return width;
}
public void setwidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getlength() {
return length;
}
public void setlength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public Rectange(double width,double length) {
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
public double getArea(double width,double length) {
rectangearea=width*length;
return rectangearea;
}
}
class Ball extends Circle{
/*
public Box(double width,double length) {
super(width,length);
}
*/
double ballarea;
double ballvolume;
Ball(){
}
public double getArea() {
ballarea=4*Math.PI*super.getradius()*super.getradius();
return ballarea;
}
public double getVolume() {
ballvolume=(4.0/3.0)*Math.PI*super.getradius()*super.getradius()*super.getradius();
return ballvolume;
}
}
class Box extends Rectange{
/* public Box(double width,double length) {
super(width,length);
}
*/
private double width;
private double length;
private double height;
double boxvolum;
double boxarea;
Box(){
}
public void setheight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public double getArea() {
boxarea=2.0*(height*super.getlength()+height*super.getwidth()+super.getlength()*super.getwidth());
return boxarea;
}
public double getVolume() {
boxvolum=height*super.getlength()*super.getwidth();
return boxvolum;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Circle circle = new Circle();
Rectange rectange = new Rectange();
Ball ball = new Ball();
Box box = new Box();
int choose =input.nextInt();
switch(choose)
{
case 1:{
double r = input.nextDouble();
if(r>=0) {
double circlearea = circle.getArea(r);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
System.out.println("Circle's area:"+String.format("%.2f", circlearea));
break;
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
case 2:{
double a = input.nextDouble();
double b = input.nextDouble();
if(a>=0&&b>=0) {
double rectangearea = rectange.getArea(a, b);
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
System.out.println("Rectangle's area:"+String.format("%.2f", rectangearea));
break;
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
case 3:{
double r = input.nextDouble();
if(r>=0) {
ball.setradius(r);
double ballarea = ball.getArea();
double ballvolume = ball.getVolume();
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
System.out.println("Ball's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f",ballarea));
System.out.println("Ball's volume:"+String.format("%.2f", ballvolume));
break;
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
case 4:{
double a = input.nextDouble();
double b = input.nextDouble();
double c = input.nextDouble();
if(a>=0&&b>=0&&c>=0) {
box.setlength(a);
box.setwidth(b);
box.setheight(c);
double boxvolum = box.getVolume();
double boxarea = box.getArea();
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
System.out.println("Box's surface area:"+String.format("%.2f", boxarea));
System.out.println("Box's volume:"+String.format("%.2f", boxvolum));
break;
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
break;
}
}
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
题目集6(7-5、7-6)
7-5
输入格式:
从键盘首先输入三个整型值(例如a b c),分别代表想要创建的Circle、Rectangle及Triangle对象的数量,然后根据图形数量继续输入各对象的属性值(均为实型数),数与数之间可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 如果图形数量非法(小于0)或图形属性值非法(数值小于0以及三角形三边关系),则输出
Wrong Format。 - 如果输入合法,则正常输出,输出内容如下(输出格式见输入输出示例):
- 各个图形的面积;
- 所有图形的面积总和;
- 排序后的各个图形面积;
- 再次所有图形的面积总和。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Circle{
double radius;
public boolean checkCircle() {
if(this.radius>0) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
public Circle(double radius) {
super();
this.radius = radius;
}
public double CircleArea(){
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}
}
class Rectangle{
double length,width;
public boolean checkRectangle() {
if(this.width>0&this.length>0) {
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
public Rectangle(double length, double width) {
super();
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
public double RectangleArea(){
return width*length;
}
}
class Triangle{
double a,b,c;
public Triangle(double a, double b, double c) {
super();
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
public double TriangleArea(){
return Math.sqrt((a+b+c)*(a+b-c)*(a+c-b)*(b+c-a))/4;
}
public boolean checkTriangle() {
double a[] = new double[3];
a[0] = this.a;
a[1] = this.b;
a[2] = this.c;
Arrays.sort(a);
if (a[0] + a[1] > a[2]) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int circlenum = input.nextInt();
int rectangenum = input.nextInt();
int trianglenum = input.nextInt();
if (circlenum >= 0 & rectangenum >= 0 & trianglenum >= 0) {
Circle circle[] = new Circle[circlenum];
Rectangle rectange[] = new Rectangle[rectangenum];
Triangle triangle[] = new Triangle[trianglenum];
ArrayList <Double> AreaList=new ArrayList<Double>();
for (int i = 0; i < circlenum; i++) {
circle[i] = new Circle(input.nextDouble());
if (circle[i].checkCircle() == false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
AreaList.add(circle[i].CircleArea());
}
for (int i = 0; i < rectangenum; i++) {
rectange[i] = new Rectangle(input.nextDouble(), input.nextDouble());
if (rectange[i].checkRectangle() == false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
AreaList.add(rectange[i].RectangleArea());
}
for (int i = 0; i < trianglenum; i++) {
triangle[i] = new Triangle(input.nextDouble(), input.nextDouble(), input.nextDouble());
if (triangle[i].checkTriangle() == false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
AreaList.add(triangle[i].TriangleArea());
}
System.out.println("Original area:");
AllArea(AreaList);
System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f\n",sumArea(AreaList));
System.out.println("Sorted area:");
for(double i:AreaList) {
System.out.printf("%.2f ",i);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f\n",sumArea(AreaList));
}
else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
public static double sumArea(ArrayList <Double> AreaList){
double a = 0;
for (double i:AreaList) {
a=a+i;
}
return a;
}
public static void AllArea(ArrayList <Double> AreaList) {
for (double i:AreaList) {
System.out.printf("%.2f ",i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
7-6
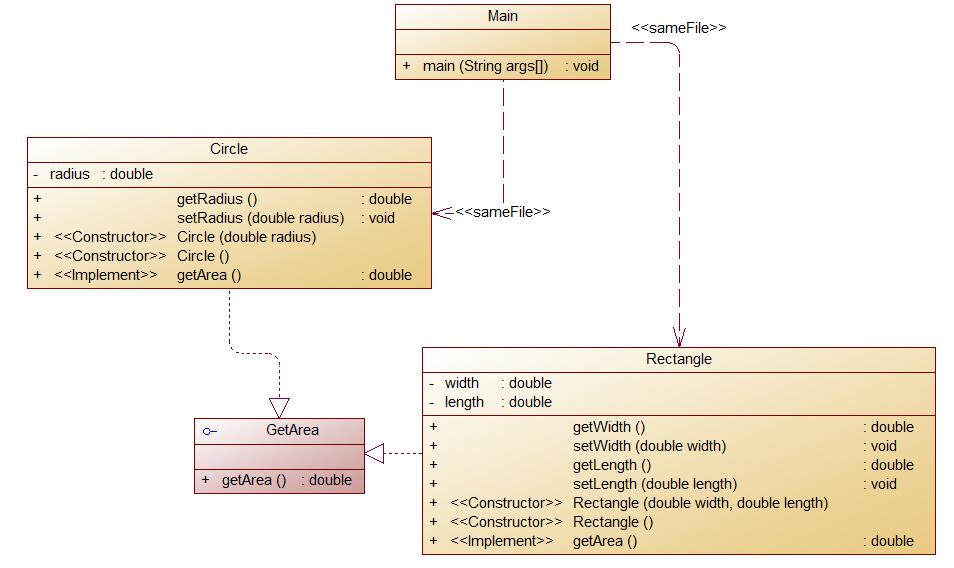
其中:
- GetArea为一个接口,无属性,只有一个GetArea(求面积)的抽象方法;
- Circle及Rectangle分别为圆类及矩形类,分别实现GetArea接口
- 要求:在Main类的主方法中分别定义一个圆类对象及矩形类对象(其属性值由键盘输入),使用接口的引用分别调用圆类对象及矩形类对象的求面积的方法,直接输出两个图形的面积值。(要求只保留两位小数)
输入格式:
从键盘分别输入圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值,用空格分开。
输出格式:
- 如果输入的圆的半径值及矩形的宽、长的值非法(≤0),则输出
Wrong Format - 如果输入合法,则分别输出圆的面积和矩形的面积值(各占一行),保留两位小数。
import java.util.Scanner;
class Rectangle implements GetArea{
private double width;
private double length;
double getWidth() {
return width;
}
void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
double getLength() {
return length;
}
void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
Rectangle(double width,double length){
}
Rectangle(){
}
public double getArea() {
double area = length*width;
return area;
}
public double getArea(double length,double width) {
double area = length*width;
return area;
}
}
class Circle implements GetArea{
double radius;
double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
Circle(double radius){
}
Circle(){
}
public double getArea() {
double area;
area = Math.PI*radius*radius;
return area;
}
public double getArea(double radius) {
double area;
area = Math.PI*radius*radius;
return area;
}
}
interface GetArea {
double getArea();
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double num1 = input.nextDouble();
double num2 = input.nextDouble();
double num3 = input.nextDouble();
Circle circle = new Circle();
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
if(num1>0&&num2>0&&num3>0) {
System.out.printf("%.2f",circle.getArea(num1));
System.out.printf("\n");
System.out.printf("%.2f",rectangle.getArea(num2,num3));
}else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
(3)对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
正则表达式定义字符串的搜索模式
正则表达式的英文全称是regular expression。搜索模式可以是简单字符,固定字符串或包含描述模式的特殊字符的复杂表达式的任何内容
由正则表达式定义的 pattern 可以同时匹配一个或多个,或者一个都没匹配到
正则表达式可用于搜索,编辑和操作文本
使用正则表达式分析或修改文本的过程称为:正则表达式应用于文本/字符串
由正则表达式定义的模式从左到右应用于文本。一旦源字符在匹配中被使用,就不能重复使用。
三:采坑心得
对于这几次的题目集,我所踩的坑明显少于前三次,但是仍然有些坑踩了进去。在类之间的关系上面,我有几次没有办法将主函数的数值传入到其他类的方法里面,导致了运算结果出现了0;
四:改进建议
这几次的题目集比上几次的好,有简单的,也有复杂的,这样就不至于得分很少。但是简单的给分有点少,5分?3分?,我觉得可以增加到10分,这样不会出现难题做不出来,得分就很少的情况。
五:总结
这三次题目集总体来说挺好的,逐渐改进,逐渐变好。课堂上采用了网课的形式,让所有人都可以看清屏幕,上课效率我感觉有了很大的提升。不足的方面也有,比如正则表达式的运用还不是很熟练,部分的方法还没有完全掌握,还需要课下的练习。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号