Ansible-playbook--配置及使用
一、playbook简介
1.1、playbook基础介绍
playbook 是 ansible 用于配置,部署,和管理被控节点的剧本。
通过 playbook 的详细描述,执行其中的一系列 tasks ,可以让远端主机达到预期的状态。playbook 就像 Ansible 控制器给被控节点列出的的一系列 to-do-list ,而被控节点必须要完成
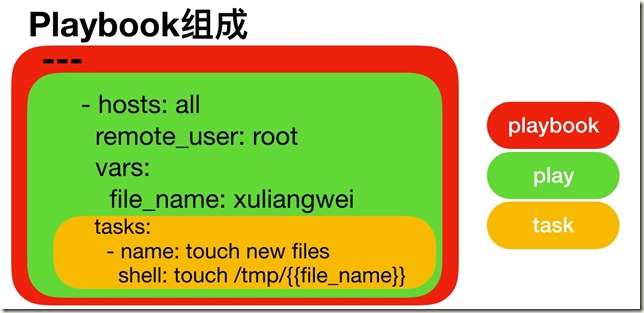
play: 定义的是主机的角色
task: 定义的是具体执行的任务
playbook: 由一个或多个play组成,一个play可以包含多个task任务
1.2、playbook优势
1)功能比ad-hoc更全
2)能很好的控制先后执行顺序, 以及依赖关系
3)语法展现更加的直观
4)ad-hoc无法持久使用,playbook可以持久使用
1.3、playbook语法
采用的语法格式是YAML(Yet Another Markup Language)。YAML语法能够简单的表示散列表,字典等数据结构
1.3.1、yaml语法格式
缩进: YAML使用一个固定的缩进风格表示层级结构,每个缩进由两个空格组成, 不能使用tabs;
冒号: 以冒号结尾的除外,其他所有冒号后面所有必须有空格;
短横线: 表示列表项,使用一个短横杠加一个空格。多个项使用同样的缩进级别作为同一列表;
Ansible-playbook采用YAML语法编写。连续的项目(即列表)用 -减号来表示,key/value(字典)用冒号:分隔。
1)列表:每一个列表成员前面都要有一个短横线和一个空格
fruits:
- Apple
- Orange
- Strawberry
- Mango
或者:
fruits: ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Strawberry', 'Mango']
2)字典:每一个成员由键值对组成,注意冒号后面要有空格
martin:
name: Martin D'vloper
job: Developer
skill: Elite
或者
martin: {name: Martin D'vloper, job: Developer, skill: Elite}
3)列表与字典混合使用
- martin:
name: Martin D'vloper
job: Developer
skills:
- python
- perl
- pascal
- tabitha:
name: Tabitha Bitumen
job: Developer
skills:
- lisp
- fortran
- erlang
1.3.2、playbook语法特性
1)以 --- (三个减号)开始,必须顶行写;
2)次行开始写Playbook的内容,但是一般要求写明该playbook的功能;
3)严格缩进,并且不能用Tab键缩进;
4)缩进级别必须是一致的,同样的缩进代表同样的级别,程序判别配置的级别是通过缩进结合换行来实现的;
5)K/V的值可同行写,也可换行写。同行使用 :分隔,换行写需要以 - 分隔;
1.4、playbook基础组件
Hosts:运行执行任务(task)的目标主机
remote_user:在远程主机上执行任务的用户
tasks:任务列表
handlers:任务,与tasks不同的是只有在接受到通知时才会被触发
templates:使用模板语言的文本文件,使用jinja2语法。
variables:变量,变量替换{{ variable_name }}
1.5、简单示例
[root@localhost ~]# cat httpd.yaml
---
- hosts: control-node #将要执行任务的主机,已经在hosts文件中定义好了,可是单个主机或主机组
remote_user: root #在目标主机上执行任务时的用户身份
vars:
- pkg: httpd
tasks:
- name: "install httpd package."
yum: name={{ pkg }} state=installed
- name: "copy httpd configure file to remote host."
copy: src=/root/conf/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd #当这个任务执行状态发生改变时,触发handlers执行.
- name: "boot httpd service."
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers: #handlers与tasks是同一级别
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
1.6、playbook命令及调用方式
用法:ansible-playbook <filename.yml> ... [options]
<filename.yml>: yaml格式的playbook文件路径,必须指明
[options]: 选项
Options:
--ask-vault-pass
#ask for vault password
#加密playbook文件时提示输入密码
-C, --check
#don't make any changes; instead, try to predict some of the changes that may occur
#模拟执行,不会真正在机器上执行(查看执行会产生什么变化)。即并不在远程主机上执行,只是测试。
-D, --diff
#when changing (small) files and templates, show the differences in those files; works great with --check
#当更新的文件数及内容较少时,该选项可显示这些文件不同的地方,该选项结合-C用会有较好的效果
-e EXTRA_VARS, --extra-vars=EXTRA_VARS
#set additional variables as key=value or YAML/JSON
#在Playbook中引入外部参数变量
--flush-cache
#clear the fact cache
#清理fact缓存,将fact清除到的远程主机缓存
--force-handlers
#run handlers even if a task fails
#强制运行handlers的任务,即使在任务失败的情况下
-f FORKS, --forks=FORKS
#specify number of parallel processes to use(default=5)
#并行任务数。FORKS被指定为一个整数,默认是5
-h, --help
#show this help message and exit
#打开帮助文档API
-i INVENTORY, --inventory-file=INVENTORY
#specify inventory host path (default=/etc/ansible/hosts) or comma separated host list.
#指定要读取的Inventory清单文件
-l SUBSET, --limit=SUBSET
#further limit selected hosts to an additional pattern
#限定执行的主机范围
--list-hosts
#outputs a list of matching hosts; does not execute anything else
#列出执行匹配到的主机,但并不会执行任何动作。
--list-tags
#list all available tags
#列出所有可用的tags
--list-tasks
#list all tasks that would be executed
#列出所有即将被执行的任务
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path=MODULE_PATH
#specify path(s) to module library (default=None)
#要执行的模块的路径
--new-vault-password-file=NEW_VAULT_PASSWORD_FILE
#new vault password file for rekey
#
--output=OUTPUT_FILE
#output file name for encrypt or decrypt; use - for stdout
#
--skip-tags=SKIP_TAGS
#only run plays and tasks whose tags do not match these values
#跳过指定的tags任务
--start-at-task=START_AT_TASK
#start the playbook at the task matching this name
#从第几条任务(START_AT_TASK)开始执行
--step
#one-step-at-a-time: confirm each task before running
#逐步执行Playbook定义的任务,并经人工确认后继续执行下一步任务
--syntax-check
#perform a syntax check on the playbook, but do not execute it
#检查Playbook中的语法书写,并不实际执行
-t TAGS, --tags=TAGS
#only run plays and tasks tagged with these values
#指定执行该tags的任务
--vault-password-file=VAULT_PASSWORD_FILE
#vault password file
#
-v, --verbose
#verbose mode (-vvv for more, -vvvv to enable connection debugging)
#执行详细输出
--version
#show program's version number and exit
#显示版本
############Connection Options,即下面时连接权限############
control as whom and how to connect to hosts
-k, --ask-pass
#ask for connection password
#
--private-key=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE, --key-file=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE
#use this file to authenticate the connection
#
-u REMOTE_USER, --user=REMOTE_USER
#connect as this user (default=None)
#指定远程主机以USERNAME运行命令
-c CONNECTION, --connection=CONNECTION
#connection type to use (default=smart)
#指定连接方式,可用选项paramiko (SSH)、ssh、local,local方式常用于crontab和kickstarts
-T TIMEOUT, --timeout=TIMEOUT
#override the connection timeout in seconds(default=10)
#SSH连接超时时间设定,默认10s
--ssh-common-args=SSH_COMMON_ARGS
#specify common arguments to pass to sftp/scp/ssh (e.g.ProxyCommand)
#
--sftp-extra-args=SFTP_EXTRA_ARGS
#specify extra arguments to pass to sftp only (e.g. -f, -l)
#
--scp-extra-args=SCP_EXTRA_ARGS
#specify extra arguments to pass to scp only (e.g. -l)
#
--ssh-extra-args=SSH_EXTRA_ARGS
#specify extra arguments to pass to ssh only (e.g. -R)
#
############Privilege Escalation Options, 即下面时权限提升权限############
control how and which user you become as on target hosts
-s, --sudo
#run operations with sudo (nopasswd) (deprecated, use become)
#相当于Linux系统下的sudo命令
-U SUDO_USER, --sudo-user=SUDO_USER
#desired sudo user (default=root) (deprecated, use become)
#使用sudo,相当于Linux下的sudo命令
-S, --su
#run operations with su (deprecated, use become)
#
-R SU_USER, --su-user=SU_USER
#run operations with su as this user (default=root)(deprecated, use become)
-b, --become
#run operations with become (does not imply password prompting)
#
--become-method=BECOME_METHOD
#privilege escalation method to use (default=sudo),valid choices: [ sudo | su | pbrun | pfexec | doas |dzdo | ksu | runas ]
#
--become-user=BECOME_USER
#run operations as this user (default=root)
#
--ask-sudo-pass
#ask for sudo password (deprecated, use become)
#传递sudo密码到远程主机,来保证sudo命令的正常运行
--ask-su-pass
#ask for su password (deprecated, use become)
#
-K, --ask-become-pass
#ask for privilege escalation password
#
注意的命令:
1)检查语法,只检查是否是yaml语法格式。并不做逻辑校验。(常使用) # ansible-playbook --syntax-check test.yml 2)模拟执行(不是真的执行) # ansible-playbook -C test.yml
关闭facts
--- - hosts: webserver gather_facts: no
二、playbook组件详解
2.1、variable--变量定义
1)定义在hosts文件中
主机变量: 192.168.200.136 http_port=808 maxRequestsPerChild=808 192.168.200.137 http_port=8080 maxRequestsPerChild=909 主机组变量: [websers] 192.168.200.136 192.168.200.137 [websers:vars] ntp_server=ntp.exampl.com proxy=proxy.exampl.com
2)定义在playbook剧本中
- hosts: all
vars: #定义变量
file_name: yaml_vars
tasks:
- name: # {{ file_name }}引用上面定义的变量
file: path=/tmp/{{ file_name }} state=touch
3)使用facts变量
facts变量是由setup模块获取远程主机的信息。 # ansible 192.168.200.136 -m setup
4)命令行传参
使用 -e或--extra-vars选项传入参数 # ansible-playbook 192.168.200.136 -e "httpd_port=808" httpd04.yml # ansible-playbook f2.yml --extra-vars "file_name=bgx_extra-vars"
5)变量定义优先级
1.extra-vars外置传参的优先级最高 [所有执行的主机都生效]
2.定义在yml文件中的优先级其次 [所有执行的主机都生效]
3.hosts文件中定义的变量优先级最低 [当前主机组定义会生效]
6)变量引用
{{ var_name }}
7)变量注册
注册变量: register关键字可以存储指定命令的输出结果到一个自定义的变量中
[root@Manager playbook]#cat variableRegister.yml
---
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: print status
shell: netstat -lntp
register: System_Status
- name: Get System_Status
debug: msg={{System_Status.stdout_lines}}
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook --syntax-check variableRegister.yml
playbook: variableRegister.yml
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook variableRegister.yml
PLAY [web] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [print status] **************************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [Get System_Status] *********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.165] => {
"msg": [
"Active Internet connections (only servers)",
"Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name ",
"tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:8005 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 31952/java ",
"tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8009 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 31952/java ",
"tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3927/nginx: master ",
"tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 31952/java ",
"tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2812 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17247/sshd ",
"tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:10050 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 18814/zabbix_agentd ",
"tcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 5993/mysqld ",
"tcp6 0 0 :::21 :::* LISTEN 1846/vsftpd "
]
}
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
2.2、templates--模板功能
template只能在palybook中使用。采用了jinga2语法,jinga2基本语法如下:
字面量:
字符串:使用单引号或双引号
数字:整型,浮点数
列表:{item1,item2,...}
字典:{key1:value1,key2:value2,...}
布尔型:true/false
算术运算:
+,-,*,/,//,%,**
比较运算:
==,!=,>,>=,<,<=
逻辑运算:
and,or,not
示例如下:
1)定义模板
[root@server tmp]# mv nginx.conf nginx.conf.j2
[root@server tmp]# vim nginx.conf.j2
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus }};
listen {{ nginxport }};
2)修改剧本,编辑nginx.yml文件

2.3、handlers--任务触发
在需要被监控的任务(tasks)中定义一个notify,只有当这个任务被执行时,才会触发notify对应的handlers去执行相应操作。例如配置文件被修改后,有可能需要重启程序,此时我们可以配置一个handlers,类似触发器。注意:handlers下的name名称必须要和它对应的notify名称相同!否则不会执行!!
[root@localhost ~]# cat httpd.yaml
---
- hosts: control-node
remote_user: root
vars:
- pkg: httpd
tasks:
- name: "install httpd package."
yum: name={{ pkg }} state=installed
- name: "copy httpd configure file to remote host."
copy: src=/root/conf/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd
- name: "boot httpd service."
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
注意事项:
1)handlers只有在其所在的任务被执行完时,它才会被运行;如果一个任务中定义了notify调用Handlers,但由于条件判断等原因,该任务未被执行,则Handlers同样不会被执行。
2)handlers只会在Play的末尾运行一次;如果想在一个Playbook的中间运行handlers,则需要使用meta模块来实现,例如:- meta: flush_handlers。
3)可以直接在Handlers中使用notify选项,实现Handlers调用Handlers。
4)可以使用listen关键字,在一个tasks任务中一次性notify多个handler。即将多个handler分为"一组",使用相同的"组名"即可,当notify对应的值为"组名"时,"组"内的所有handler都会被notify。
5)如果一个Play在运行到调用handlers的语句之前失败了,那么这个handlers将不会被执行。但是可以使用mega模块的--force-handlers选项来强制执行handlers,即使在handlers所在Play中途运行失败也能执行。需要注意:--force-handlers参数主要针对即使playbook执行失败,也要执行代码块成功了的handlers(即执行成功的task任务), 如果代码块本身执行失败(即执行失败的task任务),那么它所对应的handlers应当不会被执行!
6)handlers可以理解成另一种tasks,handlers是另一种"任务列表",可以理解handlers和tasks是"平级关系",所以他们的缩进相同。handlers的任务会被tasks中的任务进行"调用",但是,被"调用"并不意味着一定会执行,只有当tasks中的任务"真正执行"以后,handlers中被调用的任务才会执行,如果tasks中的任务并没有做出任何实际的操作,那么handlers中的任务即使被"调用",也并不会执行。handlers中可以有多个任务,被tasks中不同的任务notify。
使用handlers的场景:
1)headlers在所有tasks任务被执行完时才执行。
[root@Manager playbook]#cat handler1.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: make file task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt state=touch
notify: task1
- name: make file task2
file: path=/tmp/task2.txt state=touch
notify: task2
handlers:
- name: task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt mode=777 owner=root group=root
- name: task2
file: src=/tmp/task2.txt dest=/tmp/heihei state=link force=yes
#执行结果
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook handler1.yml
PLAY [all] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.165]
ok: [172.16.93.167]
TASK [make file task1] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
TASK [make file task2] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task1] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task2] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.16.93.167 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
2)使用meta模块,headlers会在它所对应的task任务执行完后立即被触发并执行,即在playbook的中间环节运行。
[root@Manager playbook]#cat handler2.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: make file task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt state=touch
notify: task1
- meta: flush_handlers #添加
- name: make file task2
file: path=/tmp/task2.txt state=touch
notify: task2
handlers:
- name: task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt mode=777 owner=root group=root
- name: task2
file: src=/tmp/task2.txt dest=/tmp/heihei state=link force=yes
#运行结果
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook handler2.yml
PLAY [all] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.165]
ok: [172.16.93.167]
TASK [make file task1] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
RUNNING HANDLER [task1] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [make file task2] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task2] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.16.93.167 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
3)Handlers调用Handlers
[root@Manager playbook]#cat handler3.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: make file task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt state=touch
notify: task1
- name: make file task2
file: path=/tmp/task2.txt state=touch
handlers:
- name: task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt mode=777 owner=root group=root
notify: task2
- name: task2
file: src=/tmp/task2.txt dest=/tmp/heihei state=link force=yes
#执行结果
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook handler3.yml
PLAY [all] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.165]
ok: [172.16.93.167]
TASK [make file task1] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [make file task2] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task1] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task2] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.16.93.167 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@Manager playbook]#cat handler3-2.yaml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: make file task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt state=touch
notify: task1
handlers:
- name: task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt mode=777 owner=root group=root
notify: task2
- name: task2
file: path=/tmp/task2.txt state=touch
notify: task3
- name: task3
file: src=/tmp/task2.txt dest=/tmp/heihei state=link force=yes
#执行结果
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook handler3-2.yaml
PLAY [all] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.167]
ok: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [make file task1] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task1] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task2] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
RUNNING HANDLER [task3] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
changed: [172.16.93.167]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.16.93.167 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
4)使用listen关键字,在一个tasks任务中一次性notify多个handler
listen的名称要和notify名称保持一致!
[root@Manager playbook]#cat handler4.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: make file task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt state=touch
notify: group_handler
handlers:
- name: task1
listen: group_handler
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt mode=777 owner=root group=root
- name: task2
listen: group_handler
file: path=/tmp/task2.txt state=touch
- name: task3
listen: group_handler
file: src=/tmp/task2.txt dest=/tmp/heihei state=link force=yes
#执行结果
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook handler4.yml
PLAY [all] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.167]
ok: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [make file task1] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
RUNNING HANDLER [task1] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
RUNNING HANDLER [task2] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
RUNNING HANDLER [task3] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.16.93.167 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
5)使用--force-handlers选项来强制执行handlers
--force-handlers参数主要针对即使playbook执行失败,也要执行代码块成功了的handlers(即执行成功的task任务), 如果代码块本身执行失败(即执行失败的task任务),那么它所对应的handlers应当不会被执行!
[root@Manager playbook]#cat handler5.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: make file task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt state=touch
notify: task1
- name: make file task2
file: path=/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt state=touch
notify: task2
handlers:
- name: task1
file: path=/tmp/task1.txt mode=777 owner=root group=root
- name: task2
file: src=/tmp/task2.txt dest=/tmp/heihei state=link force=yes
#执行结果
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook handler5.yml
PLAY [all] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.165]
ok: [172.16.93.167]
TASK [make file task1] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [make file task2] ***********************************************************************************************
fatal: [172.16.93.165]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "msg": "Error, could not touch target: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt'", "path": "/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt"}
fatal: [172.16.93.167]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "msg": "Error, could not touch target: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt'", "path": "/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt"}
RUNNING HANDLER [task1] **********************************************************************************************
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.16.93.167 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
#当没使用--force-handlers,由于目录/tmp/lawrence/不存在,导致task的第二个任务执行失败,这个时候handler根本没有被触发,也就不会执行。即使第一个任务执行成功,但是它对应的第一个handler也不会被执行!!
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#使用--force-handlers选项来强制执行handlers(强制执行的是:成功执行的task对应的handler)
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook handler5.yml --force-handlers
PLAY [all] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.167]
ok: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [make file task1] ***********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [make file task2] ***********************************************************************************************
fatal: [172.16.93.165]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "msg": "Error, could not touch target: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt'", "path": "/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt"}
fatal: [172.16.93.167]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "msg": "Error, could not touch target: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt'", "path": "/tmp/lawrence/task2.txt"}
RUNNING HANDLER [task1] **********************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.167]
changed: [172.16.93.165]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
172.16.93.167 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
6)日常handler应用示例
#playbook安装Apache示例
[root@m01 ~]# cat webserver.yml
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
#1.定义变量,在配置文件中调用
vars:
http_port: 8881
#2.安装httpd服务
tasks:
- name: Install Httpd Server
yum: name=httpd state=present
#3.使用template模板,引用上面vars定义的变量至配置文件中
- name: Configure Httpd Server
template: src=./httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: Restart Httpd Server
#4.启动Httpd服务
- name: Start Httpd Server
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
#5.检查Httpd服务当前的运行的端口状态
- name: Get Httpd Server Port
shell: netstat -lntp|grep httpd
register: Httpd_Port
#6.输出Httpd运行的状态至面板
- name: Out Httpd Server Status
debug: msg={{ Httpd_Port.stdout_lines }}
ignore_errors: yes
#6.如果配置文件发生变化会调用该handlers下面的模块
handlers:
- name: Restart Httpd Server
service: name=httpd state=restarted
2.4、tags--任务标签
tags用于让用户选择运行playbook中的部分代码。ansible具有幂等性,因此会自动跳过没有变化的部分,即便如此,有些代码为测试其确实没有发生变化的时间依然会非常地长。此时如果确信其没有变化,就可以通过tags跳过此些代码片断。tags可以看作是ansible的任务控制
2.4.1、内置tag
always: 除非--skip-tags指定这个标签,否则该标记为always的task一直都会执行。"--tags always"只执行标记了always的tasks;
never: 除非--tags指定了这个标签,否则该标记为never的task一直都不会执行。"--tags never"执行标记了always和never的tasks;
tagged: --tags tagged表示执行所有有tags标签的tasks任务,但不包括tags标签是never的tasks任务;--skip-tags tagged表示所有有tags标签的tasks任务都跳过,即不会执行。
untagged: --tags untagged表示执行所有没有tags标签的tasks任务和tags标签为always的tasks任务;--skip-tags untagged效果相反!
all:--tags all表示执行所有的tags标签为非never的task,包括有tags标签和无tags标签的tasks。
2.4.2、tag相关命令
"--tags 自定义的tag" :表示执行tags为指定的标签名的tasks和tags为always的tasks。如果执行命令ansible-playbook site.yml 时不指定tags,则会执行所有tags为非never的tasks
"--skip-tags 自定义tag" :表示执行所有非指定tag和非never的tasks
2.4.3、tag配置语法
语法一: tags: - tag_test 语法二: tags: tag_test 语法三: tags: ['tag_test'] #---------------------- #一个任务添加多个tags标签的语法仍然也有三种: 语法1: tags: - tag1 - tag2 语法2: tags: tag1,tag2 语法3: tags: ['tag1,tag2']
2.4.4、tags使用场景
1)一个task任务添加一个tags标签
#官方示例如下:
[root@localhost ansible]# vim example.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- yum: name={{ item }} state=installed
with_items:
- httpd
- memcached
tags:
- packages
- template: src=templates/src.j2 dest=/etc/foo.conf
tags:
- configuration
#运行
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --tags "configuration,packages"
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --tags configuration
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --tags packages
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --tags="configuration,packages"
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --tags=configuration
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --tags=packages
#使用--skip-tags跳过某个task任务
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --skip-tags configuration
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook example.yml --skip-tags=configuration
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@localhost ansible]# cat haha.yaml
---
- hosts: test_host
remote_user: root
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: task1
file: path=/opt/task1.txt state=touch
tags: make_task1
- name: task2
file: path=/opt/task2.txt state=touch
tags:
- make_task2
- name: task3
file: path=/opt/task2.txt src=/opt/task2.txt dest=/opt/heihei state=link force=yes
tags: ['link_task3']
2)一个task任务添加多个tags标签。
[root@localhost ansible]# vim https.yml
---
- hosts: test_host
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
tags:
- httpd
- package
yum:
name=httpd
state=latest
- name: start up httpd service
tags: httpd,service
service:
name: httpd
state: started
3)tags和include结合使用
通过指定标签(tags),来说明是安装tomcat7还是tomcat8
tomcat.yml文件:
--- - include: install_tomcat7.yml tags: tomcat7 - include: install_tomcat8.yml tags: tomcat8
install_tomcat7.yml文件:
---
- name: "复制文件到远程主机"
copy:
src={{ item.src }}
dest={{ item.dest }}
with_items:
- src: jdk-7u79-linux-x64.rpm
dest: /usr/local/src/
- src: java17.sh
dest: /etc/profile.d/
- name: "安装jdk"
yum:
name: /usr/local/src/jdk-7u79-linux-x64.rpm
state: present
- name: "重新加载环境变量"
shell: "source /etc/profile.d/java17.sh"
- name: "复制tomcat文件到远程服务器并解压"
unarchive:
src=apache-tomcat-7.0.64.zip
dest=/data/
copy=yes
owner=staplesapp
group=admin
- name: "对解压后的文件重命名"
shell: mv /data/apache-tomcat-7.0.64 /data/tomcat7
- name: "对tomcat进行相关配置"
shell: find /data/tomcat7/bin -name "*.sh" | xargs chmod +x
- name: "启动tomcat"
shell: 'nohup /data/tomcat7/bin/startup.sh &'
install_tomcat8.yml文件:
---
- name: "复制文件到远程主机"
copy:
src={{ item.src }}
dest={{ item.dest }}
with_items:
- src: jdk-8u111-linux-x64.rpm
dest: /usr/local/src/
- src: java18.sh
dest: /etc/profile.d/
- name: "安装jdk"
yum:
name: /usr/local/src/jdk-8u111-linux-x64.rpm
state: present
- name: "配置java环境变量"
shell: "source /etc/profile.d/java18.sh"
- name: "安装tomcat"
unarchive:
src=apache-tomcat-8.0.30.tar.gz
dest=/data/
copy=yes
owner=staplesapp
group=admin
- name: "对解压后的文件重命名"
shell: mv /data/apache-tomcat-8.0.30 /data/tomcat8
- name: "启动tomcat"
shell: 'nohup /data/tomcat8/bin/startup.sh &'
执行命令:
安装tomcat7: [root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook tomcat.yml --tags tomcat7 安装tomcat8: [root@localhost ansible]# ansible-playbook tomcat.yml --tags tomcat8
特别注意:在ansible2.8版本之后将会删除include语法,更改为import_playbook
[root@localhost ansible]# cat tomcat.yml --- - import_playbook: install_tomcat7.yml tags: tomcat7 - import_playbook: install_tomcat8.yml tags: tomcat8
2.5、include用法
如果想在playbook中重复使用任务列表,则可以使用include文件来执行此操作。ansible2.8版本之后include语法变成了import_playbook。如果还是使用include,则不会影响执行结果,只不过是有告警信息
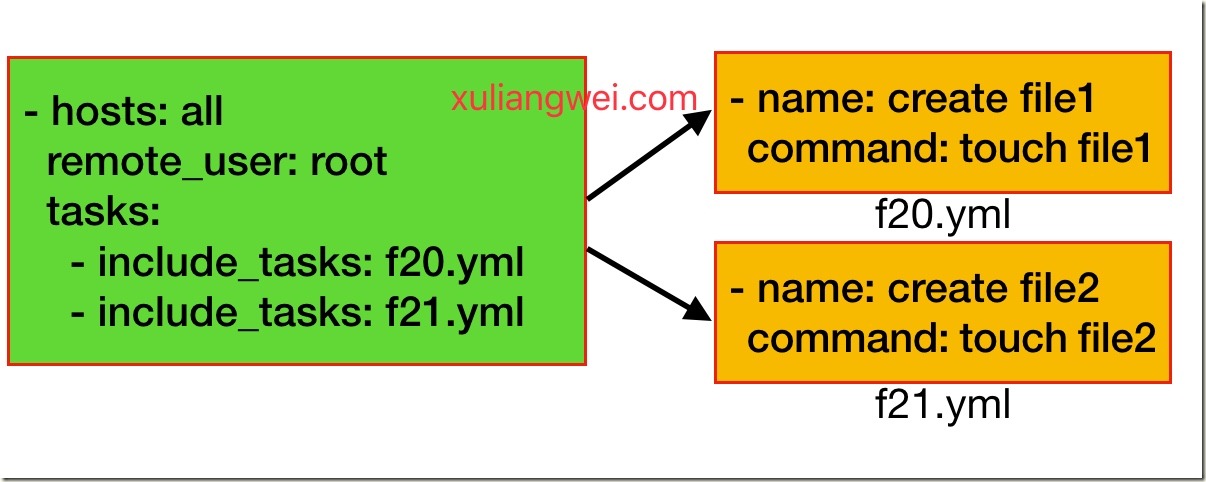
include用来动态的包含tasks任务列表,include_tasks新版/include老版
#主入口文件
[root@mha ~]# cat main.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- include_tasks: f20.yml
- include_tasks: f21.yml
#f20.yml
[root@mha ~]# cat f20.yml
- name: create file1
command: touch file1
#21.yml
[root@mha ~]# cat f21.yml
- name: create file2
command: touch file2
2.6、when--条件语句
[root@manager ~]# cat f6.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Create File
file: path=/tmp/this_is_{{ ansible_hostname }}_file state=touch
when: (ansible_hostname == "nfs") or (ansible_hostname == "backup")
#系统为centos的主机才会执行
- name: Centos Install httpd
yum: name=httpd state=present
when: (ansible_distribution == "CentOS")
#系统为ubuntu的主机才会执行
- name: Ubuntu Install httpd
yum: name=httpd2 state=present
when: (ansible_distribution == "Ubuntu")
2.7、with_items--循环语句
1)批量安装软件
[root@manager ~]# cat f7.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Installed Pkg
yum: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- wget
- tree
- lrzsz
2)批量创建用户
[root@manager ~]# cat f7.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Add Users
user: name={{ item.name }} groups={{ item.groups }} state=present
with_items:
- { name: 'testuser1', groups: 'bin' }
- { name: 'testuser2', groups: 'root' }
3)批量文件拷贝
[root@manager ~]# cat f7.yml
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Configure Rsync Server
copy: src={{ item.src }} dest=/etc/{{ item.dest }} mode={{ item.mode }}
with_items:
- {src: "rsyncd.conf", dest: "rsyncd.conf", mode: "0644"}
- {src: "rsync.passwd", dest: "rsync.passwd", mode: "0600"}
2.8、异常处理
默认Playbook会检查命令和模块的返回状态,如遇到错误就中断playbook的执行
加入参数: ignore_errors: yes 忽略错误
[root@Manager playbook]#cat ErrorIgnore.yml
---
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Ignore False
command: /bin/false
ignore_errors: yes
- name: touch new file
file: path=/tmp/ignore.txt state=touch
[root@Manager playbook]#ansible-playbook ErrorIgnore.yml
PLAY [web] ***********************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************
ok: [172.16.93.165]
TASK [Ignore False] **************************************************************************************************
fatal: [172.16.93.165]: FAILED! => {"changed": true, "cmd": ["/bin/false"], "delta": "0:00:00.043922", "end": "2020-01-09 17:15:34.985067", "msg": "non-zero return code", "rc": 1, "start": "2020-01-09 17:15:34.941145", "stderr": "", "stderr_lines": [], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []}
...ignoring
TASK [touch new file] ************************************************************************************************
changed: [172.16.93.165]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************
172.16.93.165 : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=1
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:独学而无友,则孤陋而寡闻。做一个灵魂有趣的人!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号