redis持久化
1.RDB
通过快照的方式保存数据库数据到磁盘中
1.1通过配置文件设置保存目录自动触发
redis.conf关于保存数据的触发方式
################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################ # Save the DB to disk. # # save <seconds> <changes> [<seconds> <changes> ...] # # Redis will save the DB if the given number of seconds elapsed and it # surpassed the given number of write operations against the DB. # # Snapshotting can be completely disabled with a single empty string argument # as in following example: # # save "" # # Unless specified otherwise, by default Redis will save the DB: # * After 3600 seconds (an hour) if at least 1 change was performed # * After 300 seconds (5 minutes) if at least 100 changes were performed # * After 60 seconds if at least 10000 changes were performed # # You can set these explicitly by uncommenting the following line. # # save 3600 1 300 100 60 10000
save 后参数的含义是指每过多少秒钟数据发生多少次变化就触发RDB数据库保存
比如:
save 3600 1 每过3600秒至少触发一次数据变化就生成rdb文件
save 300 100 每过300秒至少触发100次数据变化就生成rdb文件
save 60 10000 每过60秒至少触发10000次数据变化就生成rdb文件
# Enables or disables full sanitization checks for ziplist and listpack etc when # loading an RDB or RESTORE payload. This reduces the chances of a assertion or # crash later on while processing commands. # Options: # no - Never perform full sanitization # yes - Always perform full sanitization # clients - Perform full sanitization only for user connections. # Excludes: RDB files, RESTORE commands received from the master # connection, and client connections which have the # skip-sanitize-payload ACL flag. # The default should be 'clients' but since it currently affects cluster # resharding via MIGRATE, it is temporarily set to 'no' by default. # # sanitize-dump-payload no # The filename where to dump the DB dbfilename dump.rdb # Remove RDB files used by replication in instances without persistence # enabled. By default this option is disabled, however there are environments # where for regulations or other security concerns, RDB files persisted on # disk by masters in order to feed replicas, or stored on disk by replicas # in order to load them for the initial synchronization, should be deleted # ASAP. Note that this option ONLY WORKS in instances that have both AOF # and RDB persistence disabled, otherwise is completely ignored. # # An alternative (and sometimes better) way to obtain the same effect is # to use diskless replication on both master and replicas instances. However # in the case of replicas, diskless is not always an option. rdb-del-sync-files no # The working directory. # # The DB will be written inside this directory, with the filename specified # above using the 'dbfilename' configuration directive. # # The Append Only File will also be created inside this directory. # # Note that you must specify a directory here, not a file name. dir ./
dirname 持久化生成的rdb文件名
dir 文件保存的目录
1.2.手动触发
redis命令save和bgsave
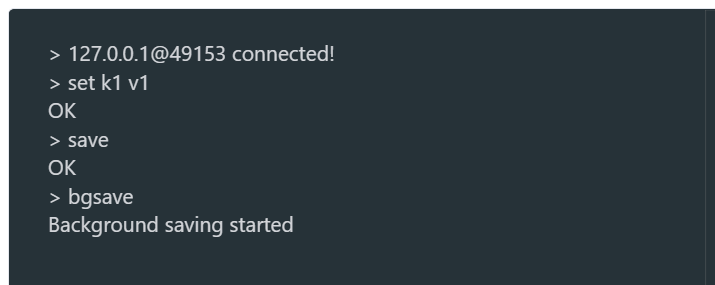
bgsave 在后台保存数据,不会阻塞
save为同步方式会造成阻塞,生产环境禁用!!!
1.3.RDB优化配置项
stop-writes-on-bagssave-error
默认yes
如果配置程no,表示你不在乎数据不一致或者有其他手段发现和控制这种不一致,在快照写入失败时,也能确保redis继续接收新的写请求(后台的bagsave出现error时候是否继续接收新的写请求)
rdbcompression
默认yes
对于存贮在磁盘中的快照,可以设置会后进行压缩存储
rdbchecksum
默认yes
在存储快照后,还可以让redis使用CRC64算法进行数据校验,如果希望胡渠道最大的性能提升,可以关闭此功能
rdb-del-sync-files
在没有持久性的情况下删除复制中使用的RDB文件启用,默认情况为no,此选项禁用
2.aof
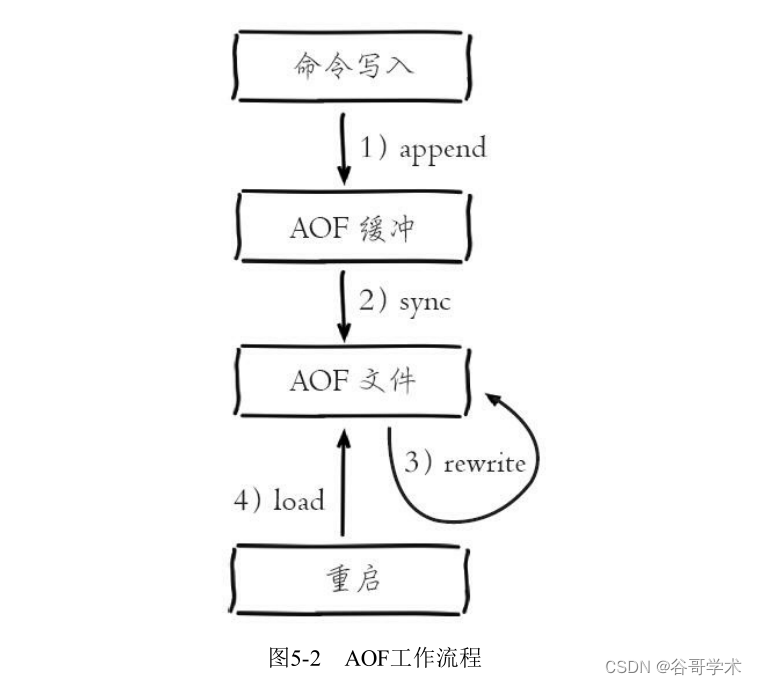
通过将redis命令写入磁盘的方式,实现数据的持久化
2.1 aof的配置
# By default Redis asynchronously dumps the dataset on disk. This mode is # good enough in many applications, but an issue with the Redis process or # a power outage may result into a few minutes of writes lost (depending on # the configured save points). # # The Append Only File is an alternative persistence mode that provides # much better durability. For instance using the default data fsync policy # (see later in the config file) Redis can lose just one second of writes in a # dramatic event like a server power outage, or a single write if something # wrong with the Redis process itself happens, but the operating system is # still running correctly. # # AOF and RDB persistence can be enabled at the same time without problems. # If the AOF is enabled on startup Redis will load the AOF, that is the file # with the better durability guarantees. # # Please check https://redis.io/topics/persistence for more information. appendonly yes
appendonly 默认为no,yes表示开始aof
# The base name of the append only file. # # Redis 7 and newer use a set of append-only files to persist the dataset # and changes applied to it. There are two basic types of files in use: # # - Base files, which are a snapshot representing the complete state of the # dataset at the time the file was created. Base files can be either in # the form of RDB (binary serialized) or AOF (textual commands). # - Incremental files, which contain additional commands that were applied # to the dataset following the previous file. # # In addition, manifest files are used to track the files and the order in # which they were created and should be applied. # # Append-only file names are created by Redis following a specific pattern. # The file name's prefix is based on the 'appendfilename' configuration # parameter, followed by additional information about the sequence and type. # # For example, if appendfilename is set to appendonly.aof, the following file # names could be derived: # # - appendonly.aof.1.base.rdb as a base file. # - appendonly.aof.1.incr.aof, appendonly.aof.2.incr.aof as incremental files. # - appendonly.aof.manifest as a manifest file. appendfilename "appendonly.aof" # For convenience, Redis stores all persistent append-only files in a dedicated # directory. The name of the directory is determined by the appenddirname # configuration parameter. appenddirname "appendonlydir"
appendfilename aof文件的文件名
appenddirname redis7.0之后才有的新参数,在dir参数的目录下,aof文件所在的路径名
# The fsync() call tells the Operating System to actually write data on disk # instead of waiting for more data in the output buffer. Some OS will really flush # data on disk, some other OS will just try to do it ASAP. # # Redis supports three different modes: # # no: don't fsync, just let the OS flush the data when it wants. Faster. # always: fsync after every write to the append only log. Slow, Safest. # everysec: fsync only one time every second. Compromise. # # The default is "everysec", as that's usually the right compromise between # speed and data safety. It's up to you to understand if you can relax this to # "no" that will let the operating system flush the output buffer when # it wants, for better performances (but if you can live with the idea of # some data loss consider the default persistence mode that's snapshotting), # or on the contrary, use "always" that's very slow but a bit safer than # everysec. # # More details please check the following article: # http://antirez.com/post/redis-persistence-demystified.html # # If unsure, use "everysec". # appendfsync always appendfsync everysec # appendfsync no
appendfsync aof的触发策略
always 只要有命令执行就触发
everysec 每秒触发
no 不触发
2.1 手动触发aof
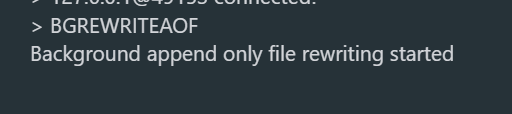
redis在同时开启RDB和AOF的情况,两种持久化方式的优先级关系


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号