生产者和消费者
生产者和消费者
1、分析
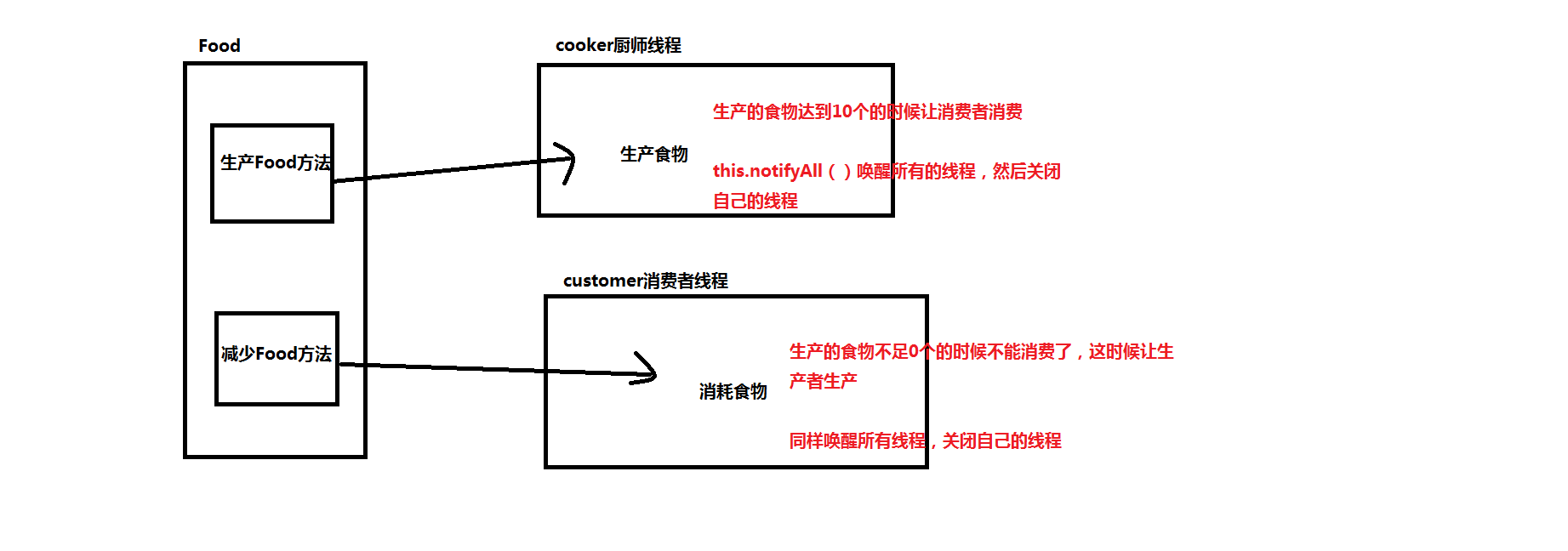
1、我们有一个共用的食物类
2、厨师可以生产这个食物
3、消费者可以消费食物
4、有食物,才能消费,所以消费的前提是食物数量比0大
5、没有食物,那就要生产,但是上限为10个,生产了10个就达到上限,不生产了
2、案例
Food食物类
public class Food {
private int count = 0;
private final int capacity = 10;
public synchronized void produceFood() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("---------");
if(count < capacity) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
System.out.println("生产了食物,现在食物有:" + count);
this.notifyAll();
} else {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public synchronized void customeFood() {
while (true) {
if(count > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
count--;
System.out.println("食物消费成功,剩余食物为:" + count);
this.notifyAll();
} else {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
Cooker类
public class Cooker implements Runnable {
private Food f;
public Cooker() {}
public Cooker(Food f) {
this.f = f;
}
@Override
public void run() {
cook();
}
public void cook() {
f.produceFood();
}
}
Customer类
public class Customer implements Runnable {
private Food f;
public Customer() {}
public Customer(Food f) {
this.f = f;
}
@Override
public void run() {
custom();
}
public void custom() {
f.customeFood();
}
}
测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Food f = new Food();
Cooker cooker = new Cooker(f);
Customer customer = new Customer(f);
new Thread(cooker).start();
new Thread(customer).start();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号