Q2Day81
在编写爬虫时,性能的消耗主要在IO请求中,当单进程单线程模式下请求URL时必然会引起等待,从而使得请求整体变慢。
同步执行
import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com'] for url in url_list: fetch_async(url) 1.同步执行
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com'] pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(5) for url in url_list: pool.submit(fetch_async, url) pool.shutdown(wait=True) 2.多线程执行
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response def callback(future): print(future.result()) url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com'] pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(5) for url in url_list: v = pool.submit(fetch_async, url) v.add_done_callback(callback) pool.shutdown(wait=True) 2.多线程+回调函数执行
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com'] pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(5) for url in url_list: pool.submit(fetch_async, url) pool.shutdown(wait=True) 3.多进程执行
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response def callback(future): print(future.result()) url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com'] pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(5) for url in url_list: v = pool.submit(fetch_async, url) v.add_done_callback(callback) pool.shutdown(wait=True) 3.多进程+回调
import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def func1(): print('before...func1......') yield from asyncio.sleep(5) print('end...func1......') tasks = [func1(), func1()] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close() 1.asyncio示例1
import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(host, url='/'): print(host, url) reader, writer = yield from asyncio.open_connection(host, 80) request_header_content = """GET %s HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n""" % (url, host,) request_header_content = bytes(request_header_content, encoding='utf-8') writer.write(request_header_content) yield from writer.drain() text = yield from reader.read() print(host, url, text) writer.close() tasks = [ fetch_async('www.cnblogs.com', '/wupeiqi/'), fetch_async('dig.chouti.com', '/pic/show?nid=4073644713430508&lid=10273091') ] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() results = loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close() 1.asyncio示例2
import aiohttp import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(url): print(url) response = yield from aiohttp.request('GET', url) # data = yield from response.read() # print(url, data) print(url, response) response.close() tasks = [fetch_async('http://www.google.com/'), fetch_async('http://www.chouti.com/')] event_loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() results = event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) event_loop.close() 2.asyncio + aiohttp
import asyncio import requests @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(func, *args): loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() future = loop.run_in_executor(None, func, *args) response = yield from future print(response.url, response.content) tasks = [ fetch_async(requests.get, 'http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/'), fetch_async(requests.get, 'http://dig.chouti.com/pic/show?nid=4073644713430508&lid=10273091') ] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() results = loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close() 3.asyncio + requests
import gevent import requests from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all() def fetch_async(method, url, req_kwargs): print(method, url, req_kwargs) response = requests.request(method=method, url=url, **req_kwargs) print(response.url, response.content) # ##### 发送请求 ##### gevent.joinall([ gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.python.org/', req_kwargs={}), gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.yahoo.com/', req_kwargs={}), gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://github.com/', req_kwargs={}), ]) # ##### 发送请求(协程池控制最大协程数量) ##### # from gevent.pool import Pool # pool = Pool(None) # gevent.joinall([ # pool.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.python.org/', req_kwargs={}), # pool.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.yahoo.com/', req_kwargs={}), # pool.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.github.com/', req_kwargs={}), # ]) 4.gevent + requests
import grequests request_list = [ grequests.get('http://httpbin.org/delay/1', timeout=0.001), grequests.get('http://fakedomain/'), grequests.get('http://httpbin.org/status/500') ] # ##### 执行并获取响应列表 ##### # response_list = grequests.map(request_list) # print(response_list) # ##### 执行并获取响应列表(处理异常) ##### # def exception_handler(request, exception): # print(request,exception) # print("Request failed") # response_list = grequests.map(request_list, exception_handler=exception_handler) # print(response_list) 5.grequests
from twisted.web.client import getPage from twisted.internet import reactor REV_COUNTER = 0 REQ_COUNTER = 0 def callback(contents): print(contents,) global REV_COUNTER REV_COUNTER += 1 if REV_COUNTER == REQ_COUNTER: reactor.stop() url_list = ['http://www.bing.com', 'http://www.baidu.com', ] REQ_COUNTER = len(url_list) for url in url_list: deferred = getPage(bytes(url, encoding='utf8')) deferred.addCallback(callback) reactor.run() 6.Twisted示例1
from twisted.web.client import getPage from twisted.internet import reactor class TwistedRequest(object): def __init__(self): self.__req_counter = 0 self.__rev_counter = 0 def __execute(self, content, url, callback): if callback: callback(url, content) self.__rev_counter += 1 if self.__rev_counter == self.__req_counter: reactor.stop() def fetch_url(self, url_callback_list): self.__req_counter = len(url_callback_list) for item in url_callback_list: url = item['url'] success_callback = item['success_callback'] error_callback = item['error_callback'] deferred = getPage(bytes(url, encoding='utf8')) deferred.addCallback(self.__execute, url, success_callback) deferred.addErrback(self.__execute, url, error_callback) reactor.run() def callback(url, content): print(url, content) def error(url, content): print(url, content) obj = TwistedRequest() obj.fetch_url([ {'url': 'http://www.baidu.com', 'success_callback': callback, 'error_callback': error}, {'url': 'http://www.google.com', 'success_callback': callback, 'error_callback': error}, ]) 6.Twisted示例2
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from tornado.httpclient import AsyncHTTPClient from tornado.httpclient import HTTPRequest from tornado import ioloop def handle_response(response): if response.error: print("Error:", response.error) else: print(response.body) # 方法同twisted # ioloop.IOLoop.current().stop() def func(): url_list = [ 'http://www.google.com', 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/test2/', ] for url in url_list: print(url) http_client = AsyncHTTPClient() http_client.fetch(HTTPRequest(url), handle_response) ioloop.IOLoop.current().add_callback(func) ioloop.IOLoop.current().start() 7.tornado
import select import socket import time class AsyncTimeoutException(TimeoutError): """ 请求超时异常类 """ def __init__(self, msg): self.msg = msg super(AsyncTimeoutException, self).__init__(msg) class HttpContext(object): """封装请求和相应的基本数据""" def __init__(self, sock, host, port, method, url, data, callback, timeout=5): """ sock: 请求的客户端socket对象 host: 请求的主机名 port: 请求的端口 port: 请求的端口 method: 请求方式 url: 请求的URL data: 请求时请求体中的数据 callback: 请求完成后的回调函数 timeout: 请求的超时时间 """ self.sock = sock self.callback = callback self.host = host self.port = port self.method = method self.url = url self.data = data self.timeout = timeout self.__start_time = time.time() self.__buffer = [] def is_timeout(self): """当前请求是否已经超时""" current_time = time.time() if (self.__start_time + self.timeout) < current_time: return True def fileno(self): """请求sockect对象的文件描述符,用于select监听""" return self.sock.fileno() def write(self, data): """在buffer中写入响应内容""" self.__buffer.append(data) def finish(self, exc=None): """在buffer中写入响应内容完成,执行请求的回调函数""" if not exc: response = b''.join(self.__buffer) self.callback(self, response, exc) else: self.callback(self, None, exc) def send_request_data(self): content = """%s %s HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n%s""" % ( self.method.upper(), self.url, self.host, self.data,) return content.encode(encoding='utf8') class AsyncRequest(object): def __init__(self): self.fds = [] self.connections = [] def add_request(self, host, port, method, url, data, callback, timeout): """创建一个要请求""" client = socket.socket() client.setblocking(False) try: client.connect((host, port)) except BlockingIOError as e: pass # print('已经向远程发送连接的请求') req = HttpContext(client, host, port, method, url, data, callback, timeout) self.connections.append(req) self.fds.append(req) def check_conn_timeout(self): """检查所有的请求,是否有已经连接超时,如果有则终止""" timeout_list = [] for context in self.connections: if context.is_timeout(): timeout_list.append(context) for context in timeout_list: context.finish(AsyncTimeoutException('请求超时')) self.fds.remove(context) self.connections.remove(context) def running(self): """事件循环,用于检测请求的socket是否已经就绪,从而执行相关操作""" while True: r, w, e = select.select(self.fds, self.connections, self.fds, 0.05) if not self.fds: return for context in r: sock = context.sock while True: try: data = sock.recv(8096) if not data: self.fds.remove(context) context.finish() break else: context.write(data) except BlockingIOError as e: break except TimeoutError as e: self.fds.remove(context) self.connections.remove(context) context.finish(e) break for context in w: # 已经连接成功远程服务器,开始向远程发送请求数据 if context in self.fds: data = context.send_request_data() context.sock.sendall(data) self.connections.remove(context) self.check_conn_timeout() if __name__ == '__main__': def callback_func(context, response, ex): """ :param context: HttpContext对象,内部封装了请求相关信息 :param response: 请求响应内容 :param ex: 是否出现异常(如果有异常则值为异常对象;否则值为None) :return: """ print(context, response, ex) obj = AsyncRequest() url_list = [ {'host': 'www.google.com', 'port': 80, 'method': 'GET', 'url': '/', 'data': '', 'timeout': 5, 'callback': callback_func}, {'host': 'www.baidu.com', 'port': 80, 'method': 'GET', 'url': '/', 'data': '', 'timeout': 5, 'callback': callback_func}, {'host': 'www.bing.com', 'port': 80, 'method': 'GET', 'url': '/', 'data': '', 'timeout': 5, 'callback': callback_func}, ] for item in url_list: print(item) obj.add_request(**item) obj.running() 史上最牛逼的异步IO模块
Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架。 其可以应用在数据挖掘,信息处理或存储历史数据等一系列的程序中。
其最初是为了页面抓取 (更确切来说, 网络抓取 )所设计的, 也可以应用在获取API所返回的数据(例如 Amazon Associates Web Services ) 或者通用的网络爬虫。Scrapy用途广泛,可以用于数据挖掘、监测和自动化测试。
Scrapy 使用了 Twisted异步网络库来处理网络通讯。整体架构大致如下
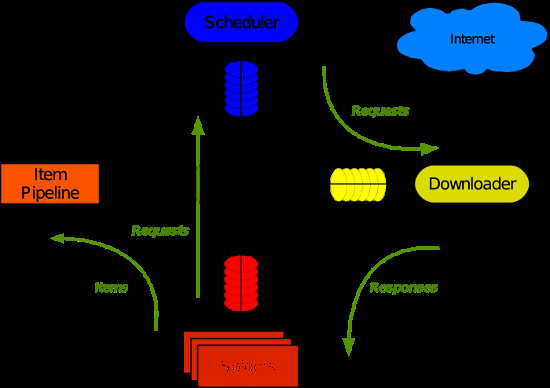
Scrapy主要包括了以下组件: •引擎(Scrapy) 用来处理整个系统的数据流处理, 触发事务(框架核心) •调度器(Scheduler) 用来接受引擎发过来的请求, 压入队列中, 并在引擎再次请求的时候返回. 可以想像成一个URL(抓取网页的网址或者说是链接)的优先队列, 由它来决定下一个要抓取的网址是什么, 同时去除重复的网址 •下载器(Downloader) 用于下载网页内容, 并将网页内容返回给蜘蛛(Scrapy下载器是建立在twisted这个高效的异步模型上的) •爬虫(Spiders) 爬虫是主要干活的, 用于从特定的网页中提取自己需要的信息, 即所谓的实体(Item)。用户也可以从中提取出链接,让Scrapy继续抓取下一个页面 •项目管道(Pipeline) 负责处理爬虫从网页中抽取的实体,主要的功能是持久化实体、验证实体的有效性、清除不需要的信息。当页面被爬虫解析后,将被发送到项目管道,并经过几个特定的次序处理数据。 •下载器中间件(Downloader Middlewares) 位于Scrapy引擎和下载器之间的框架,主要是处理Scrapy引擎与下载器之间的请求及响应。 •爬虫中间件(Spider Middlewares) 介于Scrapy引擎和爬虫之间的框架,主要工作是处理蜘蛛的响应输入和请求输出。 •调度中间件(Scheduler Middewares) 介于Scrapy引擎和调度之间的中间件,从Scrapy引擎发送到调度的请求和响应。 Scrapy运行流程大概如下: 1.引擎从调度器中取出一个链接(URL)用于接下来的抓取 2.引擎把URL封装成一个请求(Request)传给下载器 3.下载器把资源下载下来,并封装成应答包(Response) 4.爬虫解析Response 5.解析出实体(Item),则交给实体管道进行进一步的处理 6.解析出的是链接(URL),则把URL交给调度器等待抓取
一、安装 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Linux pip3 install scrapy Windows a. pip3 install wheel b. 下载twisted http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#twisted c. 进入下载目录,执行 pip3 install Twisted‑17.1.0‑cp35‑cp35m‑win_amd64.whl d. pip3 install scrapy e. 下载并安装pywin32:https://sourceforge.net/projects/pywin32/files/
二、基本使用 1. 基本命令 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 1. scrapy startproject 项目名称 - 在当前目录中创建中创建一个项目文件(类似于Django) 2. scrapy genspider [-t template] <name> <domain> - 创建爬虫应用 如: scrapy gensipider -t basic oldboy oldboy.com scrapy gensipider -t xmlfeed autohome autohome.com.cn PS: 查看所有命令:scrapy gensipider -l 查看模板命令:scrapy gensipider -d 模板名称 3. scrapy list - 展示爬虫应用列表 4. scrapy crawl 爬虫应用名称 - 运行单独爬虫应用
2.项目结构以及爬虫应用简介
project_name/ scrapy.cfg project_name/ __init__.py items.py pipelines.py settings.py spiders/ __init__.py 爬虫1.py 爬虫2.py 爬虫3.py
文件说明:
•scrapy.cfg 项目的主配置信息。(真正爬虫相关的配置信息在settings.py文件中)
•items.py 设置数据存储模板,用于结构化数据,如:Django的Model
•pipelines 数据处理行为,如:一般结构化的数据持久化
•settings.py 配置文件,如:递归的层数、并发数,延迟下载等
•spiders 爬虫目录,如:创建文件,编写爬虫规则
import scrapy class XiaoHuarSpider(scrapy.spiders.Spider): name = "xiaohuar" # 爬虫名称 ***** allowed_domains = ["xiaohuar.com"] # 允许的域名 start_urls = [ "http://www.xiaohuar.com/hua/", # 其实URL ] def parse(self, response): # 访问起始URL并获取结果后的回调函数 爬虫1.py
3. 小试牛刀
import scrapy from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http.request import Request class DigSpider(scrapy.Spider): # 爬虫应用的名称,通过此名称启动爬虫命令 name = "dig" # 允许的域名 allowed_domains = ["chouti.com"] # 起始URL start_urls = [ 'http://dig.chouti.com/', ] has_request_set = {} def parse(self, response): print(response.url) hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response) page_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="dig_lcpage"]//a[re:test(@href, "/all/hot/recent/\d+")]/@href').extract() for page in page_list: page_url = 'http://dig.chouti.com%s' % page key = self.md5(page_url) if key in self.has_request_set: pass else: self.has_request_set[key] = page_url obj = Request(url=page_url, method='GET', callback=self.parse) yield obj @staticmethod def md5(val): import hashlib ha = hashlib.md5() ha.update(bytes(val, encoding='utf-8')) key = ha.hexdigest() return key
执行此爬虫文件,则在终端进入项目目录执行如下命令:
scrapy crawl dig --nolog
对于上述代码重要之处在于:
- Request是一个封装用户请求的类,在回调函数中yield该对象表示继续访问
- HtmlXpathSelector用于结构化HTML代码并提供选择器功能
-
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- from scrapy.selector import Selector, HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse html = """<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <ul> <li class="item-"><a id='i1' href="link.html">first item</a></li> <li class="item-0"><a id='i2' href="llink.html">first item</a></li> <li class="item-1"><a href="llink2.html">second item<span>vv</span></a></li> </ul> <div><a href="llink2.html">second item</a></div> </body> </html> """ response = HtmlResponse(url='http://example.com', body=html,encoding='utf-8') # hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response) # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[2]') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id]') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id="i1"]') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@href="link.html"][@id="i1"]') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[contains(@href, "link")]') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[starts-with(@href, "link")]') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]') # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/text()').extract() # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/@href').extract() # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('/html/body/ul/li/a/@href').extract() # print(hxs) # hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li/a/@href').extract_first() # print(hxs) # ul_list = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li') # for item in ul_list: # v = item.xpath('./a/span') # # 或 # # v = item.xpath('a/span') # # 或 # # v = item.xpath('*/a/span') # print(v)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scrapy from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http.request import Request from scrapy.http.cookies import CookieJar from scrapy import FormRequest class ChouTiSpider(scrapy.Spider): # 爬虫应用的名称,通过此名称启动爬虫命令 name = "chouti" # 允许的域名 allowed_domains = ["chouti.com"] cookie_dict = {} has_request_set = {} def start_requests(self): url = 'http://dig.chouti.com/' # return [Request(url=url, callback=self.login)] yield Request(url=url, callback=self.login) def login(self, response): cookie_jar = CookieJar() cookie_jar.extract_cookies(response, response.request) for k, v in cookie_jar._cookies.items(): for i, j in v.items(): for m, n in j.items(): self.cookie_dict[m] = n.value req = Request( url='http://dig.chouti.com/login', method='POST', headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'}, body='phone=8615131255089&password=pppppppp&oneMonth=1', cookies=self.cookie_dict, callback=self.check_login ) yield req def check_login(self, response): req = Request( url='http://dig.chouti.com/', method='GET', callback=self.show, cookies=self.cookie_dict, dont_filter=True ) yield req def show(self, response): # print(response) hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response) news_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="content-list"]/div[@class="item"]') for new in news_list: # temp = new.xpath('div/div[@class="part2"]/@share-linkid').extract() link_id = new.xpath('*/div[@class="part2"]/@share-linkid').extract_first() yield Request( url='http://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=%s' %(link_id,), method='POST', cookies=self.cookie_dict, callback=self.do_favor ) page_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="dig_lcpage"]//a[re:test(@href, "/all/hot/recent/\d+")]/@href').extract() for page in page_list: page_url = 'http://dig.chouti.com%s' % page import hashlib hash = hashlib.md5() hash.update(bytes(page_url,encoding='utf-8')) key = hash.hexdigest() if key in self.has_request_set: pass else: self.has_request_set[key] = page_url yield Request( url=page_url, method='GET', callback=self.show ) def do_favor(self, response): print(response.text) 示例:自动登陆抽屉并点赞
5. 格式化处理
上述实例只是简单的处理,所以在parse方法中直接处理。如果对于想要获取更多的数据处理,则可以利用Scrapy的items将数据格式化,然后统一交由pipelines来处理。 -
import scrapy from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector from scrapy.http.request import Request from scrapy.http.cookies import CookieJar from scrapy import FormRequest class XiaoHuarSpider(scrapy.Spider): # 爬虫应用的名称,通过此名称启动爬虫命令 name = "xiaohuar" # 允许的域名 allowed_domains = ["xiaohuar.com"] start_urls = [ "http://www.xiaohuar.com/list-1-1.html", ] # custom_settings = { # 'ITEM_PIPELINES':{ # 'spider1.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 100 # } # } has_request_set = {} def parse(self, response): # 分析页面 # 找到页面中符合规则的内容(校花图片),保存 # 找到所有的a标签,再访问其他a标签,一层一层的搞下去 hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response) items = hxs.select('//div[@class="item_list infinite_scroll"]/div') for item in items: src = item.select('.//div[@class="img"]/a/img/@src').extract_first() name = item.select('.//div[@class="img"]/span/text()').extract_first() school = item.select('.//div[@class="img"]/div[@class="btns"]/a/text()').extract_first() url = "http://www.xiaohuar.com%s" % src from ..items import XiaoHuarItem obj = XiaoHuarItem(name=name, school=school, url=url) yield obj urls = hxs.select('//a[re:test(@href, "http://www.xiaohuar.com/list-1-\d+.html")]/@href') for url in urls: key = self.md5(url) if key in self.has_request_set: pass else: self.has_request_set[key] = url req = Request(url=url,method='GET',callback=self.parse) yield req @staticmethod def md5(val): import hashlib ha = hashlib.md5() ha.update(bytes(val, encoding='utf-8')) key = ha.hexdigest() return key spiders/xiahuar.py
import scrapy class XiaoHuarItem(scrapy.Item): name = scrapy.Field() school = scrapy.Field() url = scrapy.Field() items
import json import os import requests class JsonPipeline(object): def __init__(self): self.file = open('xiaohua.txt', 'w') def process_item(self, item, spider): v = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False) self.file.write(v) self.file.write('\n') self.file.flush() return item class FilePipeline(object): def __init__(self): if not os.path.exists('imgs'): os.makedirs('imgs') def process_item(self, item, spider): response = requests.get(item['url'], stream=True) file_name = '%s_%s.jpg' % (item['name'], item['school']) with open(os.path.join('imgs', file_name), mode='wb') as f: f.write(response.content) return item pipelines
ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'spider1.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 100, 'spider1.pipelines.FilePipeline': 300, } # 每行后面的整型值,确定了他们运行的顺序,item按数字从低到高的顺序,通过pipeline,通常将这些数字定义在0-1000范围内。
6.中间件
-
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your spider middleware # # See documentation in: # http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html class CustomSpiderMiddleware(object): # Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined, # scrapy acts as if the spider middleware does not modify the # passed objects. def process_spider_input(self, response, spider): # Called for each response that goes through the spider # middleware and into the spider. # Should return None or raise an exception. print('process_spider_input', len(response.text)) return None def process_spider_output(self, response, result, spider): # Called with the results returned from the Spider, after # it has processed the response. print('process_spider_output', len(response.text)) # Must return an iterable of Request, dict or Item objects. for i in result: yield i def process_spider_exception(self, response, exception, spider): # Called when a spider or process_spider_input() method # (from other spider middleware) raises an exception. # Should return either None or an iterable of Response, dict # or Item objects. print('process_spider_exception') pass def process_start_requests(self, start_requests, spider): # Called with the start requests of the spider, and works # similarly to the process_spider_output() method, except # that it doesn’t have a response associated. # Must return only requests (not items). print('process_start_requests') for r in start_requests: yield r def spider_opened(self, spider): spider.logger.info('Spider opened: %s' % spider.name) class CustomDownloaderMiddleware(object): def process_request(self, request, spider): return None def process_response(self, request, response, spider): return response def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider): return None middlewares.py
# settings.py DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { 'spider1.middlewares.CustomDownloaderMiddleware': 543, } SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = { 'spider1.middlewares.CustomSpiderMiddleware': 543, }
7. 自定制命令
- 在spiders同级创建任意目录,如:commands
- 在其中创建 crawlall.py 文件 (此处文件名就是自定义的命令)
-
from scrapy.commands import ScrapyCommand from scrapy.utils.project import get_project_settings class Command(ScrapyCommand): requires_project = True def syntax(self): return '[options]' def short_desc(self): return 'Runs all of the spiders' def run(self, args, opts): spider_list = self.crawler_process.spiders.list() for name in spider_list: self.crawler_process.crawl(name, **opts.__dict__) self.crawler_process.start() crawlall.py
- 在settings.py 中添加配置 COMMANDS_MODULE = '项目名称.目录名称'
- 在项目目录执行命令:scrapy crawlall




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号