ssm整合开发
基本知识:
标准的可以分为三层(MVC模式:model view control)
(1)数据访问层(dao持久层):主要是对原始数据(数据库或者文本文件等存放数据的形式)的操作层,是对数据的操作,具体为业务逻辑层或表示层提供数据服务。
(2)业务逻辑层(service):主要是对数据层的操作,对数据业务逻辑处理,对数据的操作进行组合。
(3)表示层(web):主要表示WEB方式,如果逻辑层相当强大和完善,无论表现层如何定义和更改,逻辑层都能完善地提供服务。主要对用户的请求接受,以及数据的返回,为客户端提供应用程序的访问。
一、项目解析图
项目搭建基本图和一些jar包的解析。
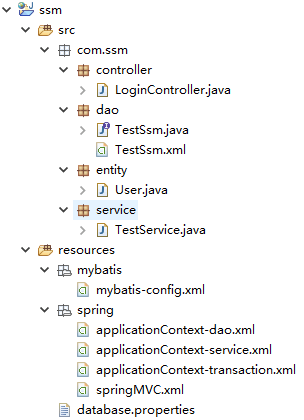
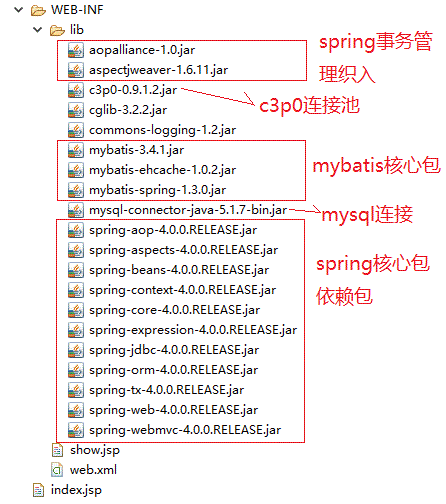
注意: 导入的jar包和各种配置文件中的约束需要对应。要不然很容易会出错。
二、配置mybatis-config.xml配置文件
在整合的开发中,不需要配置太多的东西。可以配置一下别名。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <typeAliases> <!-- 进行别名控制 --> <package name="com.ssm.entity"/> </typeAliases> <!-- 后面使用mapper扫描包的方式,这里就不作配置了 --> </configuration>
三、配置applicationContext-dao.xml
主要是用来整合dao层。把数据库连接池交给spring来管理,并且配置好SqlSession工厂、mapper扫描器。
mapper扫描器,扫描操作dao层的文件。包括 方法接口、sql.xml映射文件。
dao层是对原始数据的操作。为service层提供服务。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd "> <!-- 外部连接properties文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:database.properties"/> <!-- 配置数据库连接池 这里使用c3p0数据库连接池--> <bean id="datasource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置SqlSession工厂 --> <bean name="SqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="datasource"></property> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置mapper扫描器 --> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <!-- 扫描包路径,如果需要扫描多个包,中间使用半角逗号隔开 --> <property name="basePackage" value="com.ssm.dao"></property> //com.ssm.dao是接口方法和sql映射文件的包 <property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="SqlSessionFactory"/> </bean> </beans>
四、配置database.properties文件
主要用来配置连接数据库的代码。也可以在这里设置一些编码的格式。
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///chat //填写数据库名称 jdbc.username= 省略 //数据库权限名称 jdbc.password= 省略 //数据库权限密码
五、配置applicationContext-service.xml配置文件
主要是对service的整合管理,就是业务逻辑层,对具体的业务进行操作,对数据层进行操作。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd "> <!-- 打开Spring的Annotation支持 --> <context:annotation-config /> <!-- 设定Spring 去哪些包中找Annotation --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.ssm.service"/> //com.ssm.service 是业务逻辑层 </beans>
六、配置applicationContext-transaction.xml (扩展)
进行事务管理操作。保持数据的一致性和统一性。根据业务需要来进行搭建。这里使用了基于注解的aop配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd "> <!-- 事务管理器 对mybatis操作数据库事务控制,spring使用jdbc的事务控制类 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!--配置 数据源 datasource在applicationContext-dao.xml中配置了 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="datasource" /> </bean> <!--使用基于注解方式配置事务 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true"/> </beans>
七、配置springMVC.xml配置文件
主要是对view表现层的视图的管理。也可以配置一些信息校验、图片上传等。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.1.xsd"> <!-- 配置mvc支持 annotation--> <mvc:annotation-driven/> <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> <!--包扫描的方式,找到controller--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.ssm.controller"></context:component-scan> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> </beans>
八、配置web.xml
主要配置一些spring的监听器、前端控制器和访问方式。也可以配置过滤器等。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <!--监听器--> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext-*.xml</param-value> </context-param>
<!--前端控制器--> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring/springMVC.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.action</url-pattern> //设置访问方式 </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
九、创建对应的实体类
实体类中的属性名称的设置,设置为和数据库中的字段的名称一致。方便后期的调用,而且不需要指定resultMap
public class User { private String name; private String password; //补全get、set、方法 }
十、配置dao层
是对原始的数据进行操作。因为这里用了mapper扫描包的方式。并且使用了mapper动态开发。所以,需要把方法接口和sql映射文件放到统一包里面。并且需要名称相同。
//(1)接口方法//创建实体类的时候,创建的属性名称和mysql的表对应 public interface TestSsm { public User testing(String name); } //(2) sql映射文件 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.ssm.dao.TestSsm"> <select id="testing" parameterType="String" resultType="user"> select * from user where name = #{name} </select> </mapper>
十一、配置service层
针对具体的问题的操作,也可以理解成对数据层的操作,对数据业务逻辑处理。
@Service //标记了service层 @Transactional //注解事务管理 public class TestService { @Resource TestSsm test; //引入mapper中的接口。进行操作 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED) public User getUser(String name) { User user = test.testing(name); return user; } }
十二、配置controller层
controller是对service层中方法的调用、用户访问的url管理,并有返回view的功能等。
@Controller @RequestMapping("/login") public class LoginController { @Resource TestService test; //引入service层的方法。 @RequestMapping(value="/getways") public String getWays(HttpServletRequest request) { //查找后台数据库用户名称是 huang的信息 User user = test.getUser("huang"); request.setAttribute("user", user); return "show"; //返回视图 } }
十三、配置显示的页面
//show.jsp 用户名:${user.getName()} 密码:${user.getPassword()} //index.jsp <jsp:forward page="/login/getways.action"></jsp:forward>
最后打开浏览器。输入http://localhost:8080/ssm/index.jsp 则可以显示用户名和密码。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号