二叉树(Binary Tree)也称为二分树,二元树、对分树等,是树型结构的一种常见类型
二叉树可以定义为结点的有限集合,这个集合或为空集,或者由一个根结点与两个互不相交的、分别成为这个树的左子树和右子树的二叉树组成。
可以由空的左子树或右子树,或者左右子树皆为空,由此可见二叉树由五种基本形态
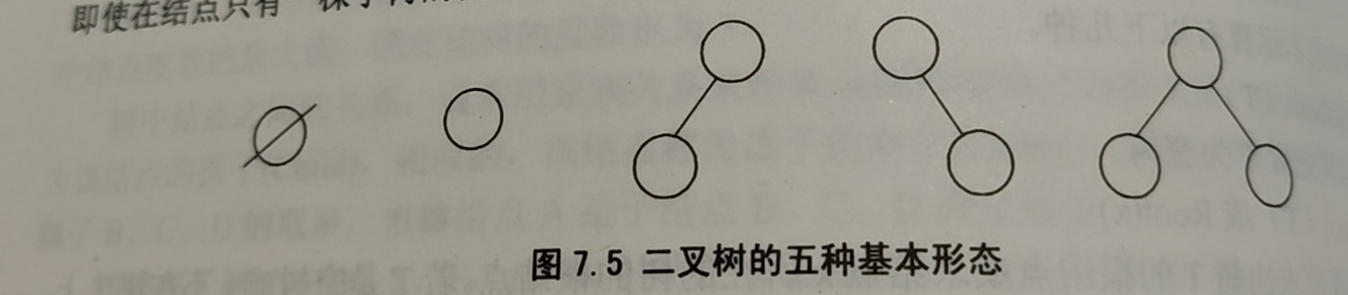
二叉树和树的最主要的区别是:二叉树中结点的子树要区分为左子树和右子树,即使在节点只有一颗子树的情况下也要明确指出该子树是左子树还是右子树
两种特殊的二叉树
满二叉树:如果一个二叉树的任何节点或者树叶结点,或有两棵非空子集,则此二叉树成为满二叉树
完全二叉树:若一棵二叉树至多只有最下面的两层上结点的度可以小于2,其余各层节点的度必须为2.并且最下面一层的结点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置上,则此二叉树为完全二叉树

二叉树的性质
1.在二叉树的第i层上最多有 2的(i-1)次方 个结点
2.深度为k的二叉树最多有 2的k方-1 个结点
3.包含n 个结点的二叉树的分支树有n-1
4.对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点为n0,度为2 的结点数位n2 则 n0=n2+1
5.具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度k为log n +1
.....
@Data
public class Student implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String studentName;
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer id, String studentName) {
this.id = id;
this.studentName = studentName;
}
}
@Data
public class Node {
public Student student;
public Node leftChild,rightChaild;
public Node() {
}
public Node(Student student, Node leftChild, Node rightChaild) {
this.student = student;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChaild = rightChaild;
}
}
package com.example.tree.binary;
import com.example.common.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
public class BinaryTreeTest {
@Test
public void testPrev() {
Node rootNode = createTree();
prev(rootNode);
System.out.println();
mid(rootNode);
System.out.println();
pos(rootNode);
}
/**
* 先序
*
* @param root
*/
public void prev(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.getStudent().getStudentName() + " ");
prev(root.getLeftChild());
prev(root.getRightChaild());
}
}
/**
* 中序
*
* @param root
*/
public void mid(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
mid(root.getLeftChild());
System.out.print(root.getStudent().getStudentName() + " ");
mid(root.getRightChaild());
}
}
/**
* 后序
*
* @param root
*/
public void pos(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
pos(root.getLeftChild());
pos(root.getRightChaild());
System.out.print(root.getStudent().getStudentName() + " ");
}
}
private Node init() {
Student A = new Student(1, "A");
Node rootNode = new Node(A, null, null);
Student B = new Student(2, "B");
Node nodeB = new Node(B, null, null);
Student C = new Student(3, "C");
Node nodeC = new Node(C, null, null);
Student D = new Student(4, "D");
Node nodeD = new Node(D, null, null);
Student E = new Student(5, "E");
Node nodeE = new Node(E, null, null);
Student F = new Student(6, "F");
Node nodeF = new Node(F, null, null);
Student G = new Student(7, "G");
Node nodeG = new Node(G, null, null);
rootNode.setLeftChild(nodeB);
nodeB.setLeftChild(nodeC);
nodeB.setRightChaild(nodeD);
nodeD.setLeftChild(nodeE);
nodeD.setRightChaild(nodeF);
nodeE.setRightChaild(nodeG);
return rootNode;
}
private Node createTree() {
Student A = new Student(1, "A");
Node rootNode = new Node(A, null, null);
Student B = new Student(2, "B");
Node nodeB = new Node(B, null, null);
Student C = new Student(3, "C");
Node nodeC = new Node(C, null, null);
Student D = new Student(4, "D");
Node nodeD = new Node(D, null, null);
Student E = new Student(5, "E");
Node nodeE = new Node(E, null, null);
Student F = new Student(6, "F");
Node nodeF = new Node(F, null, null);
Student G = new Student(7, "G");
Node nodeG = new Node(G, null, null);
nodeE.setRightChaild(nodeG);
nodeD.setLeftChild(nodeE);
nodeD.setRightChaild(nodeF);
nodeB.setRightChaild(nodeD);
nodeB.setLeftChild(nodeC);
rootNode.setLeftChild(nodeB);
return rootNode;
}
}
非递归的先序,中序和后序
/**
* 先序遍历非递归
*
* @param rootNode
*/
private void prev1(Node rootNode) {
Node p;
Node[] nodes = new Node[10];//临时适用用于存储右子树
int top = -1;
p = rootNode;
do {
while (p != null) {
System.out.print(p.getStudent().getStudentName() + " ");
if (p.getRightChaild() != null) {
// 将有值的右节点放到数组中
nodes[++top] = p.getRightChaild();
}
p = p.getLeftChild();
}
if (top >= 0) {
p = nodes[top--];
}
} while (top > 0 || p != null);
}
/**
* 中序非递归
*
* @param root
*/
public void mid1(Node root) {
Node p;//临时节点
Node[] nodes = new Node[10];//临时适用用于存储右子树
int top = 0;
p = root;
do {
while (p != null) {
nodes[top++] = p;
p = p.getLeftChild();
}
if (top > 0) {
p = nodes[--top];
System.out.print(p.getStudent().getStudentName() + " ");
p = p.getRightChaild();
}
} while (top > 0 | p != null);
}
/**
* 后序非递归
* 左 右 根
*
* @param root
*/
public void pos1(Node root) {
Node p;//临时节点
Node[] nodes = new Node[10];//临时适用用于存储右子树
int top = 0;
int[] flag = new int[10];
p = root;
do {
// 第一个循环拿到根节点最左侧结点,遍历左左子树
while (p != null) {
nodes[top] = p;
flag[top] = 0;
p = p.getLeftChild();
top++;
}
while (top > 0 && flag[top-1] == 1) {
top--;
p = nodes[top];
System.out.print(p.getStudent().getStudentName() + " ");
}
if (top > 0 && flag[top - 1] == 0) {
p = nodes[top - 1];
flag[top - 1] = 1;
p = p.getRightChaild();
}
} while (top > 0);
}
计算二叉树的叶子结点
@Test
public void testCount(){
System.out.println("计算数的叶子节点有" + countLeaf(createTree(),0));
}
/**
* 计算叶子结点
* @param p
* @param num
* @return
*/
public int countLeaf(Node p,int num){
if (p!=null){
if (p.getLeftChild()==null&&p.getRightChaild()==null){
num++;
}
num = countLeaf(p.getLeftChild(),num);
num = countLeaf(p.getRightChaild(),num);
}
return num;
}
计算二叉树的深度
@Test
public void testdepth() {
System.out.println("计算树的深度 " + treeDepth(createTree()));
System.out.println("计算树的深度 " + treeDepth2(createTree()));
}
/**
* 二叉树的深度
*
* @param p
* @return
*/
public int treeDepth(Node p) {
// 定义局部记录数深度,左子树深度,右子树深度
int h = 0, lh, rh;
if (p != null) { // 结点为空,深度为0
lh = treeDepth(p.getLeftChild());
rh = treeDepth(p.getRightChaild());
if (lh >= rh) {
h = lh + 1;
} else {
h = rh + 1;
}
}
return h;
}
public int treeDepth2(Node p) {
if (p != null) {
int left = treeDepth2(p.getLeftChild());
int right = treeDepth2(p.getRightChaild());
return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号