Swift中创建有动态交互性的用户界面UIDynamics之UIAttachmentBehavior,UIDynamicItemBehavior的使用(二)
前言:动力项目关联UIAttachmentBehavior的使用
- 吸附主要发生在:元素与锚点、元素与元素之间。
- 当元素与锚点连接,元素的运动依赖于锚点。
- 当元素与元素连接,两个元素的运动彼此影响。
- 有的吸附行为支持两个元素和一个锚点。
如果喜欢UIkit的动力行为所内置的默认物理特性,但是想使用动力行为为控制的动力项目设置不同的特征,比如质量和弹性,如何实现呢,这里就需要用到这个类UIDynamicItemBehavior
元素和锚点之前的吸附

class ViewController: UIViewController{
var anchorView :UIView!
var dynamicItem1View :UIView!
var animator:UIDynamicAnimator?
var attachmentBehavior :UIAttachmentBehavior?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
anchorView = UIView.init(frame: CGRect.init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 10, height: 10))
anchorView.center = CGPoint.init(x: 175, y: 250)
anchorView.backgroundColor = UIColor.red
view.addSubview(anchorView)
dynamicItem1View = UIView.init(frame: CGRect.init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 50, height: 50))
dynamicItem1View.center = CGPoint.init(x: 125, y: 125)
dynamicItem1View.backgroundColor = UIColor.blue
view.addSubview(dynamicItem1View)
}
override func touchesBegan(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
animator = UIDynamicAnimator.init(referenceView: view)
let gravity = UIGravityBehavior.init(items: [dynamicItem1View])
animator?.addBehavior(gravity)
let collision = UICollisionBehavior.init(items: [dynamicItem1View] as! [UIDynamicItem])
collision.translatesReferenceBoundsIntoBoundary = true//确保动画对象使用父视图作为参考视图进行初始化
animator!.addBehavior(collision)
attachmentBehavior = UIAttachmentBehavior.init(item: dynamicItem1View, attachedToAnchor: anchorView.center)
attachmentBehavior!.length = 50
animator!.addBehavior(attachmentBehavior!)
}
}
元素和锚点之间的吸附,offset参数设置元素吸附力作用点的偏移量

attachmentBehavior = UIAttachmentBehavior.init(item: dynamicItem1View, offsetFromCenter: UIOffset.init(horizontal: 25, vertical: 0), attachedToAnchor: anchorView.center)
元素和元素之间的吸附

import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController{
var dynamicItem1View :UIView!
var dynamicItem2View :UIView!
var animator:UIDynamicAnimator?
var attachmentBehavior :UIAttachmentBehavior?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
dynamicItem1View = UIView.init(frame: CGRect.init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 50, height: 50))
dynamicItem1View.center = CGPoint.init(x: 125, y: 125)
dynamicItem1View.backgroundColor = UIColor.black
view.addSubview(dynamicItem1View)
let redView1 = UIView.init(frame: CGRect.init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 10, height: 10))
redView1.backgroundColor = UIColor.red
dynamicItem1View.addSubview(redView1)
redView1.center = CGPoint.init(x: 25, y: 25)
dynamicItem2View = UIView.init(frame: CGRect.init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 50, height: 50))
dynamicItem2View.center = CGPoint.init(x: 175, y: 250)
dynamicItem2View.backgroundColor = UIColor.blue
view.addSubview(dynamicItem2View)
let redView0 = UIView.init(frame: CGRect.init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 10, height: 10))
redView0.backgroundColor = UIColor.red
dynamicItem2View.addSubview(redView0)
redView0.center = CGPoint.init(x: 25, y: 25)
}
override func touchesBegan(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
animator = UIDynamicAnimator.init(referenceView: view)
let gravity = UIGravityBehavior.init(items: [dynamicItem1View])
animator?.addBehavior(gravity)
let collision = UICollisionBehavior.init(items: [dynamicItem1View,dynamicItem2View] as! [UIDynamicItem])
collision.translatesReferenceBoundsIntoBoundary = true//确保动画对象使用父视图作为参考视图进行初始化
animator!.addBehavior(collision)
attachmentBehavior = UIAttachmentBehavior.init(item: dynamicItem1View, attachedTo: dynamicItem2View)
attachmentBehavior!.length = 100
animator!.addBehavior(attachmentBehavior!)
}
}
元素和元素之间的吸附设置偏移量

attachmentBehavior = UIAttachmentBehavior.init(item: dynamicItem1View, offsetFromCenter: UIOffset.init(horizontal: 0, vertical: -25), attachedTo: dynamicItem2View, offsetFromCenter: UIOffset.init(horizontal: 0, vertical: 25))
//我们可以通过anchorPoint属性获得锚点位置,附发生在元素和元素之间的时候,该属性的值为(0, 0)
@property (readwrite, nonatomic) CGPoint anchorPoint;
//作用点的距离
@property (readwrite, nonatomic) CGFloat length;
//振动频率,值越大,弹性运动的频率越快
@property (readwrite, nonatomic) CGFloat frequency;
//弹性阻力 值越大,阻力越大,弹性运动震动的幅度越小。
@property (readwrite, nonatomic) CGFloat damping; // 1: critical damping
//旋转阻力,指围绕一点旋转所受的阻力,默认值0.0,值越大,阻力越大。
@property (readwrite, nonatomic) CGFloat frictionTorque
//运动范围
@property (readwrite, nonatomic) UIFloatRange attachmentRange
UIDynamicItemBehavior的使用
- allowsRotation :允许动力项目在动画过程中发生旋转
- resistance:动力项目移动时的阻力,可以从0到CGFLOAT_MAX
- friction:在其他动力项目碰撞或者发生摩擦是,应该有多大的摩擦力,值越高,摩擦力越大
- elasticity:0.0到1.0的浮点数,值定理了动力项目可以有多大的弹性
- density:一个浮点数,0到1,默认1,对象的质量,就是密度,同样狂傲越低重量越轻
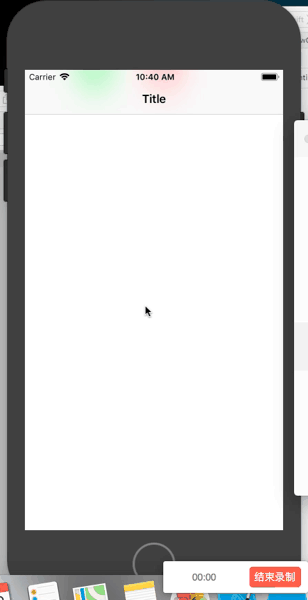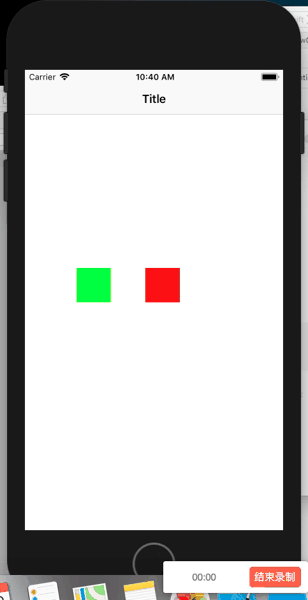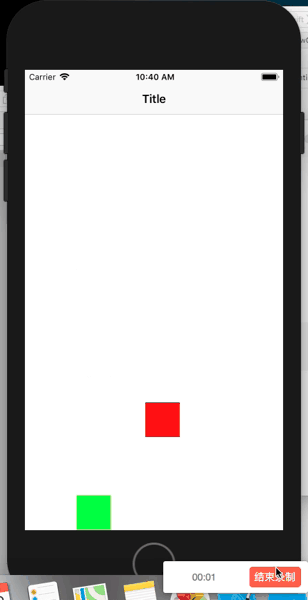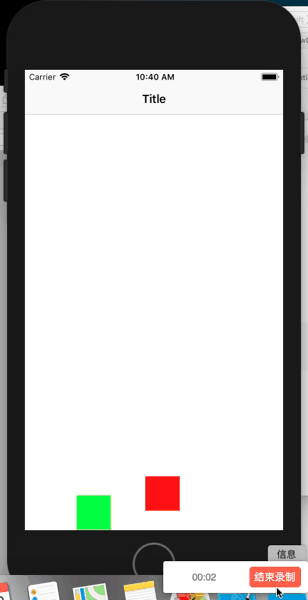
class ViewController: UIViewController{
var topView:UIView!
var bottomView:UIView!
var animator:UIDynamicAnimator?
func newViewWithCenter(center:CGPoint,backgroundColor:UIColor) ->UIView{
let newView = UIView.init(frame: CGRect.init(x: 0, y: 0, width: 50, height: 50))
newView.center = center
newView.backgroundColor = backgroundColor
return newView
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
topView = newViewWithCenter(center: CGPoint.init(x: 100, y: 0), backgroundColor: UIColor.green)
bottomView = newViewWithCenter(center: CGPoint.init(x: 200, y: 0), backgroundColor: UIColor.red)
view.addSubview(topView)
view.addSubview(bottomView)
}
override func touchesBegan(_ touches: Set<UITouch>, with event: UIEvent?) {
animator = UIDynamicAnimator.init(referenceView: view)
let gravity = UIGravityBehavior.init(items: [topView,bottomView])
animator?.addBehavior(gravity)
let collision = UICollisionBehavior.init(items: [topView,bottomView])
collision.translatesReferenceBoundsIntoBoundary = true
animator!.addBehavior(collision)
let moreElastiItem = UIDynamicItemBehavior.init(items: [bottomView])
moreElastiItem.elasticity = 1
let lessElastiItem = UIDynamicItemBehavior.init(items: [topView])
moreElastiItem.elasticity = 0.5
animator?.addBehavior(moreElastiItem)
animator?.addBehavior(lessElastiItem)
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号