反射
解释
Java 的反射机制是指在运行状态中,对于任意一个类都能够知道这个类所有的属性和方法; 并且对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能成为Java语言的反射机制。
反射的基本使用
Class对象获取
Class.forName静态方法
Class class1 = Class.forName("reflection.TestReflection");
- 使用类的
.class方法
Class class2 = TestReflection.class;
- 使用实例对象的
getClass()方法
TestReflection testReflection = new TestReflection();
Class class3 = testReflection.getClass();
反射创建对象、方法、构造器
反射有两种创建对象的方法
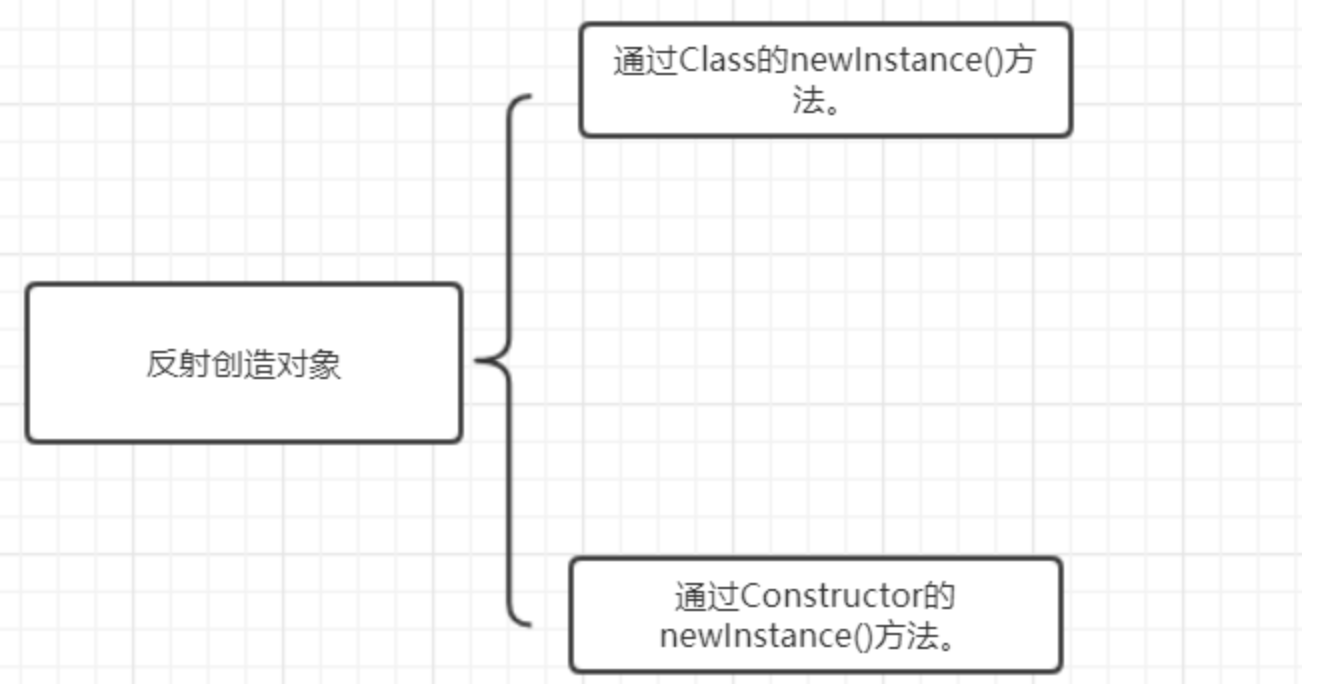
方法1在JDK9已经被标记为弃用,所以这里只介绍第二种方式
public Demo() {
System.out.println("无参构造");
};
private Demo(String s) {
System.out.println("有参构造: "+s);
}
首先我们需要准备好对应的Class对象,可以参考上一节,在获取构造函数时,对于公有构造函数,我们使用getConstructor,如果是有参构造,那么我们在这个有参构造中传入参数对应的Class对象,比如有一个String参数,那么我们使用.getConstructor(String.class),如果是私有构造,那么在得到Constructor后,使用得到的Constructor对象的方法.setAccessible(true)
把访问权限设置为true,最后使用Constructor对象的方法newInstance(args)即可,示例如下:
public Demo() {
System.out.println("无参构造");
};
private Demo(String s) {
System.out.println("有参构造: "+s);
}
public Demo(String s, String s1) {
System.out.println("有参公有 " + s + " " + s1);
}
Class class1 = Demo.class;
Constructor constructor = class1.getConstructor();
Demo o = (Demo)constructor.newInstance();
Constructor declaredConstructor = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Demo obj = (Demo)declaredConstructor.newInstance("hello");
Constructor constructor1 = class1.getConstructor(String.class, String.class);
Demo o1 = (Demo) constructor1.newInstance("hello", "world");
获取成员属性
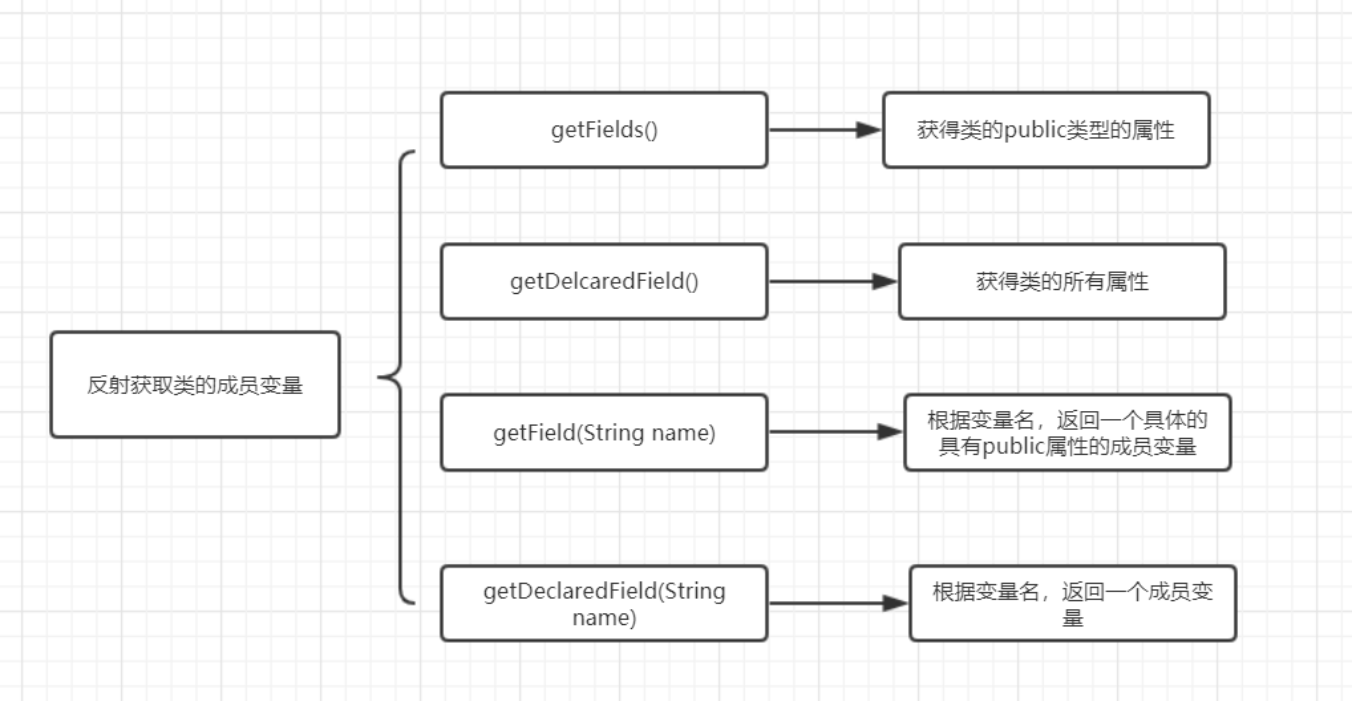
上图注意第二个获取所有成员变量少了一个s,无需代码示例,很容易理解。
获取类方法
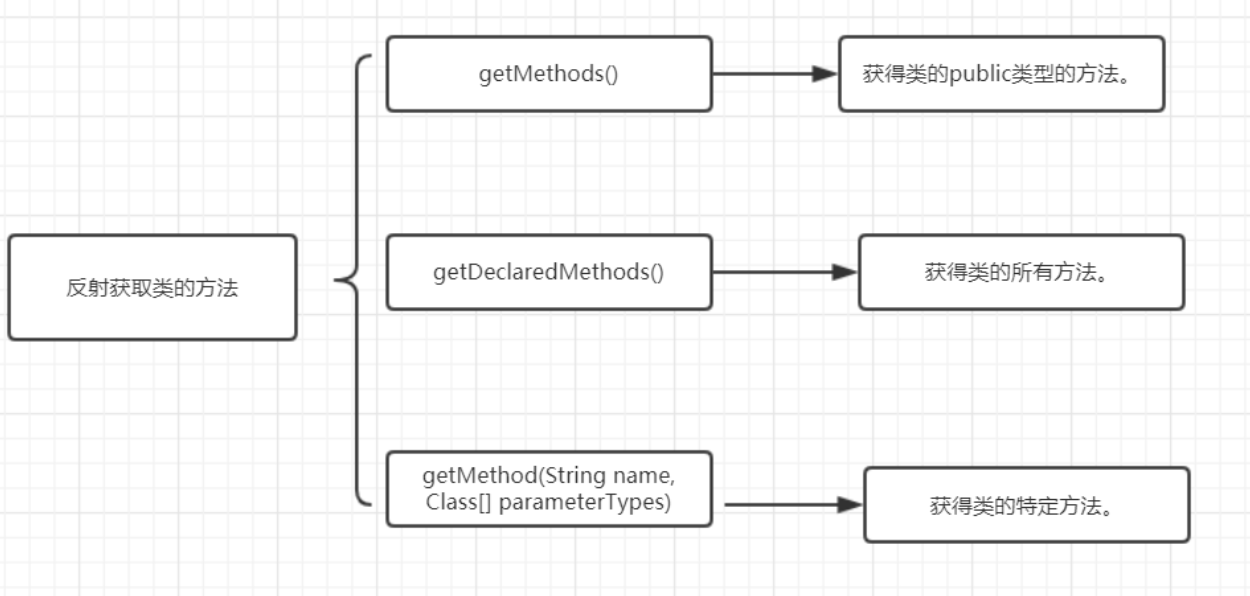
简单使用
public class ReflectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<Demo> clazz = Demo.class;
Demo instance = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// --- 操作私有字段 ---
Field f4 = clazz.getDeclaredField("test4");
f4.setAccessible(true);
f4.set(instance, "这是反射的力量");
// --- 操作私有方法 ---
Method m = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("sayHi", String.class);
m.setAccessible(true);
m.invoke(instance, "小明");
System.out.println("修改结果: " + f4.get(instance));
}
}
class Demo {
private void sayHi(String name) {
System.out.println("public method sayHi " + name);
}
public String test3 = "hello world";
private String test4 = "hello xm";
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号