Java学习笔记--异常
异常

异常分类
-
检查性异常
-
运行时异常
-
错误
异常体系结构
Java把异常当作错误来处理,她又如下继承关系
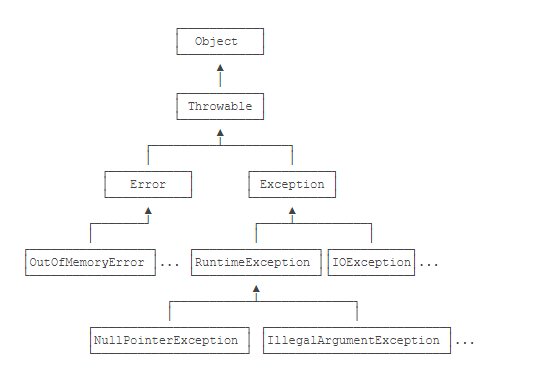
异常分为两大类
-
Error
-
Exception
ERROR:

EXCEPTION:

异常处理机制
-
捕获异常
-
抛出异常
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 1; int b = 0; //Ctrl + Alt + T 生成异常捕获 try { // 监控区域 System.out.println(a/b); // 捕获多个错误:类型从小到大 }catch (Error e){//catch(异常类型)用于捕获异常 System.out.println("程序错误"); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("程序异常"); }finally {// 无论是否捕获到异常都会执行 System.out.println("Closed"); } // finally 非必须,一般用于关闭资源、IO } }public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { new Test1().check(1,0); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // // 假设这个方法处理不了这个异常,方法向上抛出 public void check(int a, int b) throws ArithmeticException{ if (b==0){ throw new ArithmeticException();//主动抛出异常,一般在方法中使用 } }
自定义异常
自定义异常的步骤

//自定义异常
public class MyException extends Exception{
private int detail;
public MyException(int detail) {
this.detail = detail;
}
// toString打印异常信息
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyException{"+detail+'}';
}
}
public class MyExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new MyExceptionTest().test(11);
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void test(int a)throws MyException{
if (a>10){
throw new MyException(a);
}
System.out.println("OK");
}
}
异常使用





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号