如果知道了地球上两个地方的纬度和经度,就可以使用哈弗森大圆距离公式计算它们之间大概的距离。在小精灵中可以使用math步骤进行公式中的三角函数的计算。
If the latitude and longitude of two places on the Earth are known, the approximate distance
between them can be calculated using the Haversine Great Circle Distance formula. The formula
includes some trigonometrical calculations that can be done in Gremlin using the math step.
如果你对于更好的理解哈弗森数学公式感兴趣,您可以从这找到更多信息。https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haversine_formula
If you are interested in better understanding the mathematics used by the
Haversine formula, details can be found here.
在本节中笔者包含了两个查询。第一个计算AUS和DFW之间的呀离,用一个不灵活的方法。它反应了笔者在小精灵上计算哈弗森距离的第一次尝试。机场的代码嵌入在了查询中。这个可以效奏后,笔者实现了一个更通用的查询,这个会更好一些。第二个查询允许指定任意的启程点和目的地。
In this section I have included two queries. The first calculates the distance between Austin and
Dallas Fort Worth using a somewhat inflexible approach. This reflects my first attempt to create a
query that computes Great Circle distances all in Gremlin. The airport codes are embedded in the
query. Having got that working I realized a more generic query would be better. The second
example allows an arbitrary source and destination to be specified.
现在看查询。首先步骤的数字看起来有点让人却步,但如果您一节一节地看,它实际上相当的直观。哈弗森公式需要一些常数值。这些值通过withSideEffect步骤进入到查询句语中。第一个常量rdeg表示了一度的弧度值。这是Pi除以180的结果。第二个常数gcmiles代表了地球每英里的平均度数。地球这个不规则的球形,它的半径更接近于地极。
Let’s take a look at the queries. At first, the number of steps used may look a bit daunting, but if you
work your way through it section by section it’s actually fairly straightforward. The Haversine
formula needs a couple of constant values. These are injected into the query using withSideEffect
steps. The first constant, rdeg represents one degree in radians. This is the result from dividing PI
by 180. The second constant gcmiles represents the average radius of the Earth in miles. This allows
for the imperfect spherical shape of the Earth where the radius varies closer to the poles.
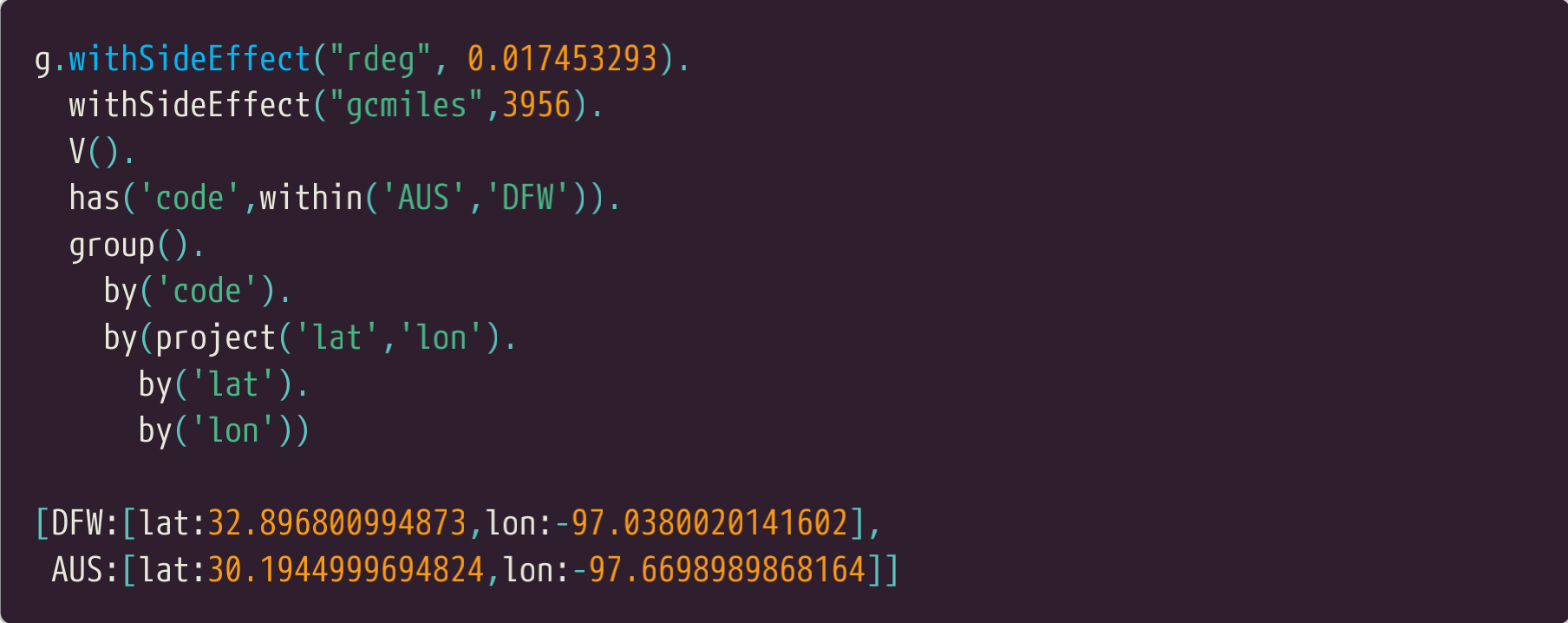
在笔者的编写查询的首次尝试中,笔者用到一个has步骤,project步骤来找到从AUS到DFW的机场,然后用机场的代码生成了一个组,键是机场代码,值是它们的经纬度坐标。如果我们只取查询的一部分,运行它,这是我们得到的返回。
In my first attempt at producing a query, I used a has step to find the AUS and DFW airports and
then produced a group with the airport codes being the keys and a projection of their latitude and
longitude being the values. If we take just that part of the query and run it this is what we get back.
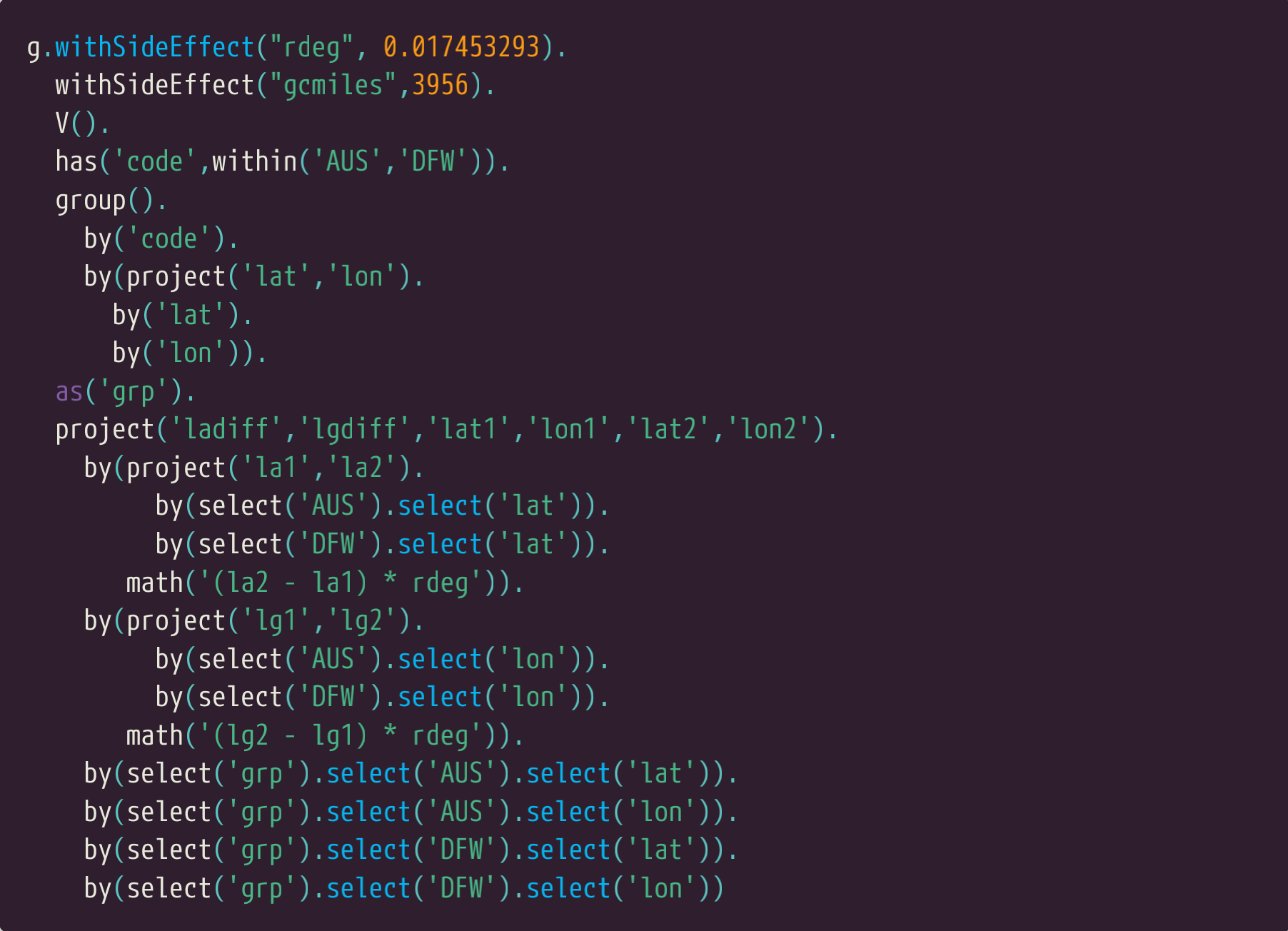
哈弗森公式需工我们计算两个点经纬度的不同。查询的下一部分会做这些。用到一个 project步骤project('ladiff,lgdiff,lat1,lon1,lat2,lon2)' 来收集我们需要的所有值的。
The Haversine formula requires us to calculate the differences between the latitude and longitude
of the two coordinates. The next part of the query does that. A project step project('ladiff,lgdiff,lat1
,lon1,lat2,lon2)' is used to collect all the values we need.
这是结果,map中包含了两者之间的差异及起点和终点的坐标。
Here are the results. A map has been generated containing the differences as well as the original
coordinates.

这样收集值的目的是它们可以用来给math步骤提供数据来完成计算。从这个例子中要知道的一个关键点就是math步骤可以用前边的project步骤来提供值。最后计算进行了必要的三角函数的处理,这是哈弗森公式所需要的。这是笔者用小精灵解决这个问题的第一个完整的版本。
The purpose of collecting the values like this is so they can be fed into the math step to complete the
calculation. One key takeaway from this example is the way that a math step can be fed values from
a prior project step. The final calculations perform the necessary trigonometry as required by the
Haversine formula. Here is the complete version of my first attempt at solving this problem in
Gremlin.
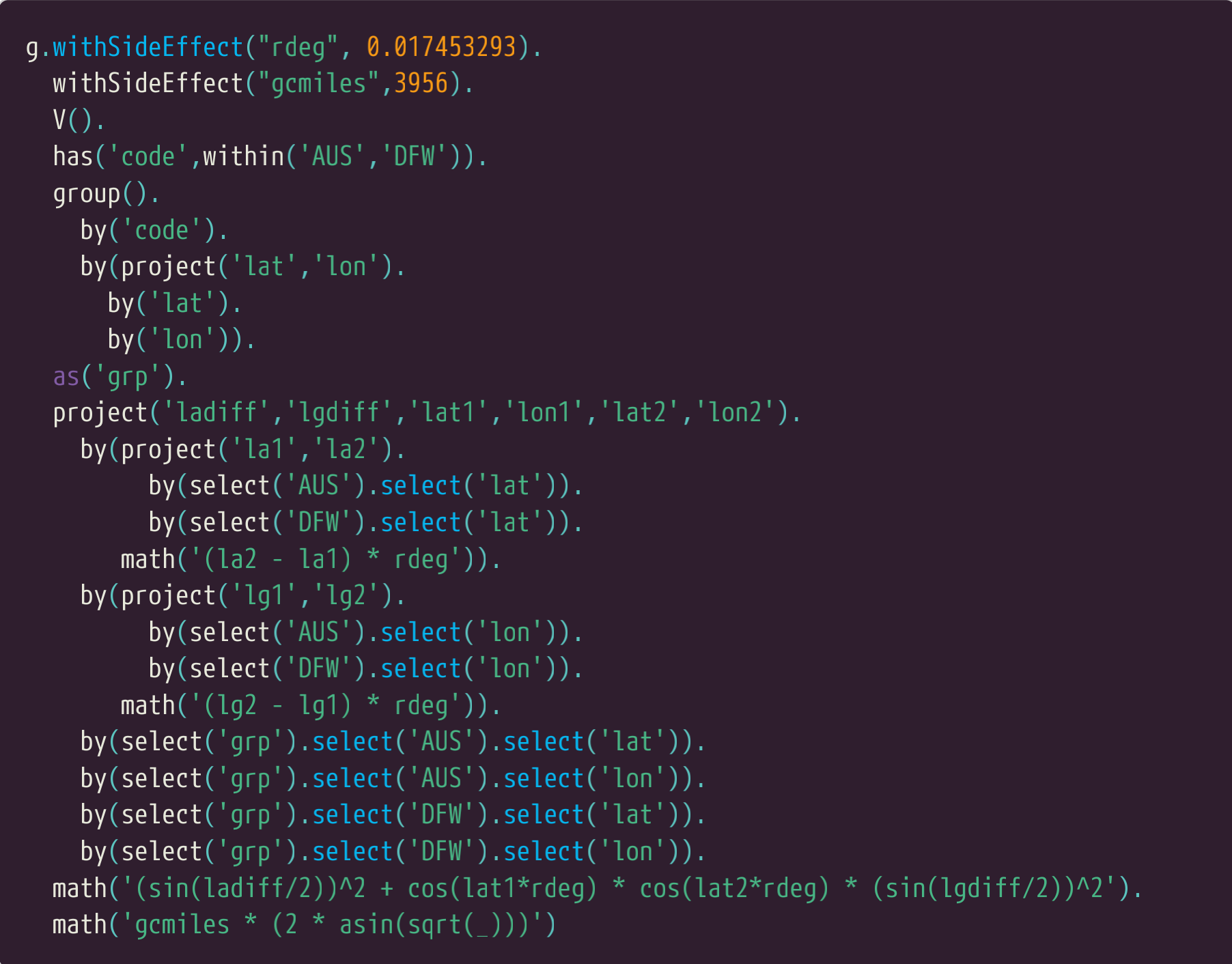
我们看到从AUS到DFW之间的距离大约是190英里。
We can see that the distance from Austin to Dallas Fort Worth is approximately 190 miles.

一些调整可以让这个查询更灵活。笔者需要有一个查询,您可以在开始提供两个机场的代码。 这就让这个查询更加参数化,当进行程的时候。这与笔者的第一个尝试最大的不同是起始机场和目的地机场在最开始并且每个都做了标记。 group步骤被一个select步骤取代,并有了一个标签grp.查询可以用grp来引用它。
A few adjustments are needed to make the query more flexible. I wanted to have a query where
you just provide any two airport codes at the start. This makes it easy to parameterize the query
when working with code. The main difference from my first attempt is that the source and target
airports are located at the start and individually labelled. The group step is replaced by a select step
and given a label of "grp". The remainder of the query refers to "grp" as needed.
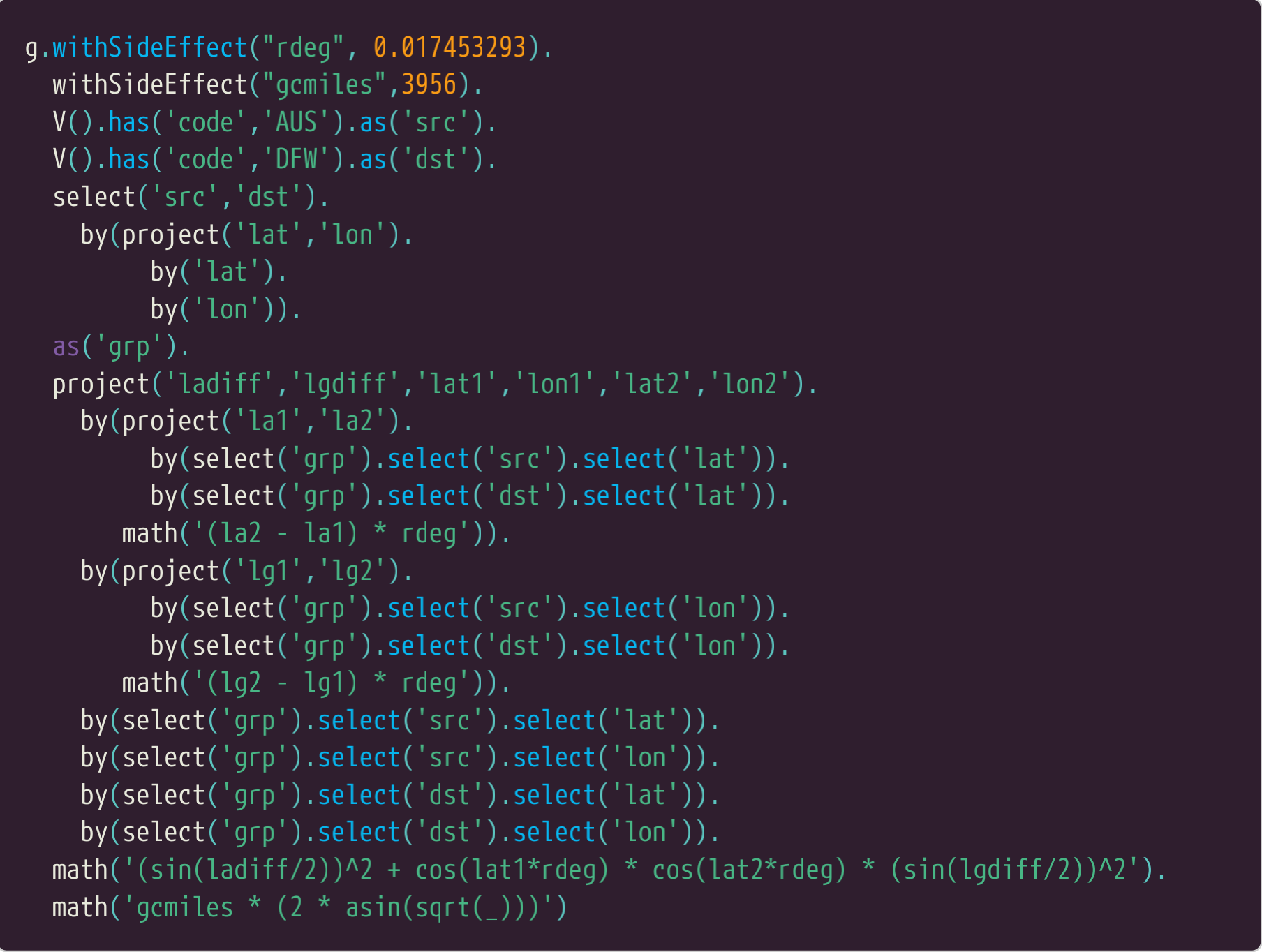
这个更通用的版本的查询的结果和前边的一样。
The result from the more general purpose version of the query is the same as before.

这个查询的代码可以从样例代码文件夹找到。
The code for this query is available in the sample-code folder at https://github.com/
krlawrence/graph/blob/master/sample-code/great-circle.groovy
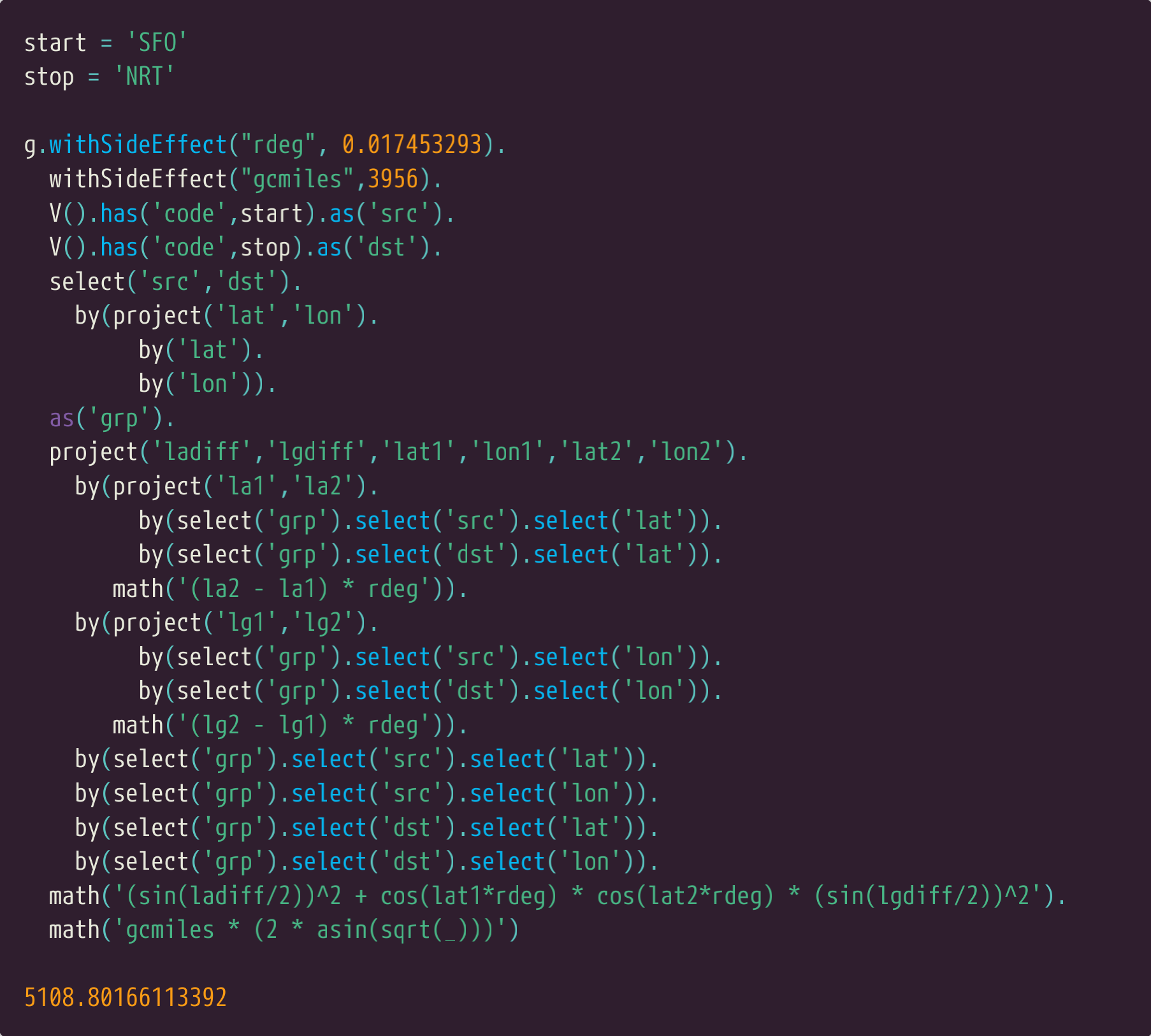
我们可以更进一步,参数化这个查询。下面显示的每个东西都是用小精灵控制台完成的,但是它也代表了您可以在应用程序中使用这个查询。
We can go one step further and parameterize the query. Everything shown below can be done using
the Gremlin Console but it also represents the way you might use this query within an application.
这次SFO和NRT是起程点和目的地。
This time San Francisco and Tokyo Narita are used as the origin and destination.
我们会在“杰森图地理空间API”这一节中再次讨论进行地理空间查询的话题,会有更多的杰森图提供的能力会被讨论到。
We will revisit the topic of performing geospatial queries in the "The JanusGraph GeoSpatial API"
section where some additional capabilities that JanusGraph offers are discussed.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号