20201709-黄世洋 四到五次Java作业总结
一、前言:
1、第四次作业分析:
题量:三
知识点:7-1水文数据校验处理涉及正则表达式,7-2日期问题面对对象设计涉及对象和类的相关知识(此时题目没有要求要用到正则表达式),7-3图形继承涉及对象和类和继和多态。
2、第五次作业分析:
题量:五
知识点:7-1找出最长单词所涉及的知识点有正则表达式和字符串处理。7-2合并两个有序数组为新的有序数组涉及数组相关知识。7-3对整形数据排序涉及数组和排序问题,三种排序方法,冒泡排序法、选择排序法、插入排序法。7-4统计Java程序中关键词出现的次数涉及接口和正则表达式以及字符串处理。7-5涉及对象和类以及继承和多态。
3、第六次作业分析:
题量:六
知识点:7-1QQ号检验涉及正则表达式和字符串处理。7-2字符排序涉及字符串处理和正则表达式。7-3验证码检验涉及正则表达式和字符串处理。7-4学号检验涉及正则表达式和字符串处理。7-5图形继承与多态涉及对象和类以及继承和多态。7-6图形接口及多态性涉及接口和多态。
总分析:
三次作业题量适中。7-4作业有三题,但每一题难度有点大。7-5作业有五题,其中一题难度有点大,其他题所占分数较小。7-6作业有六题,每道题难度都适中。三次题目中所涉及的知识点有:正则表达式、对象和类、继承和多态、数组、字符串处理、接口。其中,继承和多态、正则表达式所占比例较大。这三次作业中对我来说有难度的仍是正则表达式,由于上次正则表达式没有学习,这几次有难度的正则表达式仍是我最大的缺陷。
二、设计与分析:
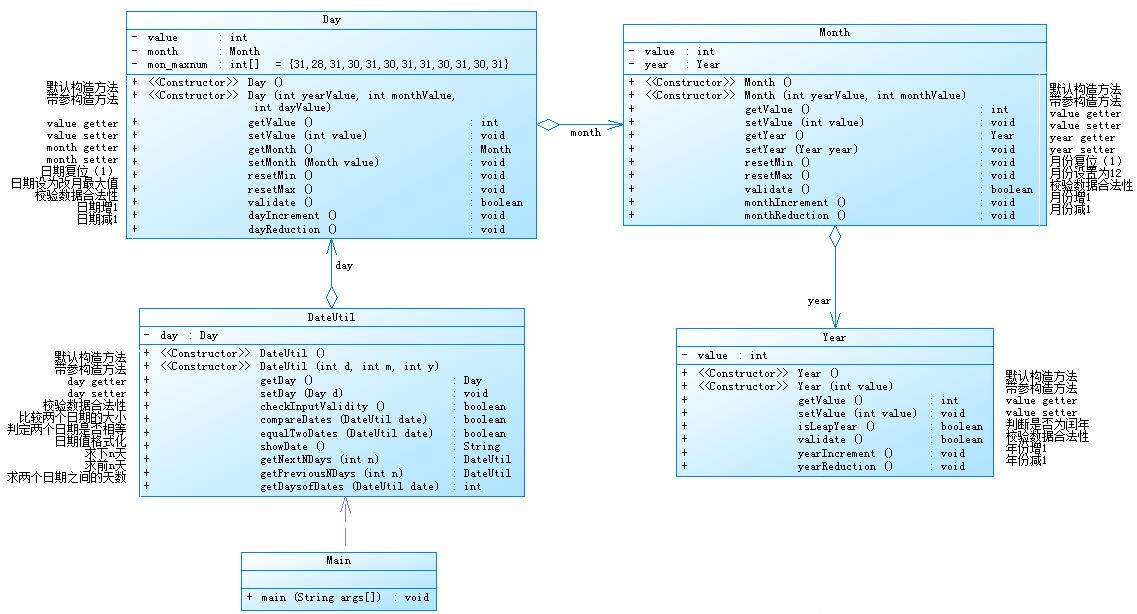
1、题目集4中7-2与题目集5中7-5两种日期聚合设计的思路及比较:
a、题目集4中7-2思路:
具体思路老师已在题中给出:
源代码:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] Args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int a = input.nextInt(); switch (a) { case 1: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getNextNdays(n); System.out.println(date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } break; case 2: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getPreviousNdays(n); System.out.println(date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break; case 3: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int ys = input.nextInt(); int ms = input.nextInt(); int ds = input.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); DateUtil dates = new DateUtil(ys,ms,ds); if (date.checkInputValidity()&&dates.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println(date.getDaysofDates(dates)); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Year{ private int value; Year(){ } Year(int value){ this.value=value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value=value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public boolean isLeapYear(int year) { boolean k=false; if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0) k=true; return k; } public boolean validate(){ if (this.getValue()>=1900&&this.getValue()<=2050) return true; else return false; } public void yearIncrement(){ this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } public void yearReduction(){ this.setValue(this.getValue()-1); } } class Month{ private int value; private Year year; Month(){ } Month(int yearValue,int month){ year = new Year(yearValue); //year.setValue(yearValue); this.setValue(month); } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } public Year getYear() { return year; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void resetMin(){ this.setValue(1); } public void resetMax(){ this.setValue(12); } public boolean validate(){ if (value>=1&&value<=12&&year.validate()) return true; else return false; } public void monthIncrement(){ if (this.getValue() == 12) { resetMin(); year.yearIncrement(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } } public void monthReduction(){ if (this.getValue() == 1) { resetMax(); year.yearReduction(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()-1); } } } class Day { private int value; private Month month; private int[] mon_maxnum1= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; private int[] mon_maxnum2 = {31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; Day(){ } Day(int yearValue,int monthvalue,int dayvalue){ month = new Month(yearValue,monthvalue); // month.getYear().setValue(yearValue); // month.setValue(monthvalue); this.setValue(dayvalue); } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void resetMin(){ this.value = 1; } public void resetMax(){ if (month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue())) { this.setValue(mon_maxnum2[month.getValue()-1]); } else this.setValue(mon_maxnum1[month.getValue()-1]);; } public boolean valiDate(){ if (month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue())) { if (value >= 1 && value <= 31 && (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)) return true; else if (value >= 1 && value <= 30 && (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)) return true; else if (value>=1&&value<=29&&month.getValue()==2) return true; else return false; } else { if (value >= 1 && value <= 31 && (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)) return true; else if (value >= 1 && value <= 30 && (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)) return true; else if (value>=1&&value<=28&&month.getValue()==2) return true; else return false; } } public void dayIncrement(){ if(month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue())) { if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum2[month.getValue()-1]) { month.monthIncrement(); resetMin(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } } else { if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum1[month.getValue()-1]) { month.monthIncrement(); resetMin(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } } } public void dayReduction(){ if (this.getValue()== 1) { month.monthReduction(); resetMax(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()-1); } } } class DateUtil { private Day day; DateUtil(){ } DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){ day = new Day(y,m,d); // day.getMonth().setValue(m); // day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); //// day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); //// day.getMonth().setValue(m); // day.setValue(d); } public void setDay(Day day) { this.day = day; } public Day getDay() { return day; } public boolean checkInputValidity(){ if (day.getMonth().getYear().validate()&&day.getMonth().validate()&&day.valiDate()) return true; else return false; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil d2){ if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true; else if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return true; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getValue()>d2.getDay().getValue()) return true; else if (day.getValue()<d2.getDay().getValue()) return false; else return true; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil d2){ if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getValue()>d2.getDay().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getValue()<d2.getDay().getValue()) return false; else return true; } public String showDate(){ return day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue(); } public DateUtil getNextNdays(int n){ do { day.dayIncrement(); n--; }while (n!=0); DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); return date1; } public DateUtil getPreviousNdays(int n){ do { day.dayReduction(); n--; }while (n!=0); DateUtil date2 = new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getValue()); return date2; } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil da2){ int x = 0; if (this.equalTwoDates(da2)) { return 0; } else if (this.compareDates(da2)) { do { day.dayReduction(); x++; }while (!this.equalTwoDates(da2)); } else do { day.dayIncrement(); x++; }while (!this.equalTwoDates(da2)); return x; } }
说明:
Year类、Month类、Day类、DateUtil类依次是聚集关系。聚集是关联的一种特殊关系,代表了两个对象之间的归属关系。Month类中有Year类,Day类中有Month类,而DateUtil类中也有Day类,因此它们两两聚合。每一个类中都有相应的日期值、相应的值增减的方法、相应值的合法性检测方法,以及相应类的构造方法。
功能实现:
求下n天:在输入相关的值之后会进行一次数据的合法性校验。年、月、日都有相关的自增的方法,Day的自增方法和Month相关,到月末的那一天之后一天会调用一次Month的自增方法,Day的值变为最小。月到12月自增方法会调用Year的自增方法,然后Month的值变为最小。就这样循环n次Day的自增方法求得下n天。
相关部分代码:
int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getNextNdays(n); System.out.println(date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }
求前n天:思路同上,把自增方法改为自减方法即可。
相关部分代码:
case 2: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getPreviousNdays(n); System.out.println(date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break;
求两个日期相差天数:
DateUtil中有比较日期是否相同的方法,先比较两个日期的大小,设置一个数i=0,在设置一个循环,每次循环较小的日期加一,每循环一次i的值加一,直到两个日期相等。
相关部分代码:
case 3: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int ys = input.nextInt(); int ms = input.nextInt(); int ds = input.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); DateUtil dates = new DateUtil(ys,ms,ds); if (date.checkInputValidity()&&dates.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println(date.getDaysofDates(dates)); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break;
做题中遇到的问题:
在做题中遇到的最大问题就是对象和类的相关问题,类的构造方法以及类中方法和类中私有属性的调用问题。
解决方法:
查阅书籍后得知,自定义构造方法中如果涉及自定义类需在这个构造方法中new出一个新的另一个类并给它赋值。
b、题目集5中7-5题的思路:
具体类的设计老师已经给出:

源代码:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] Args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int a = input.nextInt(); switch (a) { case 1: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getNextNdays(n); System.out.println(y+"-"+m+"-"+d+" next "+n+" days is:"+date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } break; case 2: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getPreviousNdays(n); System.out.println(y+"-"+m+"-"+d+" previous "+n+" days is:"+date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break; case 3: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int ys = input.nextInt(); int ms = input.nextInt(); int ds = input.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); DateUtil dates = new DateUtil(ys,ms,ds); if (date.checkInputValidity()&&dates.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("The days between "+date.showDate()+" and "+dates.showDate()+" are:"+date.getDaysofDates(dates)); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Year{ private int value; Year(){ } Year(int value){ this.value=value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value=value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public boolean isLeapYear(int year) { boolean k=false; if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0) k=true; return k; } public boolean validate(){ if (this.getValue()>=1820&&this.getValue()<=2020) return true; else return false; } public void yearIncrement(){ this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } public void yearReduction(){ this.setValue(this.getValue()-1); } } class Month{ private int value; private Year year; Month(){ } Month(int yearValue,int month){ year = new Year(yearValue); //year.setValue(yearValue); this.setValue(month); } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } public Year getYear() { return year; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void resetMin(){ this.setValue(1); } public void resetMax(){ this.setValue(12); } public boolean validate(){ if (value>=1&&value<=12&&year.validate()) return true; else return false; } public void monthIncrement(){ if (this.getValue() == 12) { resetMin(); year.yearIncrement(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } } public void monthReduction(){ if (this.getValue() == 1) { resetMax(); year.yearReduction(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()-1); } } } class Day { private int value; private Month month; private int[] mon_maxnum1= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; private int[] mon_maxnum2 = {31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; Day(){ } Day(int yearValue,int monthvalue,int dayvalue){ month = new Month(yearValue,monthvalue); // month.getYear().setValue(yearValue); // month.setValue(monthvalue); this.setValue(dayvalue); } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setMonth(Month month) { this.month = month; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void resetMin(){ this.value = 1; } public void resetMax(){ if (month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue())) { this.setValue(mon_maxnum2[month.getValue()-1]); } else this.setValue(mon_maxnum1[month.getValue()-1]);; } public boolean valiDate(){ if (month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue())) { if (value >= 1 && value <= 31 && (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)) return true; else if (value >= 1 && value <= 30 && (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)) return true; else if (value>=1&&value<=29&&month.getValue()==2) return true; else return false; } else { if (value >= 1 && value <= 31 && (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)) return true; else if (value >= 1 && value <= 30 && (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)) return true; else if (value>=1&&value<=28&&month.getValue()==2) return true; else return false; } } public void dayIncrement(){ if(month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue())) { if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum2[month.getValue()-1]) { month.monthIncrement(); resetMin(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } } else { if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum1[month.getValue()-1]) { month.monthIncrement(); resetMin(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } } } public void dayReduction(){ if (this.getValue()== 1) { month.monthReduction(); resetMax(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()-1); } } } class DateUtil { private Day day; DateUtil(){ } DateUtil(int y,int m,int d){ day = new Day(y,m,d); // day.getMonth().setValue(m); // day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); //// day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(y); //// day.getMonth().setValue(m); // day.setValue(d); } public void setDay(Day day) { this.day = day; } public Day getDay() { return day; } public boolean checkInputValidity(){ if (day.getMonth().getYear().validate()&&day.getMonth().validate()&&day.valiDate()) return true; else return false; } public boolean compareDates(DateUtil d2){ if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return true; else if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return true; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getValue()>d2.getDay().getValue()) return true; else if (day.getValue()<d2.getDay().getValue()) return false; else return true; } public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil d2){ if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getYear().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()>d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getMonth().getValue()<d2.getDay().getMonth().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getValue()>d2.getDay().getValue()) return false; else if (day.getValue()<d2.getDay().getValue()) return false; else return true; } public String showDate(){ return day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue(); } public DateUtil getNextNdays(int n){ if (n<=365) { do { day.dayIncrement(); n--; }while (n!=0); DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); return date1; } else { do { day.dayIncrement(); n--; }while (day.getMonth().getValue()!=12&&day.getValue()!=31); do { if (day.getMonth().getYear().isLeapYear(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue())) n=n-366; else n=n-365; day.getMonth().getYear().setValue(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+1); }while (n<366) ; while (n!=0) { day.dayIncrement(); n--; } day.setValue(day.getValue()-1); DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()); return date1; } } public DateUtil getPreviousNdays(int n){ do { day.dayReduction(); n--; }while (n!=0); DateUtil date2 = new DateUtil(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getValue()); return date2; } public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil da2){ int x = 0; if (this.equalTwoDates(da2)) { return 0; } else if (this.compareDates(da2)) { do { day.dayReduction(); x++; }while (!this.equalTwoDates(da2)); } else do { day.dayIncrement(); x++; }while (!this.equalTwoDates(da2)); return x; } }
说明:
DateUtil类分别和Year类、Month类、Day类是聚合关系,DateUtil类的实现的功能更多。
功能实现:
求下n天:在输入相关的值之后会进行一次数据的合法性校验。年、月、日都有相关的自增的方法,Day的自增方法和Month相关,到月末的那一天之后一天会调用一次Month的自增方法,Day的值变为最小。月到12月自增方法会调用Year的自增方法,然后Month的值变为最小。就这样循环n次Day的自增方法求得下n天。
相关部分代码:
case 1: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getNextNdays(n); System.out.println(y+"-"+m+"-"+d+" next "+n+" days is:"+date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format");
求前n天:思路同上,把自增方法改为自减方法即可。
相关部分代码:
case 2: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int n = input.nextInt(); Year y1 = new Year(y); Month m1 = new Month(y,m); Day d1 = new Day(y,m,d); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); if (y1.validate()&& m1.validate()&& d1.valiDate()) { date.getPreviousNdays(n); System.out.println(y+"-"+m+"-"+d+" previous "+n+" days is:"+date.showDate()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break;
求两个日期相差天数:
DateUtil中有比较日期是否相同的方法,先比较两个日期的大小,设置一个数i=0,在设置一个循环,每次循环较小的日期加一,每循环一次i的值加一,直到两个日期相等。
相关部分代码:
case 3: { int y = input.nextInt(); int m = input.nextInt(); int d = input.nextInt(); int ys = input.nextInt(); int ms = input.nextInt(); int ds = input.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(y,m,d); DateUtil dates = new DateUtil(ys,ms,ds); if (date.checkInputValidity()&&dates.checkInputValidity()) System.out.println("The days between "+date.showDate()+" and "+dates.showDate()+" are:"+date.getDaysofDates(dates)); else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); }break;
做题过程中遇到的问题:
最大的问题就是在计算前(后)n天时会遇到运行超时的问题。
解决方法:
把之前的用一天一天循环的方法换为先增到整年再用剩余的天数减去下一年的天数,年份加一。
c、7-2、7-5两种日期类设计的比较
7-2和7-5最大的区别是7-2是把Year类、Month类、Day类两两相聚和。而7-5是Year类、Month类、Day类依次和DateUtil类聚合,各有各的优势。
7-2优势:更能体现日、月、年之间的关系。缺点:方法不够统一,代码更复杂,不够简明。
7-5优势:方法统一,核心统一到一个类中。缺点:不能清楚地体现年、月、日之间的关系。
2、题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用:
a、题目集4(7-3)设计的思路和具体技术运用:
具体类的设计:

源代码:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main4 { public static void main(String[] Args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int n = input.nextInt(); switch (n) { case 1: { double x = input.nextDouble(); if (x<=0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { Circle c1 = new Circle(); c1.setRadius(x); System.out.println(c1.toString()); System.out.println(c1.toString1()); System.out.printf("Circle's area:%.2f",c1.getArea()); } } break; case 2: { double x = input.nextDouble(); double y = input.nextDouble(); if (x<=0||y<=0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle(); r1.setLength(x); r1.setWidth(y); System.out.println(r1.toString()); System.out.println(r1.toString2()); System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f",r1.getArea()); } } break; case 3: { double x = input.nextDouble(); if (x<=0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { Ball b1 = new Ball(); b1.setRadius(x); System.out.println(b1.toString()); System.out.println(b1.toString1()); System.out.println(b1.toString3()); System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f\n",b1.getArea()); System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f",b1.getTiji()); } } break; case 4: { double x = input.nextDouble(); double y = input.nextDouble(); double z = input.nextDouble(); if (x<=0||y<=0||z<=0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { Box a1 = new Box(); a1.setHeight(x); a1.setLength(y); a1.setWidth(z); System.out.println(a1.toString()); System.out.println(a1.toString2()); System.out.println(a1.toString4()); System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f\n",a1.getArea()); System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f",a1.getTiji()); } } break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Shape{ Shape(){ } public String toString(){ return "Constructing Shape"; } public double getArea(){ double area=0; return area; } } class Circle extends Shape{ Circle(){ } public String toString1(){ return "Constructing Circle"; } private double radius; public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } @Override public double getArea() { return (Math.PI*radius*radius); } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ Rectangle(){ } public String toString2(){ return "Constructing Rectangle"; } private double width; private double length; public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getLength() { return length; } @Override public double getArea() { return width*length; } } class Ball extends Circle{ Ball(){ } public String toString3(){ return "Constructing Ball"; } @Override public double getArea() { return 4*Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius(); } public double getTiji(){ return (4*Math.PI*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius()*super.getRadius())/3; } } class Box extends Rectangle{ Box(){ } public String toString4(){ return "Constructing Box"; } private double height; public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } public double getHeight() { return height; } @Override public double getArea() { return 2*getHeight()*getLength()+2*getHeight()*getWidth()+2*getWidth()*getLength(); } public double getTiji(){ return getHeight()*getWidth()*getLength(); } }
思路说明:
Shape类是所有图形类的父类,Circle类和Rectangle类继承Shape类,Ball类继承Cilcle类,Box类继承Rectangle类。Shape类中有求面积方法,当时还不知道抽象方法,那个方法就是随便返回了一个值,在其他的具体类中有重写了具体的求面积和体积的方法。
功能实现:
先建立相关的对象,输入对象的相关的属性值之后,调用对象的求面积或者体积的方法求得相应的面积和体积,最后输出。
做题中遇到的问题:
当时给我的疑惑就是Shape类中的那个getAear()方法怎么写,因为Shape没有具体的实例,不知道怎么写,当时还不知道抽象类和抽象方法,所以不知道怎么办。
解决方法:
当时没有解决,就随便写了一下,随便返回了一个值,然后再之后的方法中再重写求面积的方法。
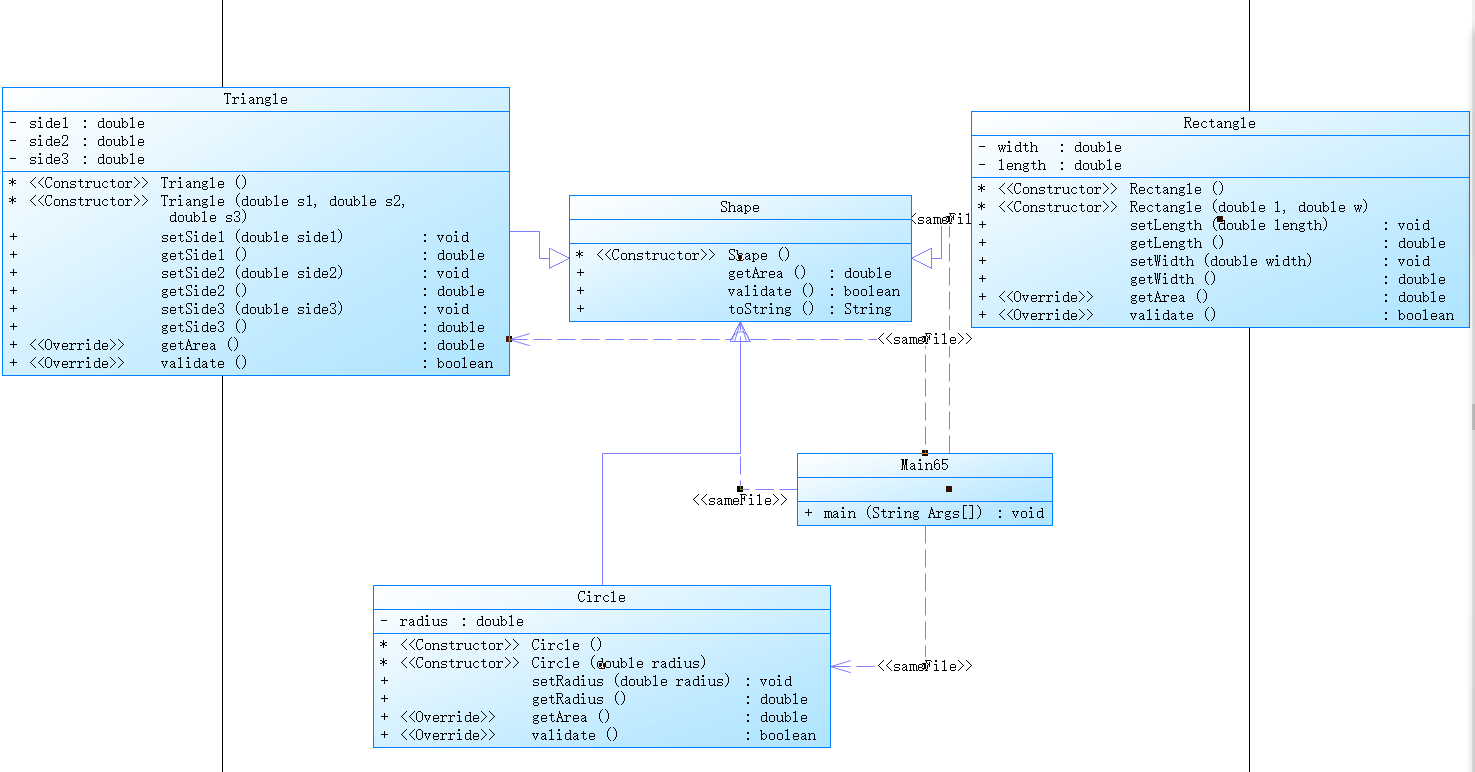
b、题目集6(7-5)设计的思路和具体技术运用:
具体类的设计:
源代码:

import java.lang.reflect.Array; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main65 { public static void main(String[] Args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int cs = input.nextInt(); int rs = input.nextInt(); int ts = input.nextInt(); if (cs==0||rs==0||ts==0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else if (cs == 0 && rs == 0 && ts == 0) { System.out.println("Original area:\n"); System.out.println("Sum of area:0.00"); System.out.println("Sorted area:\n"); System.out.println("Sum of area:0.00"); } else { int i = 0; ArrayList<Circle> circles = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Rectangle> rectangles = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Triangle> triangles = new ArrayList<>(); for (i = 0; i < cs; i++) { double r = input.nextDouble(); Circle circle = new Circle(r); circles.add(circle); } for (i = 0; i < rs; i++) { double l = input.nextDouble(); double w = input.nextDouble(); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(l, w); rectangles.add(rectangle); } for (i = 0; i < ts; i++) { double s1 = input.nextDouble(); double s2 = input.nextDouble(); double s3 = input.nextDouble(); Triangle triangle = new Triangle(s1, s2, s3); triangles.add(triangle); } boolean tof1 = true; boolean tof2 = true; boolean tof3 = true; for (i = 0; i < cs; i++) { if (!circles.get(i).validate()) { tof1 = false; break; } else if (i == cs - 1 && circles.get(i).validate()) tof1 = true; } for (i = 0; i < rs; i++) { if (!rectangles.get(i).validate()) { tof2 = false; break; } else if (i == rs - 1 && rectangles.get(i).validate()) tof2 = true; } for (i = 0; i < ts; i++) { if (!triangles.get(i).validate()) { tof3 = false; break; } else if (i == ts - 1 && triangles.get(i).validate()) tof3 = true; } if (tof1 && tof2 && tof3) { double sum = 0; System.out.print("Original area:\n"); double[] areas = new double[cs + rs + ts]; for (i = 0; i < cs; i++) { System.out.printf("%.2f ", circles.get(i).getArea()); sum = sum + circles.get(i).getArea(); areas[i] = circles.get(i).getArea(); } for (i = 0; i < rs; i++) { System.out.printf("%.2f ", rectangles.get(i).getArea()); sum = sum + rectangles.get(i).getArea(); areas[cs + i] = rectangles.get(i).getArea(); } for (i = 0; i < ts; i++) { System.out.printf("%.2f ", triangles.get(i).getArea()); sum = sum + triangles.get(i).getArea(); areas[cs + rs + i] = triangles.get(i).getArea(); } System.out.printf("\nSum of area:%.2f", sum); System.out.print("\nSorted area:"); Arrays.sort(areas); for (i = 0; i < cs + rs + ts; i++) { if (i == 0) System.out.printf("\n%.2f ", areas[i]); else System.out.printf("%.2f ", areas[i]); } System.out.printf("\nSum of area:%.2f", sum); } else System.out.print("Wrong Format"); } } } class Shape{ Shape(){ } public double getArea(){ double area = 0; return area; } public boolean validate(){ return false; } public String toString(){ return "String"; } } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; Circle(){ } Circle(double radius){ this.setRadius(radius); } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public double getArea(){ return Math.PI*this.radius*this.radius; } public boolean validate() { if (this.getRadius()<=0) return false; else return true; } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ private double width; private double length; Rectangle(){} Rectangle(double l,double w){ this.setLength(l); this.setWidth(w); } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public double getArea() { return this.width*this.length; } public boolean validate() { if (this.getWidth()<=0&&this.getLength()<=0) return false; else return true; } } class Triangle extends Shape{ private double side1; private double side2; private double side3; Triangle(){ } Triangle(double s1,double s2,double s3){ this.setSide1(s1); this.setSide2(s2); this.setSide3(s3); } public void setSide1(double side1) { this.side1 = side1; } public double getSide1() { return side1; } public void setSide2(double side2) { this.side2 = side2; } public double getSide2() { return side2; } public void setSide3(double side3) { this.side3 = side3; } public double getSide3() { return side3; } public double getArea() { double p =(this.side1+this.side2+this.side3)/2; double d = p*(p-side1)*(p-side2)*(p-side3); double s = Math.sqrt(d); return s; } public boolean validate() { if (this.getSide1()<0&&this.getSide2()<0&&this.getSide3()<0) return false; else if (this.getSide1()+this.getSide2()>this.getSide3()&&this.side1+this.side3>this.side2&&this.side2+this.side3>this.side1) return true; else return false; } }
思路说明:
大概的设计和上次差不多,这次知道了抽象类和抽象方法,就在这次的题中得到了运用。
功能实现:
先建立相关的对象,输入对象的相关的属性值之后,调用对象的求面积或者体积的方法求得相应的面积和体积,最后输出。
问题:
知道了抽象类和抽象方法之后就感觉这次的题没有什么问题。
解决方法:
去提前学习老师要讲的东西。
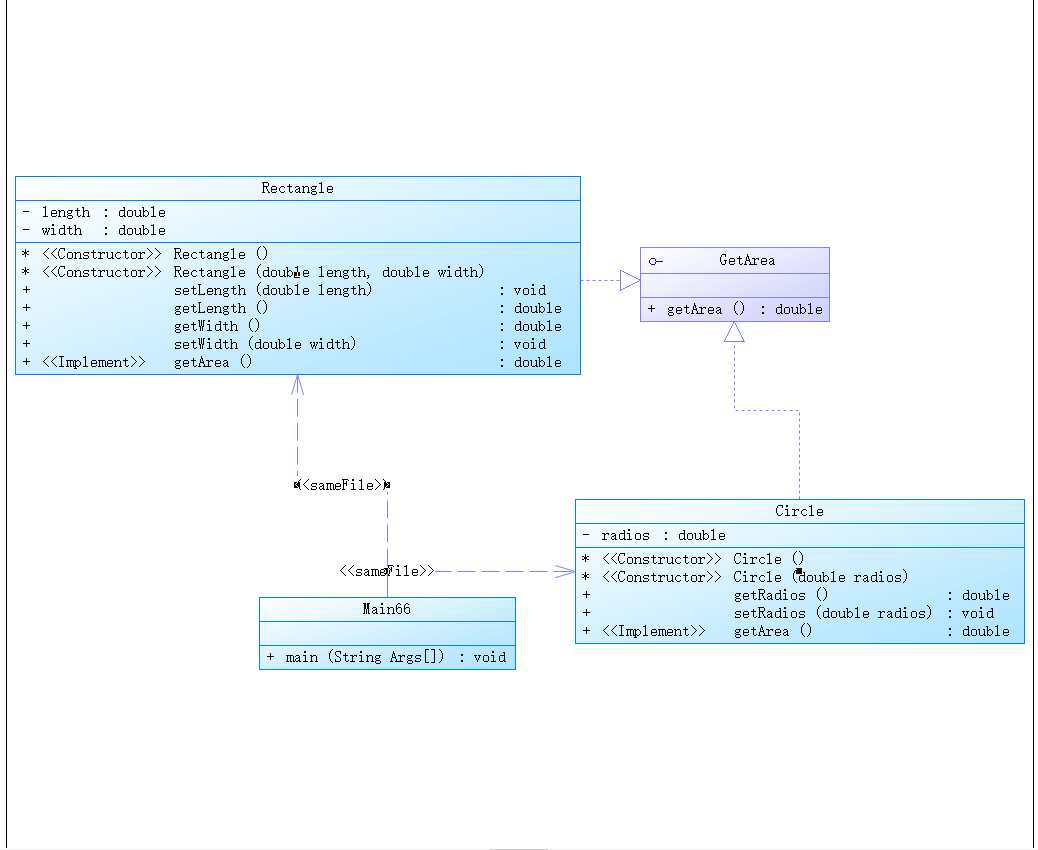
c、题目集6(7-6)设计的思路和具体技术运用:
具体类的设计:
源代码:

import java.util.Scanner; public class Main66 { public static void main(String[] Args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); double r = input.nextDouble(); double l = input.nextDouble(); double w = input.nextDouble(); Circle circle = new Circle(r); Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(l,w); if (r>0&&l>0&&w>0) { System.out.printf("%.2f\n",circle.getArea()); System.out.printf("%.2f",rectangle.getArea()); } else System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } interface GetArea{ public abstract double getArea(); } class Circle implements GetArea { private double radios; Circle(){ } Circle(double radios) { this.radios = radios; } public double getRadios() { return radios; } public void setRadios(double radios) { this.radios = radios; } @Override public double getArea() { return Math.PI*this.radios*this.radios; } } class Rectangle implements GetArea { private double length; private double width; Rectangle(){ } Rectangle(double length,double width) { this.width = width; this.length = length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getLength() { return length; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } @Override public double getArea() { return this.length*this.width; } }
思路说明:
这次老师要求要用到接口,于是就把这次中的求面积的方法单独做成了一个接口,以实现求他功能。
学习了相关知识以后就没有什么问题。
c、三次图形设计作业的总结:
第一次作业中出现的问题,在第二次作业中的学习中得到了解决,通过这三次的图形设计作业我学到了抽象类、抽象方法、以及接口的相关知识,解决了我在第一次作业中的困惑。
3、对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结:
分析:
这三次作业中有一个大题,三个小题,大题难度较大,三道小题没什么问题。
总结:
这次总结一下Java中Pattern类与Matcher类
我在网上看的一个博客有一句话:
Pattern和Matcher Pattern 一个Pattern是一个正则表达式经编译后的表现模式。 Matcher 一个Matcher对象是一个状态机器,它依据Pattern对象做为匹配模式对字符串展开匹配检查。 首先一个Pattern实例订制了一个所用语法与PERL的类似的正则表达式经编译后的模式,然后一个Matcher实例在这个给定的Pattern实例的模式控制下进行字符串的匹配工作。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「二十同学」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18298439/article/details/88974940
这句话说明了Pattern类和Matcher类之间的关系以及他们对正则表达式的运作,我的理解就是Pattern用来建立一个正则表达式的Pattern类对象,然后Matcher类再来与已创建的Pattern类对象进行匹配工作。
下面就谈一谈Pattern类和Matcher类
Pattern类:
Pattern类的构造器是私有的,不能用new来创造Pattern对象,Pattern调用静态方法compile返回Pattern实例。
a、对象的创建:Pattern.compile();将给定的正则表达式编译并赋予给Pattern类
b、Pattern.tostring()和Pattern.pattern():返回该Patter对象所编译的正则表达式。
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("\\d+");
System.out.println(p.toString());// 输出\d+
System.out.println(p.pattern());// 输出\d+
c、Pattern.split():此方法用于分隔字符串。
Pattern p=Pattern.compile("\\d+");
String[] str=p.split("我的QQ是:456456我的电话是:0532214我的邮箱是:aaa@aaa.com");
Pattern.split()可直接返回一个数组。
d、Pattern.matcher():
用于快速匹配字符串,该方法适合用于只匹配一次,且匹配全部字符串.
Pattern.matches("\\d+","2223");//返回true
Pattern.matches("\\d+","2223aa");//返回false,需要匹配到所有字符串才能返回true,这里aa不能匹配到
Pattern.matches("\\d+","22bb23");//返回false,需要匹配到所有字符串才能返回true,这里bb不能匹配到
Pattern.matcher()返回的是boolean型的结果。
Matcher类:
Matcher类的构造方法也是私有的,不能随意创建,只能通过Pattern.matcher(CharSequence input)方法得到该类的实例.
a、获取Matcher类的实例
Pattern p=Pattern.compile("\\d+");
Matcher m=p.matcher("22bb23");
m.pattern();//返回p 也就是返回该Matcher对象是由哪个Pattern对象的创建的
b、Matcher.matches():匹配Pattern实例,只有完全匹配时才会返回true。
c、Matcher.lookingAt():从目标字符串开始位置进行匹配。只有在有匹配且匹配的某一子串中包含目标字符串第一个字符的情况下才会返回true。
d、Matcher.regionStart():报告此匹配器区域的开始索引。end()方法返回的是匹配器的状态from。
e、Matcher.regionend():报告此匹配器区域的结束索引(不包括)。end()方法返回的是匹配器的状态to。
4、题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结:
这一题当时做的时候也不会,之后我又看了看相关的集合的知识,在这里做一下总结。(由于我只学了Collection集合和Map集合,就先只总结这两种)
Collection集合:
主要有两大类:List类和Set类
List类:有索引,可以储存重复元素,可以保证存储顺序。
Set类:没有索引,不可以储存重复元素,不可以保证存储顺序。
Collection类中的一些方法:
boolean add():添加元素
boolean remove():删除集合中的某个元素
void clear():清空集合中的所有元素
boolean contain():判断集合中是否包含某个元素
boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
int size():获取长度
Object[ ] toArray():将集合转换为一个数组
Map类集合:
特点:
1.Map集合是一个双列集合,一个元素包含两个值(一个key, 一个value)
2.Map集合中的元素,key和value的数据类型可以相同,也可以不同
3.Map集合中的元素, key是不允许重复的,value是可以重复的
4.Map集合中的元素, key和value是一 一对应
HashMap集合的特点:
1.HashMap集合底层是哈希表:查询的速度特别的快
2. HashMop集合是一一个无序的集合,存储元素和提出元素的顺序有可能不一致
LinkedHashMap的特点:
1.LinkedHashMop集合底层是哈希表+链表(保证迭代的顺序)
2.LinkedHashMap集合是一个有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的
Map集合的一些方法:
put(k,v):放进去一个元素。
contain(k):是否包含键k
contain(v):是否包含值v
clear():清楚所有元素
三、采坑心得
做题的过程中遇到了两个给我印象特别深的错误(坑)
第一个:计算日期时的循环。(第五次作业的7-5)
具体的图已经找不到了(当时pta出问题了提交之后测试点全是内部错误,之后都没管过现在已经看不了那里的错误了),就说一下具体情况吧。
在第四次作业时求下n天使用的一天一天的循环,代码如下:
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue()))
{
if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum2[month.getValue()-1])
{
month.monthIncrement();
resetMin();
}
else
{
this.setValue(this.getValue()+1);
}
}
else
{
if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum1[month.getValue()-1])
{
month.monthIncrement();
resetMin();
}
else
{
this.setValue(this.getValue()+1);
}
}
但是在第五次作业中就不行了,显示运行超时,当时不知道怎么办,我们寝室一个人就说这个循环太久了,直接一年一年的加算了,结果还真过了,当时感觉就是一些小细节都应该注意到,这样对以后编程有很大帮助。
修改后代码如下:
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear(month.getYear().getValue())) { if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum2[month.getValue()-1]) { month.monthIncrement(); resetMin(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } } else { if (this.getValue()== mon_maxnum1[month.getValue()-1]) { month.monthIncrement(); resetMin(); } else { this.setValue(this.getValue()+1); } }
第二个坑:
第二个就是我在之前已经提到过的第一次图形设计题中的那个Shape类中的getaera方法不知道怎么办,当时我就用最愚蠢的方法直接随便返回了一个值如图:

之后学了抽象类和抽象方法之后就没有问题了,以后老师布置作业前需要提前一张学习东西这样做题就不会这么麻烦了。
四、改进建议:
以后老师可以把做的pta上题讲一讲。
五、总结:
这三次的作业我感觉我学到了很多,对类的掌握更加深刻,继承、多态都感觉有很大进步,还有接口,集合,对它们的理解个更深刻。同时我也认识到了自身的不足,尤其是在学习效率这方面有待提高,其中很大一部分原因就是没有提前预习,以后要在每次上课及作业发布之前预习相关知识。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号