基于树的迷宫算法
基于树的迷宫算法
完整代码
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
class maze
{
private:
int rows;
int cols;
int start_x;
int start_y;
int end_x;
int end_y;
char **matrix;
enum direction {UP = 0,LEFT = 1,DOWN = 2,RIGHT = 3};
public:
maze(int rows,int cols);
~maze();
public:
void print_maze(void);
void create_maze(void);
void find_exitance(int move_x,int move_y);
bool vaild_move(int move_x,int move_y);
int Get_Start_Point_X(void);
int Get_Start_Point_Y(void);
};
maze::maze(const int rows,const int cols)
{
cout << "create the maze structure" << endl;
this->rows = rows;
this->cols = cols;
this->start_x = 0;
this->start_y = 0;
this->end_x = 0;
this->end_y = 0;
for(int x = 0; x < rows; x++) {
this->matrix = new char *[cols];
for(int y = 0; y < cols; y++) {
this->matrix[y] = new char;
}
}
}
maze::~maze()
{
cout << "destory the maze structure" << endl;
delete this->matrix;
}
void maze::print_maze(void)
{
for(int x = 0; x < this->rows; x++) {
for(int y = 0; y < this->cols; y++) {
cout << this->matrix[x][y];
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void maze::create_maze(void)
{
int Entry = 0, Exit = 0;
//add rand seed aim to cause many different data
srand((int)time(NULL));
//(1)create the plane
for(int x = 0; x < this->rows; x++) {
for(int y = 0; y < this->cols; y++) {
this->matrix[x][y] = '#';
}
}
//(2)choose the direction of entrance and exitance
do {
Entry = rand() % 4;
Exit = rand() % 4;
} while(Entry == Exit);
//(3)define the wall four direction about entrance
if(Entry == this->UP) {
this->start_x = 0;
this->start_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
} else if(Entry == this->LEFT) {
this->start_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->start_y = 0;
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
} else if(Entry == this->RIGHT) {
this->start_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->start_y = this->cols - 1;
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
} else { //down
this->start_x = this->rows - 1;
this->start_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
}
//(4)define the wall four direction about exitance
if(Exit == this->UP) {
this->end_x = 0;
this->end_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
} else if(Exit == this->LEFT) {
this->end_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
this->end_y = 0;
} else if(Exit == this->RIGHT) {
this->end_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->end_y = this->cols - 1;
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
} else { //down
this->end_x = this->rows - 1;
this->end_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
}
//(5)fill the step on the wall
#if 0
for(int x = 1; x <= this->rows - 2; x++) {
for(int y = 1; y <= this->cols - 2; y++) {
this->matrix[x][y] = rand()% 2 == 0 ? '0' : '#';
}
}
#else
int temp_x = 0;
int temp_y = 0;
for(int loop = 1;loop < (this->rows-2)*(this->cols-2); loop++) {
temp_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows-2);
temp_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols-2);
this->matrix[temp_x][temp_y] = '0';
}
#endif
this->print_maze();
}
void maze::find_exitance(int move_x,int move_y)
{
static bool judge = false;
static int succ = 0;
this->matrix[move_x][move_y] = 'x';
//cout << "move_x = " << move_x << ", move_y = " << move_y << endl; //debug the program
if(move_x == this->end_x && move_y == this->end_y) {
cout << "the exitance is finded" << endl;
this->print_maze();
succ++;
return;
}
//(1)UP
if(this->vaild_move(move_x - 1,move_y)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x - 1,move_y);
}
//(2)LEFT
if(this->vaild_move(move_x,move_y - 1)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x,move_y - 1);
}
//(3)RIGHT
if(this->vaild_move(move_x,move_y + 1)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x,move_y + 1);
}
//(4)DOWN
if(this->vaild_move(move_x + 1,move_y)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x + 1,move_y);
}
//this->print_maze(); //debug the program
if(judge == false) {
cout << "the entrance is block" << endl;
return;
}
if(judge == true && move_x == this->start_x && move_y == this->start_y && succ == 0) {
cout << "try all prossiblilty,not chance to go home!" << endl;
return;
}
}
bool maze::vaild_move(int move_x, int move_y)
{
#if 1
return (move_x >= 0 && move_x <= this->rows - 1 && move_y >= 0 && move_y <= this->cols - 1 \
&& this->matrix[move_x][move_y] != 'x' && this->matrix[move_x][move_y] != '#');
#else
//optimize some calculate method
return (move_x >= 0 && move_x < this->rows && move_y >= 0move_y < this->cols \
&& this->matrix[move_x][move_y] != 'x' && this->matrix[move_x][move_y] != '#');
#endif
}
int maze::Get_Start_Point_X(void)
{
return this->start_x;
}
int maze::Get_Start_Point_Y(void)
{
return this->start_y;
}
int main(void)
{
maze *my_maze = new maze(6,6);
my_maze->create_maze();
my_maze->find_exitance(my_maze->Get_Start_Point_X(),my_maze->Get_Start_Point_Y());
free(my_maze);
}
详细解释
以完整代码中6行6列的迷宫进行说明
create_maze函数说明
void maze::create_maze(void)
{
int Entry = 0, Exit = 0;
//add rand seed aim to cause many different data
srand((int)time(NULL));
//(1)create the plane
for(int x = 0; x < this->rows; x++) {
for(int y = 0; y < this->cols; y++) {
this->matrix[x][y] = '#';
}
}
//(2)choose the direction of entrance and exitance
do {
Entry = rand() % 4;
Exit = rand() % 4;
} while(Entry == Exit);
//(3)define the wall four direction about entrance
if(Entry == this->UP) {
this->start_x = 0;
this->start_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
} else if(Entry == this->LEFT) {
this->start_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->start_y = 0;
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
} else if(Entry == this->RIGHT) {
this->start_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->start_y = this->cols - 1;
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
} else { //down
this->start_x = this->rows - 1;
this->start_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->start_x][this->start_y] = '0';
}
//(4)define the wall four direction about exitance
if(Exit == this->UP) {
this->end_x = 0;
this->end_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
} else if(Exit == this->LEFT) {
this->end_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
this->end_y = 0;
} else if(Exit == this->RIGHT) {
this->end_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows - 2);
this->end_y = this->cols - 1;
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
} else { //down
this->end_x = this->rows - 1;
this->end_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols - 2);
this->matrix[this->end_x][this->end_y] = '0';
}
//(5)fill the step on the wall
#if 0
for(int x = 1; x <= this->rows - 2; x++) {
for(int y = 1; y <= this->cols - 2; y++) {
this->matrix[x][y] = rand()% 2 == 0 ? '0' : '#';
}
}
#else
int temp_x = 0;
int temp_y = 0;
for(int loop = 1;loop < (this->rows-2)*(this->cols-2); loop++) {
temp_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows-2);
temp_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols-2);
this->matrix[temp_x][temp_y] = '0';
}
#endif
this->print_maze();
}
create_maze的作用其实就是创建迷宫。创建迷宫有五个步骤,分别对应注释:
(1)打好地基,建立一个6*6的'#'方阵
(2)选择两堵墙,总共有四堵墙,我们规定入口和出口一定要在不同的墙壁上。也就是需要定义入口和出口在不同的墙壁上。这里只是定义方向而已
(3)选择入口墙壁
(4)选择出口墙壁
(5)填满空区域,因为我们只定义了入口和出口,但是还没有内容
下面,为了更好的理解笔者所述的话,笔者分别编辑了图片对这些步骤进行说明,也方便以后回顾的时候会有清晰的记忆^~^!!!
对应(1)步骤
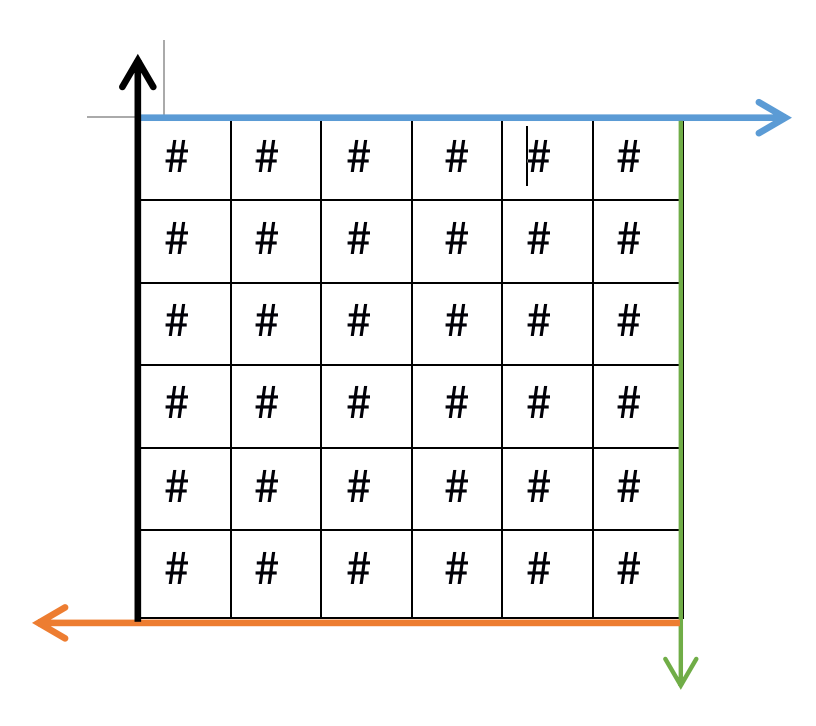
对应(2)步骤,定义四个方向
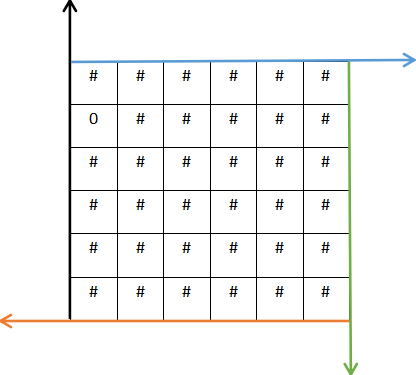
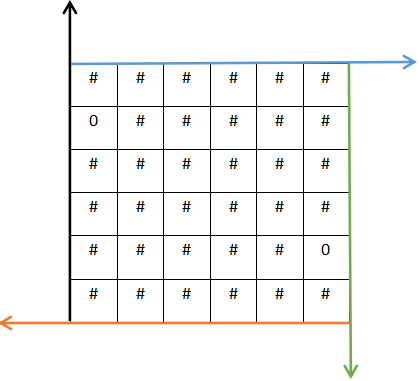
对应(3)步骤,选择一堵任意的墙作为入口
我们现在选择黑色线方向作为入口,其对应y轴是固定的,即 (这里为1不是0是因为假如把0放到去左上角就会出现含义混乱,因为此时黑线和蓝线相交于一点,从代码的含义来看方向就不具有唯一性了)1 < x < 5(这里小于5和大于1的原理是一样的,都要保证各个墙壁方向的唯一性),y=0,对应代码的写法是x = 1+rand()%(rows-2),y = 0
同理所得:
假如以蓝色线方向作为入口,x = 0,1 < y < 5,对应代码的写法是x = 0,y = 1 + rand()%(cols-2)
假如以绿色线方向作为入口,1 < x < 5,y = 5(6-1,下标值),对应代码的写法是x = 1+rand()%(rows-2),y = cols-1
假如以橙色线方向作为入口,x = 5(6-1,下标值),1 < y < 5, 对应代码的写法是x=rows-1,y = 1+rand()%(cols-2)
对应(4)步骤,选择一堵任意的墙作为出口
我们现在选择以绿色方向线的墙壁作为出口,根据(3)步骤的说明我们可以得出,此时绿色方向线作为出口的x,y的范围分别为1 < x < 5,y = 5(6-1,下标值),对应代码为x=1+rand()%(rows-2),y=cols-1
同理所得:
假如以蓝色线方向作为出口,x = 0,1 < y < 5,对应代码的写法是x = 0,y = 1 + rand()%(cols-2)
假如以橙色线方向作为出口,x = 5(6-1,下标值),1 < y < 5, 对应代码的写法是x=rows-1,y = 1+rand()%(cols-2)
假如以黑色线方向作为出口,1 < x < 5,y=0, 对应代码的写法是x = 1+rand()%(rows-2),y = 0
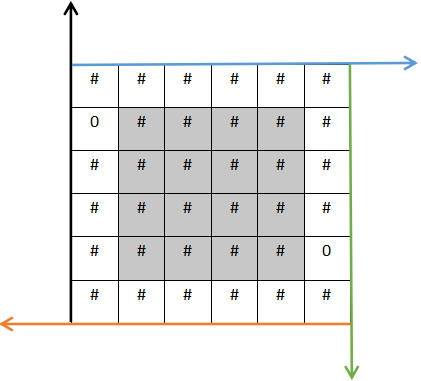
对应(5)步骤,填满非墙壁的空区域
对于我们现在所用的6*6矩阵我们可以通过任意的算法来把阴影空间补充满,我这边采用了两种算法:
1.遍历阴影部分的区域一次,随机分配可通行区域(即'0'),对应被注释的部分
2.对于此例子而言,把4*4个坑当作是16种分配的机会,每个坑每次被分配为'0'的机会都为1/16,对应未被注释的部分
//(5)fill the step on the wall
#if 0
for(int x = 1; x <= this->rows - 2; x++) {
for(int y = 1; y <= this->cols - 2; y++) {
this->matrix[x][y] = rand()% 2 == 0 ? '0' : '#';
}
}
#else
int temp_x = 0;
int temp_y = 0;
for(int loop = 1;loop < (this->rows-2)*(this->cols-2); loop++) {
temp_x = 1 + rand()%(this->rows-2);
temp_y = 1 + rand()%(this->cols-2);
this->matrix[temp_x][temp_y] = '0';
}
#endif
通过了如上部分的图解,一个迷宫就自建好了,接着就是寻找出口了!!!
find_exitance函数说明
void maze::find_exitance(int move_x,int move_y)
{
static bool judge = false;
static int succ = 0;
this->matrix[move_x][move_y] = 'x';
//cout << "move_x = " << move_x << ", move_y = " << move_y << endl; //debug the program
if(move_x == this->end_x && move_y == this->end_y) {
cout << "the exitance is finded" << endl;
this->print_maze();
succ++;
return;
}
//(1)UP
if(this->vaild_move(move_x - 1,move_y)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x - 1,move_y);
}
//(2)LEFT
if(this->vaild_move(move_x,move_y - 1)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x,move_y - 1);
}
//(3)RIGHT
if(this->vaild_move(move_x,move_y + 1)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x,move_y + 1);
}
//(4)DOWN
if(this->vaild_move(move_x + 1,move_y)) {
judge = true;
this->find_exitance(move_x + 1,move_y);
}
//this->print_maze(); //debug the program
if(judge == false) {
cout << "the entrance is block" << endl;
return;
}
if(judge == true && move_x == this->start_x && move_y == this->start_y && succ == 0) {
cout << "try all prossiblilty,not chance to go home!" << endl;
return;
}
}
find_exitance函数的作用就是通过不断的循迹迷宫,找到最终的出口
(1)先给定一个坐标,并将其置为'x',代表已经找过此路了,增加判断,假若当前坐标的(x,y)与终点坐标的(x,y)对应上了,我们则判定已经找到了迷宫的出口
(2)寻找上边位置是否可通行,如若可以通行,则将坐标定为上边的位置,重新回到(1)步骤继续查找,如若不可以通行,则继续进行(3)步骤
(3)寻找左边位置是否可通行,如若可以通行,则将坐标定为左边的位置,重新回到(1)步骤继续查找,如若不可以通行,则继续进行(4)步骤
(4)寻找右边位置是否可通行,如若可以通行,则将坐标定为右边的位置,重新回到(1)步骤继续查找,如若不可以通行,则继续进行(5)步骤
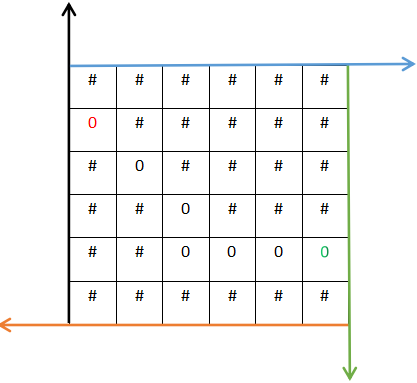
(5)寻找下边位置是否可通行,如若可以通行,则将坐标定为下边的位置,重新回到(1)步骤继续查找,如若不可以通行,则我们就要分析两种特殊的情况,我们将以生动的图像对两种特殊情况进行阐述
第一种特殊情况,入口直接被封死(入口被标定为红色,出口被标定为绿色)
第二种特殊情况,入口没被封死,但是走着走着发现无路可走了(入口被标定为红色,出口被标定为绿色)
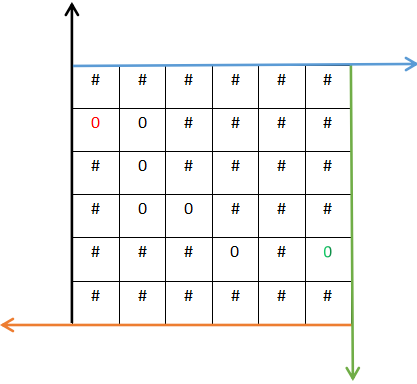
Note:为什么迷宫能够往回走,主要是基于入栈和弹栈的原理,栈的作用可以临时存储局部变量,故当有的路径发现走不通的时候,自然而然会弹栈,弹栈的过程就相当于回溯了,如果对栈有不理解的地方可以自行查阅栈的基本原理,笔者不才,就不在此篇章中展开论述了



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号