1 编译运行附件中的代码,提交运行结果截图,并说明程序功能
2 修改代码,把同步资源个数减少为3个,把使用资源的线程增加到 (你的学号%3 + 4)个,编译代码,提交修改后的代码和运行结果截图
1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM 3
int queue[NUM];
sem_t blank_number, product_number;
void *producer ( void * arg )
{
static int p = 0;
for ( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &blank_number );
queue[p] = rand() % 5;
printf("Product %d \n", queue[p]);
p = (p+1) % NUM;
sleep ( rand() % 5);
sem_post( &product_number );
}
}
void *consumer ( void * arg )
{
static int c = 0;
for( ;; ) {
sem_wait( &product_number );
printf("Consume %d\n", queue[c]);
c = (c+1) % NUM;
sleep( rand() % 5);
sem_post( &blank_number );
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[] )
{
pthread_t pid, cid;
sem_init( &blank_number, 0, NUM );
sem_init( &product_number, 0, 0);
pthread_create( &pid, NULL, producer, NULL);
pthread_create( &cid, NULL, consumer, NULL);
pthread_join( pid, NULL );
pthread_join( cid, NULL );
sem_destroy( &blank_number );
sem_destroy( &product_number );
return 0;
}
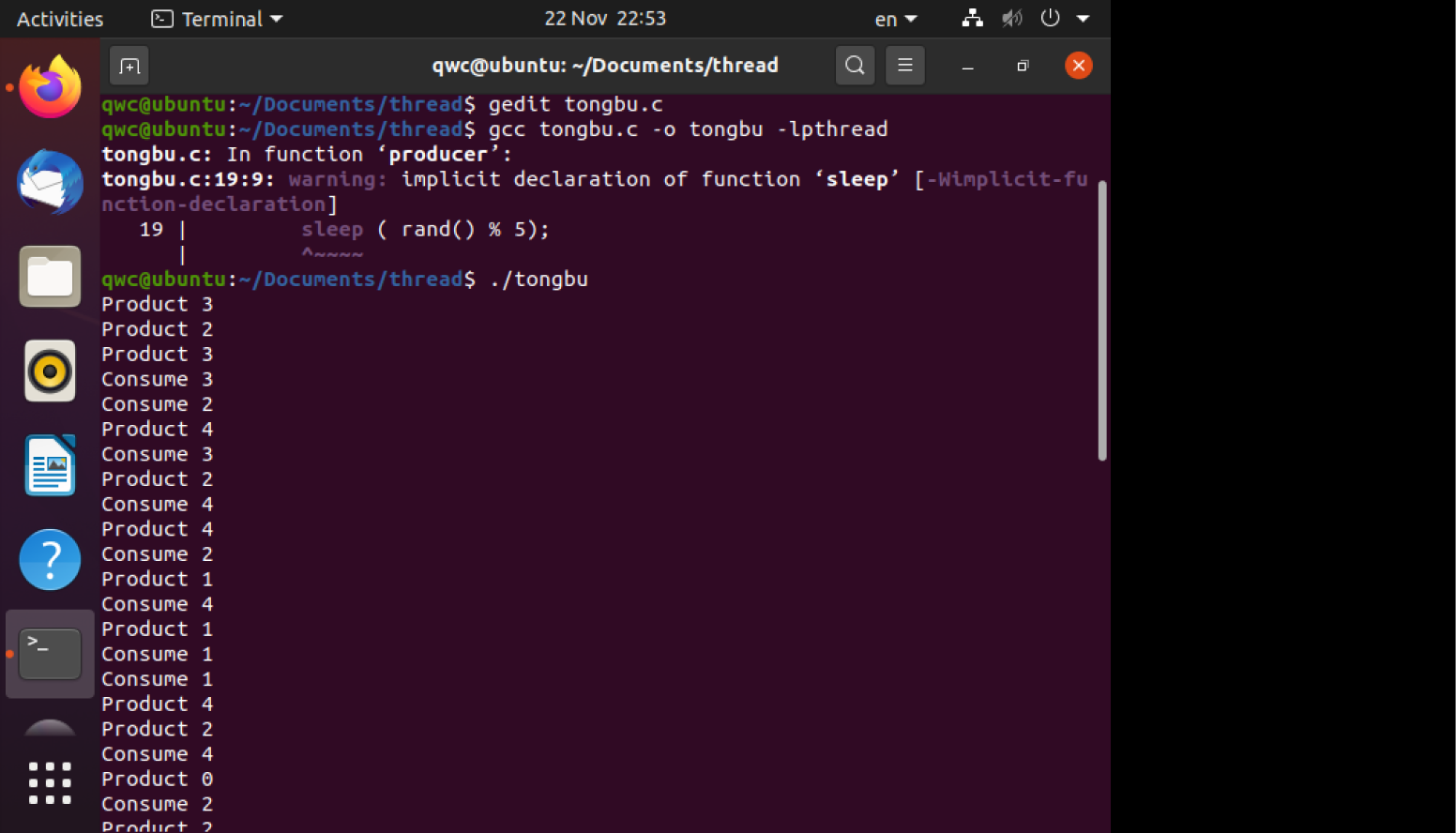
程序可理解为生产者消费者问题,初始状态为空,而后每一个生产者都要把自己生产的产品放入缓冲池,每个消费者从缓冲池中取走产品消费。在这种情况下,生产者消费者进程同步,只有通过互通消息才知道是否能存入产品或者取走产品。
2.学号%3+4=5,线程数为5,代码同上1



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号