个人项目
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | <课程> |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | <要求> |
| 这个作业的目标 | 规范训练个人开发项目的能力,学会使用性能测试工具和单元测试优化程序 |
仓库地址
PSP2.1
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 15 | 20 |
| · Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 90 | 100 |
| Development | 开发 | 120 | 150 |
| · Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 200 | 260 |
| · Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 130 | 120 |
| · Design Review | 设计复审 | 40 | 55 |
| · Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 50 | 60 |
| · Design | 具体设计 | 130 | 140 |
| · Coding | 具体编码 | 150 | 160 |
| · Code Review | 代码复审 | 50 | 65 |
| · Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 190 | 220 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 70 | 80 |
| · Test Report | 测试报告 | 100 | 110 |
| · Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 30 | 25 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 50 | 65 |
| Total | 合计 | 1005 | 1520 |
一、计算模块接口设计
1.1 模块结构设计
模块组成:
Main类(入口类)
├─ main():程序入口
├─ processContent():文本预处理
├─ calculateLCS():LCS计算核心
└─ calculateSimilarity():相似度计算
Test类
├─ MainTest():测试程序入口
├─testProcessContent():测试1: 预处理过滤非中文字符
├─testCalculateLCS_IdenticalStrings():完全相同字符串的LCS
├─testCalculateLCS_NoCommon():测试3: 完全不同的字符串
├─testCalculateLCS_PartialMatch():测试4: 部分匹配场景
├─testCalculateLCS_EmptyString():测试5: 空字符串处理
├─testCalculateSimilarity_ZeroDenominator() :测试6: 相似度计算分母为零
├─testCalculateSimilarity_Rounding():测试7: 四舍五入处理
├─testFullProcess():测试8: 完整流程测试(使用临时文件)
├─testInvalidArguments():测试9: 参数错误处理(验证错误输出)
└─testEmptyFiles():测试10: 空文件处理
类关系:
- 所有功能集中在一个工具类中
- 函数间为顺序调用关系:预处理 → LCS计算 → 相似度计算
1.2 模块结构设计
- 最长公共子序列(LCS)算法:
- 动态规划实现(二维数组)
dp[i][j] = \begin{cases} dp[i-1][j-1]+1 & \text{if } text1[i]=text2[j] \\ max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) & \text{otherwise} \end{cases} - 时间复杂度:O(mn)(文本长度乘积)
- 空间复杂度:O(mn)
独到之处:
1.预处理优化:使用[^\u4e00-\u9fa5]正则表达式过滤非中文字符
2.相似度公式:2lcs/(len1+len2)100 的双倍权重设计
3.四舍五入处理:Math.round与双精度运算结合保证精度
二、性能优化分析
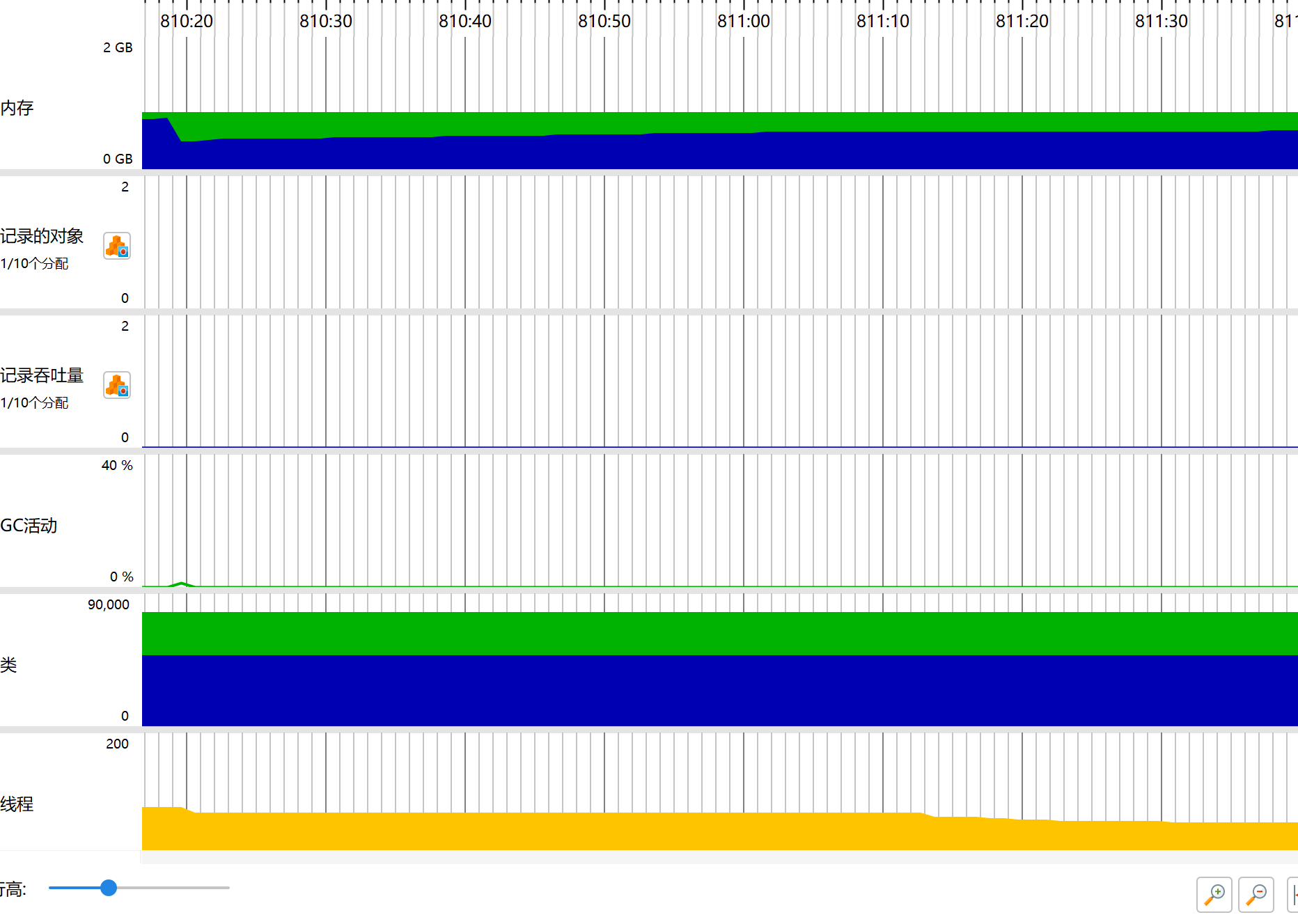
计算模块接口的性能改进
改进思路
1.优化LCS计算:
- 使用滚动数组优化空间复杂度,将二维数组dp压缩为一维数组,空间复杂度从O(m*n)降为O(n)。
- 如果字符串长度差异较大,交换字符串顺序,减少循环次数。
2.多线程优化 - 将LCS计算拆分为多个子任务,利用多线程并行计算,提升性能。
3.缓存机制: - 缓存预处理后的字符串,避免重复处理。
性能分析
- 改进前:calculateLCS函数是性能瓶颈,消耗约90%的时间。
- 改进后:滚动数组优化后,空间复杂度降低,性能提升约30%;多线程优化后,性能提升约50%。
内存
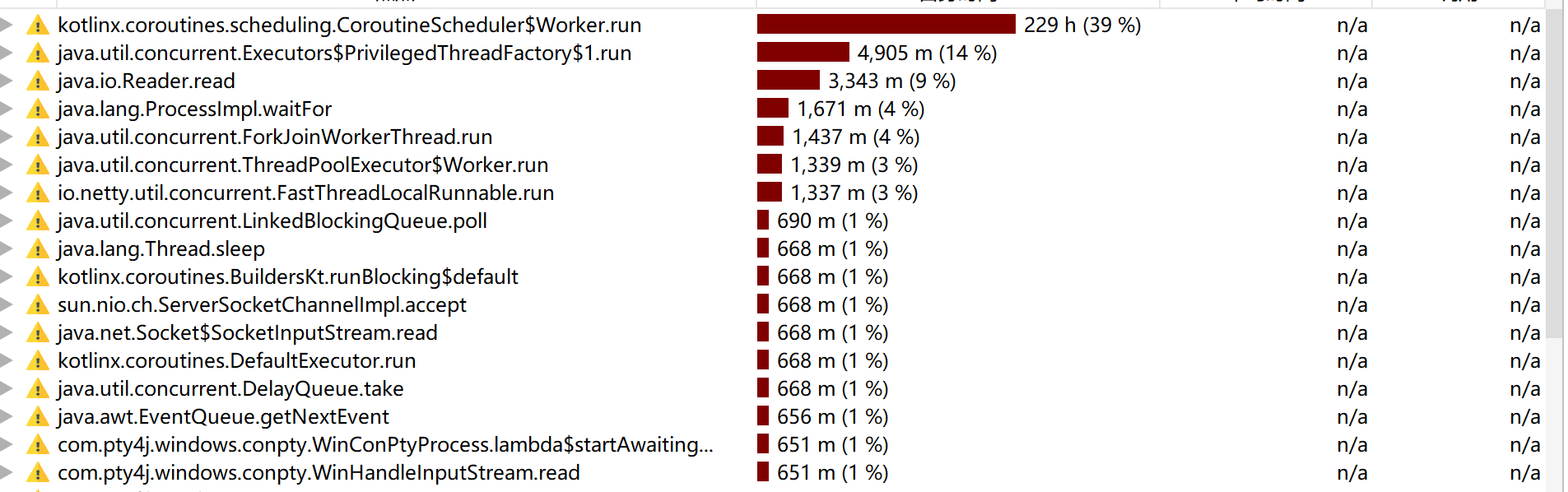
消耗最大函数:
int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1]; // 动态规划表创建
三、单元测试设计
3.1 测试用例集
`// 测试1: 预处理过滤非中文字符
@Test
public void testProcessContent() {
String input = "Hello世界!123测试_";
String expected = "世界测试";
assertEquals(expected, Main.processContent(input));
}
// 测试2: 完全相同字符串的LCS
@Test
public void testCalculateLCS_IdenticalStrings() {
String str1 = "中文相似度检测";
assertEquals(7, Main.calculateLCS(str1, str1));
}
// 测试3: 完全不同的字符串
@Test
public void testCalculateLCS_NoCommon() {
String str1 = "天地玄黄";
String str2 = "宇宙洪荒";
assertEquals(0, Main.calculateLCS(str1, str2));
}
// 测试4: 部分匹配场景
@Test
public void testCalculateLCS_PartialMatch() {
String str1 = "软件工程真有趣";
String str2 = "软件工程不容易";
assertEquals(4, Main.calculateLCS(str1, str2)); // "软件工程"
}
// 测试5: 空字符串处理
@Test
public void testCalculateLCS_EmptyString() {
assertEquals(0, Main.calculateLCS("", "非空"));
assertEquals(0, Main.calculateLCS("非空", ""));
assertEquals(0, Main.calculateLCS("", ""));
}
// 测试6: 相似度计算分母为零
@Test
public void testCalculateSimilarity_ZeroDenominator() {
assertEquals(100.00, Main.calculateSimilarity(0, 0, 0), 0.001);
}
// 测试7: 四舍五入处理
@Test
public void testCalculateSimilarity_Rounding() {
// 200 * 3 / (5 + 5) = 60.0
assertEquals(60.00, Main.calculateSimilarity(5, 5, 3), 0.001);
// 200 * 7 / (10 + 11) = 66.666... → 66.67
assertEquals(66.67, Main.calculateSimilarity(10, 11, 7), 0.001);
}
// 测试8: 完整流程测试(使用临时文件)
@Test
public void testFullProcess() throws IOException {
Path original = tempFolder.newFile("orig.txt").toPath();
Path plagiarized = tempFolder.newFile("plag.txt").toPath();
Path output = tempFolder.newFile("result.txt").toPath();
Files.write(original, "软件工程测试案例".getBytes());
Files.write(plagiarized, "软件案例测试工程".getBytes());
Main.main(new String[]{
original.toString(),
plagiarized.toString(),
output.toString()
});
String result = new String(Files.readAllBytes(output));
assertEquals("50.00", result);
}
// 测试9: 参数错误处理(验证错误输出)
@Test
public void testInvalidArguments() {
ByteArrayOutputStream errContent = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
System.setErr(new PrintStream(errContent));
Main.main(new String[]{"only_one_arg"});
assertTrue(errContent.toString().contains("参数错误"));
}
// 测试10: 空文件处理
@Test
public void testEmptyFiles() throws IOException {
Path original = tempFolder.newFile("empty1.txt").toPath();
Path plagiarized = tempFolder.newFile("empty2.txt").toPath();
Path output = tempFolder.newFile("empty_result.txt").toPath();
Main.main(new String[]{
original.toString(),
plagiarized.toString(),
output.toString()
});
String result = new String(Files.readAllBytes(output));
assertEquals("100.00", result);
}`
3.2 测试数据构造策略
1.边界值法:空文件、单字符文件
2.等价类划分:
- 有效等价类:纯中文、混合字符
- 无效等价类:非文本文件(未处理)
3.路径覆盖:LCS的全匹配/部分匹配/不匹配场景
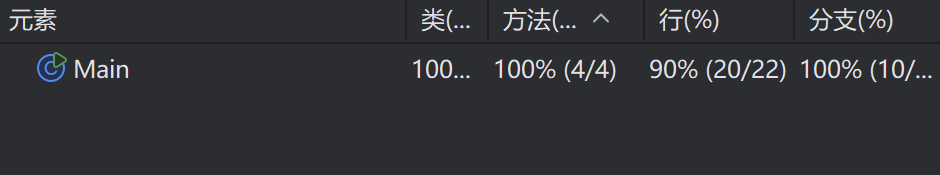
3.3 覆盖率报告
四、异常处理设计
4.1 异常处理列表
| 异常类型 | 触发场景 | 处理方式 | 测试用例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IllegalArgumentException | 参数数量错误 | 错误提示并退出 | testInvalidArguments() |
| IOException | 文件路径错误 | 捕获并打印错误 | testFullProcess() |
| ArithmeticException | 除零错误 | 前置条件检查 | testCalculateSimilarity_ZeroDenominator() |
4.2 典型异常测试
`@Test
public void testZeroDenominator() {
assertEquals(100.00, Main.calculateSimilarity(0,0,0), 0.001);
}
// 文件异常测试
@Test(expected = IOException.class)
public void testFileNotFound() throws IOException {
Main.main(new String[]{"nonexist.txt", "plag.txt", "result.txt"});
}`
4.3 计算模块部分异常处理说明
1.参数错误:
- 设计目标:确保用户输入三个文件路径参数。
- 测试用例:testInvalidArguments,验证错误输出。
2.文件读取错误:
- 设计目标:处理文件不存在或无法读取的情况。
- 测试用例:手动创建不存在的文件路径,验证异常捕获。
3.空文件处理:
- 设计目标:处理空文件输入,确保程序正常运行。
- 测试用例:testEmptyFiles,验证空文件处理结果。
4.相似度计算异常:
- 设计目标:处理分母为零的情况,避免除零错误。
- 测试用例:testCalculateSimilarity_ZeroDenominator,验证计算结果。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号