变量
变量的作用
Variables are used to store information to be referenced and manipulated in a computer program. They also provide a way of labeling data with a descriptive name, so our programs can be understood more clearly by the reader and ourselves. It is helpful to think of variables as containers that hold information. Their sole purpose is to label and store data in memory. This data can then be used throughout your program.
变量的定义规范
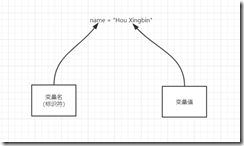
name = "Hou Xingbin"
变量的定义规则
变量名只能是 字母、数字或下划线的任意组合
变量名的第一个字符不能是数字
以下关键字不能声明为变量名['and', 'as', 'assert', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'exec', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'print', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
定义方式
驼峰体
AgeOfHouxingbin = 18
NumberOfHouxingbin = 22
下划线
age_of_houxingbin = 18
number_of_houxingbin = 22
推荐使用下划线作为变量名,不过也要看个人习惯~
变量定义不好的方式
- 变量名为中文、拼音
- 变量名过长
- 变量名词不达意
常量
常量即指不变的量,如pai 3.141592653..., 或在程序运行过程中不会改变的量
在Python中没有一个专门的语法代表常量,程序员约定俗成用变量名全部大写代表常量
AGE_OF_HOUXINGBIN
本文选自老男孩Python教程


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号