一、普通绘图
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 4 # 绘制普通图像 5 x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 50) 6 y1 = 2 * x + 1 7 y2 = x**2 8 9 plt.figure() 10 # 在绘制时设置lable, 逗号是必须的 11 l1, = plt.plot(x, y1, label = 'line') 12 l2, = plt.plot(x, y2, label = 'parabola', color = 'red', linewidth = 1.0, linestyle = '--') 13 14 # 设置坐标轴的取值范围 15 plt.xlim((-1, 1)) 16 plt.ylim((0, 2)) 17 18 # 设置坐标轴的lable 19 plt.xlabel('X axis') 20 plt.ylabel('Y axis') 21 22 # 设置x坐标轴刻度, 原来为0.25, 修改后为0.5 23 plt.xticks(np.linspace(-1, 1, 5)) 24 # 设置y坐标轴刻度及标签, $$是设置字体 25 plt.yticks([0, 0.5], ['$minimum$', 'normal']) 26 27 # 设置legend 28 plt.legend(handles = [l1, l2,], labels = ['a', 'b'], loc = 'best') 29 plt.show()
二、自定义单峰函数
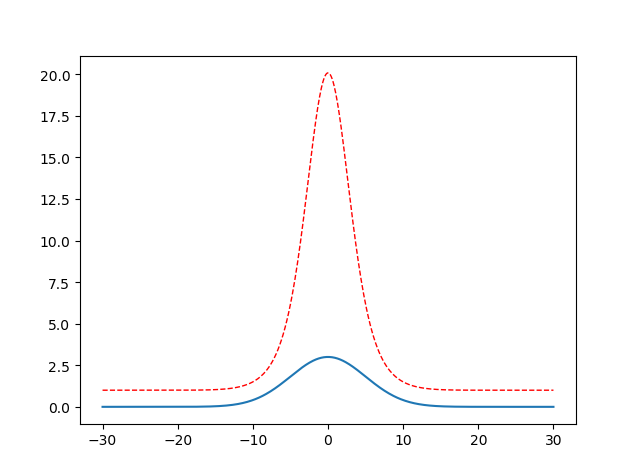
1 import math 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 x = np.linspace(-30, 30, 500) 6 y = [] 7 y2 = [] 8 a = 3 9 b = 0 10 c = 25 11 for i in x : 12 # 类似高斯函数,a 代表峰值, b对称轴位置,c方差 13 temp = a * math.exp(-(i-b)**2 / (2 * c)) 14 y.append(temp) 15 #对上一个单峰函数值进行放大处理,红色虚线部分 16 y2.append(math.exp(temp)) 17 18 plt.figure() 19 l1= plt.plot(x, y, label = 'line') 20 l2, = plt.plot(x, y2, label = 'parabola', color = 'red', linewidth = 1.0, linestyle = '--') 21 plt.show()
三、画subplot子图(2 x 2 为例)
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 t=np.arange(0.0,2.0,0.1) 3 s=np.sin(t*np.pi) 4 plt.subplot(2,2,1) #要生成两行两列,这是第一个图plt.subplot('行','列','编号') 5 plt.plot(t,s,'b--') 6 plt.ylabel('y1') 7 plt.subplot(2,2,2) #两行两列,这是第二个图 8 plt.plot(2*t,s,'r--') 9 plt.ylabel('y2') 10 plt.subplot(2,2,3)#两行两列,这是第三个图 11 plt.plot(3*t,s,'m--') 12 plt.subplot(2,2,4)#两行两列,这是第四个图 13 plt.plot(4*t,s,'k--') 14 plt.show()

点图和线图
fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(221, projection='3d') ax.plot(array_normal[:,0],array_normal[:,1],array_normal[:,2]) plt.subplot(2,2,2) plt.plot(np.arange(0,sample_len,1), signal_normal) normal_pow = array_normal[:,2] ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223, projection='3d') ax3.plot(array_anomaly[:,0],array_anomaly[:,1],array_anomaly[:,2]) anomaly_pow = array_anomaly[:,2] plt.subplot(2,2,4) plt.scatter(np.arange(0,sample_len,1), signal_anomaly) plt.show()

【Reference】
[1] https://www.jianshu.com/p/de223a79217a
[2] https://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6777945.html


