JAVA高效编程二(流编程)
基本介绍



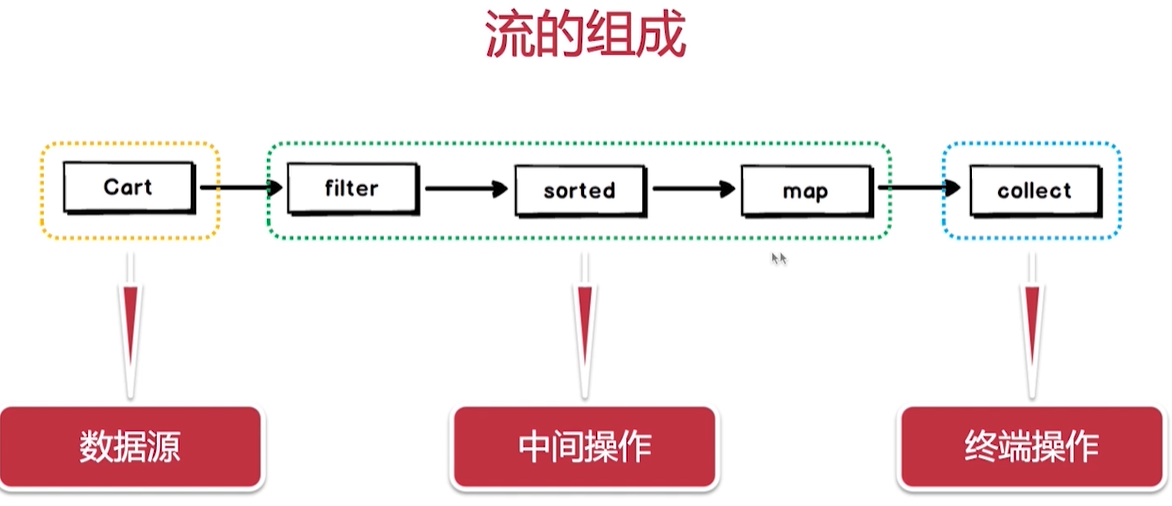
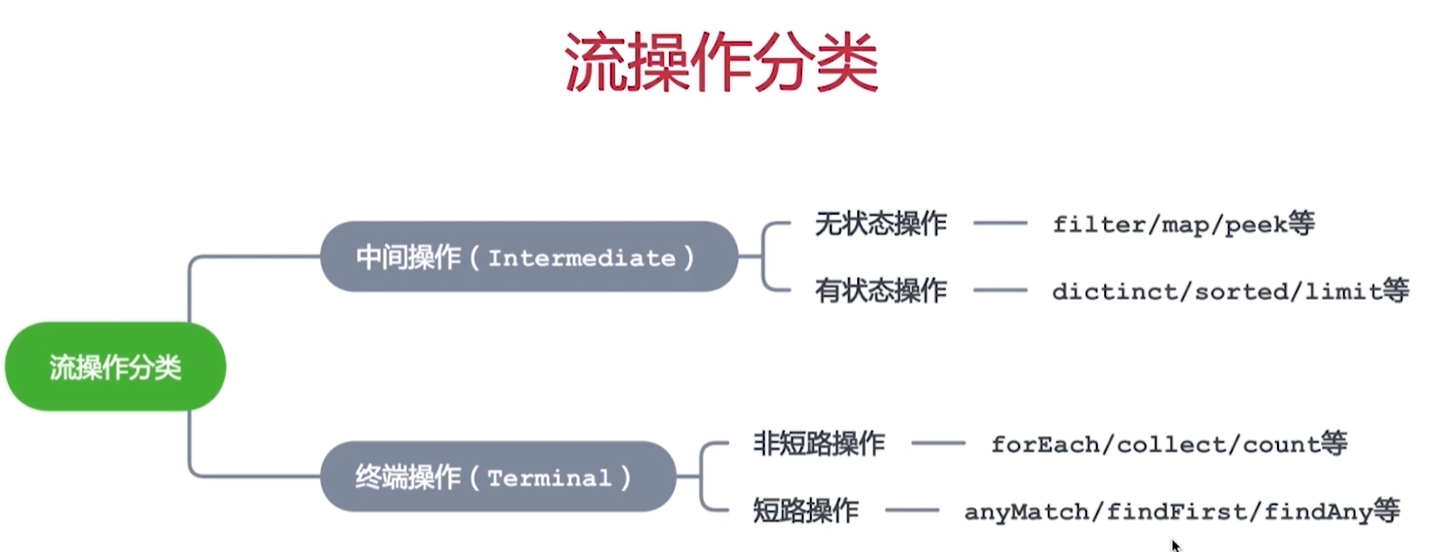

使用方法
/**
* 演示流的各种操作
*/
public class StreamOperator {
List<Sku> list;
@Before
public void init() {
list = CartService.getCartSkuList();
}
/**
* filter使用:过滤掉不符合断言判断的数据
*/
@Test
public void filterTest() {
list.stream()
// filter 满足条件的保留,不满足条件的过滤
.filter(sku ->
SkuCategoryEnum.BOOKS
.equals(sku.getSkuCategory()))
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* map使用:将一个元素转换成另一个元素
*/
@Test
public void mapTest() {
list.stream()
// map 映射 从sku实例元素转换成skuName字符串元素,并不是指转化成一个HashMap
.map(sku -> sku.getSkuName())
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* flatMap使用:扁平化,将一个对象转换成流
*/
@Test
public void flatMapTest() {
list.stream()
// flatMap 从一个流转化成另一个流
.flatMap(sku -> Arrays.stream(
sku.getSkuName().split("")))
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* peek使用:对流中元素进行遍历操作,与forEach类似,但不会销毁流元素
*/
@Test
public void peek() {
list.stream()
// peek 和forEach操作的区别是peek可以重复操作,但forEach是终端操作,只能操作一次
// peek是一个惰性操作,如果peek后面没有其他有状态中间操作,会将数据逐条的和forEach交替执行
.peek(sku -> System.out.println(sku.getSkuName()))
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* sort使用:对流中元素进行排序,可选则自然排序或指定排序规则。有状态操作
*/
@Test
public void sortTest() {
list.stream()
.peek(sku -> System.out.println(sku.getSkuName()))
//sort 默认升序,调用reverse方法可以转换成降序
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Sku::getTotalPrice))
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* distinct使用:对流元素进行去重。有状态操作
*/
@Test
public void distinctTest() {
list.stream()
.map(sku -> sku.getSkuCategory())
// distinct
.distinct()
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* skip使用:跳过前N条记录。有状态操作
*/
@Test
public void skipTest() {
list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Sku::getTotalPrice))
// skip
.skip(3)
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* limit使用:截断前N条记录。有状态操作
*/
@Test
public void limitTest() {
list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparing(Sku::getTotalPrice))
.skip(2 * 3)
// limit skip和limit结合起来可以实现类似于分页的效果
.limit(3)
.forEach(item ->
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(
item, true)));
}
/**
* allMatch使用:终端操作,短路操作。所有元素匹配,返回true
*/
@Test
public void allMatchTest() {
boolean match = list.stream()
.peek(sku -> System.out.println(sku.getSkuName()))
// allMatch
.allMatch(sku -> sku.getTotalPrice() > 100);
System.out.println(match);
}
/**
* anyMatch使用:任何元素匹配,返回true
*/
@Test
public void anyMatchTest() {
boolean match = list.stream()
.peek(sku -> System.out.println(sku.getSkuName()))
// anyMatch
.anyMatch(sku -> sku.getTotalPrice() > 100);
System.out.println(match);
}
/**
* noneMatch使用:任何元素都不匹配,返回true
*/
@Test
public void noneMatchTest() {
boolean match = list.stream()
.peek(sku -> System.out.println(sku.getSkuName()))
// noneMatch 注意这里数字的写法,第一次见到,用来实现千分位,方便阅读
.noneMatch(sku -> sku.getTotalPrice() > 10_000);
System.out.println(match);
}
/**
* 找到第一个
*/
@Test
public void findFirstTest() {
Optional<Sku> optional = list.stream()
.peek(sku -> System.out.println(sku.getSkuName()))
// findFirst
.findFirst();
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(optional.get(), true));
}
/**
* 找任意一个
*/
@Test
public void findAnyTest() {
Optional<Sku> optional = list.stream()
.peek(sku -> System.out.println(sku.getSkuName()))
// findAny 在并行速度上比findFirst要快,但是返回结果是随机的,不具有幂等性
.findAny();
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(optional.get(), true));
}
/**
* max使用:
*/
@Test
public void maxTest() {
OptionalDouble optionalDouble = list.stream()
// 获取总价
.mapToDouble(Sku::getTotalPrice)
.max();
System.out.println(optionalDouble.getAsDouble());
}
/**
* min使用
*/
@Test
public void minTest() {
OptionalDouble optionalDouble = list.stream()
// 获取总价
.mapToDouble(Sku::getTotalPrice)
.min();
System.out.println(optionalDouble.getAsDouble());
}
/**
* count使用
*/
@Test
public void countTest() {
long count = list.stream()
.count();
System.out.println(count);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号