一、前言
本次pta航空货物管理系统题目分为两次,依旧是后一次在前一次基础上进行迭代,第一次是考察类设计,第二次在上一次基础上加了一些要求,主要考察Java的继承与多态,题量我觉得适中,难度的话相比前一次大作业的电梯调度程序感觉低了一些,主要是因为这次的题目比较轻算法而更加考察我们的类设计,对Java的继承多态的认识。需要我们认真考虑设计类与类之间的关系,运用继承,多态,封装这三大java三大核心技术,并在写代码的时候,尽可能遵循单一职责原则(每个类只负责单一功能),里氏代换原则(子类对象可以替换掉父类对象,并且不破坏系统),开闭原则(系统对扩展开放,对修改关闭,可以通过增加新类或方法来扩展功能),合成复用原则(尽量使用组合而非继承来实现功能),依赖倒转原则(依赖于抽象,而非具体的实现)。不过答题过程中还是碰到了一些问题,具体后面详细分析。
二、设计与分析
第一次航空货运管理系统设计分析
题目要求:
某航空公司“航空货运管理系统”中的空运费的计算涉及多个因素,通常包括货物重量/体积、运输距离、附加费用、货物类型、客户类型以及市场供需等。空运以实际重量(Gross Weight)和体积重量(Volume Weight)中的较高者作为计费重量。
计算公式:
体积重量(kg) = 货物体积(长×宽×高,单位:厘米)÷ 6000
本次题目模拟某客户到该航空公司办理一次货运业务的过程:航空公司提供如下信息:
航班信息(航班号,航班起飞机场所在城市,航班降落机场所在城市,航班日期,航班最大载重量)
客户填写货运订单并进行支付,需要提供如下信息:
客户信息(姓名,电话号码等)
货物信息(货物名称,货物包装长、宽、高尺寸,货物重量等)
运送信息(发件人姓名、电话、地址,收件人姓名、电话、地址,所选航班号,订单日期)
支付方式(支付宝支付、微信支付)
一个货运订单可以运送多件货物,每件货物均需要根据重量及费率单独计费。
具体的格式输出要求我就省略了。主要是题目要求应用到单一职责原则、里氏代换原则、开闭原则以及合成复用原则。
从题目可以看出本次题目并不是很注重算法,而是看重我们对于代码类与类间的关系理解,怎么通过设计原则来设计代码。
设计类图:
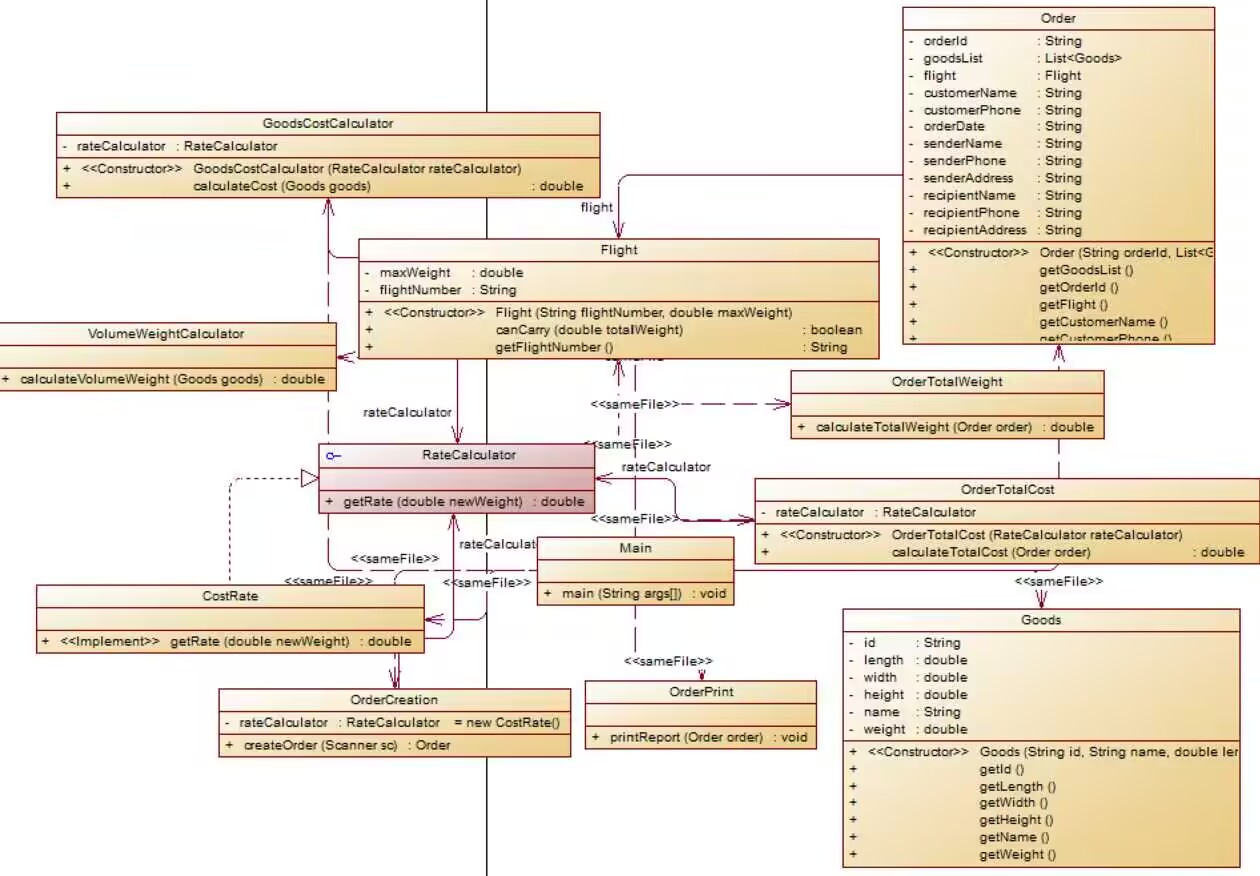
基本上是做到了类设计要求的单一职责原则,每个类尽量只完成自己该完成的事情,而不去把其他类要做的放这个类里,代码的可读性也会更好。
Souce Monitor分析结果:
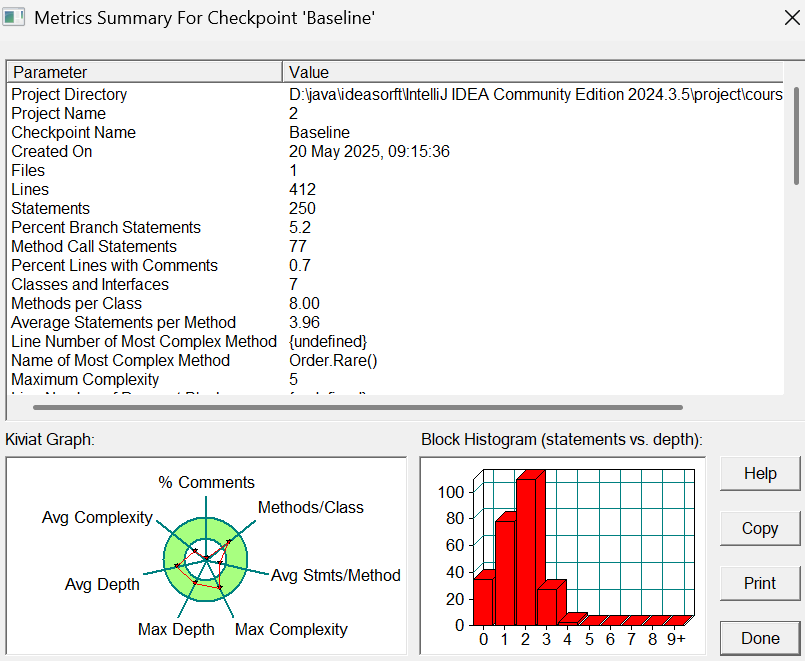
可以看到一是代码的注释比较少,再就是复杂度还有一些地方嵌套语句可能较多。
一般大作业的第一次题目由于比较陌生所耗时间和问题都会比较多,本次实验我也碰到了一些问题,一个是我写代码其实重写过一遍的,因为我第一次写可能只是想着先把题目要求实现了再说,想着后面再重新改一下代码让他变得符合各种设计原则,但其实这样做并不好,一个是这样挺累的,而且时间耗费的也多,如果我写完了代码直接提交对了我就没分了(因为不符合题目设计原则)再就是我们写代码其实就是应该要把类设计原则牢记于心,只有这样才能把代码写好,而且往往也会轻松一些,以后不管是迭代重构都会减少很多的任务量。然后就是我写作业的时候遇到了由于换行符没有消除而导致的输入输出问题,当时卡了我挺久的,所以有所收获。
第二次航空货运管理系统设计分析
题目要求:
本次作业费率与货物类型有关,货物类型分为普通货物、危险货物和加急货物三种,每种货物的费率计算也都不相同,同时还引入了用户的类型,有(Individual/Corporate)其中,折扣率是指不同的用户类型针对每个订单的运费可以享受相应的折扣,在本题中,用户分为个人用户和集团用户,其中个人用户可享受订单运费的9折优惠,集团用户可享受订单运费的 8 折优惠。还有支付方式的增加,支付方式(支付宝支付、微信支付、现金支付),所以要多设计一个支付类,并且用到继承与多态。
设计类图:
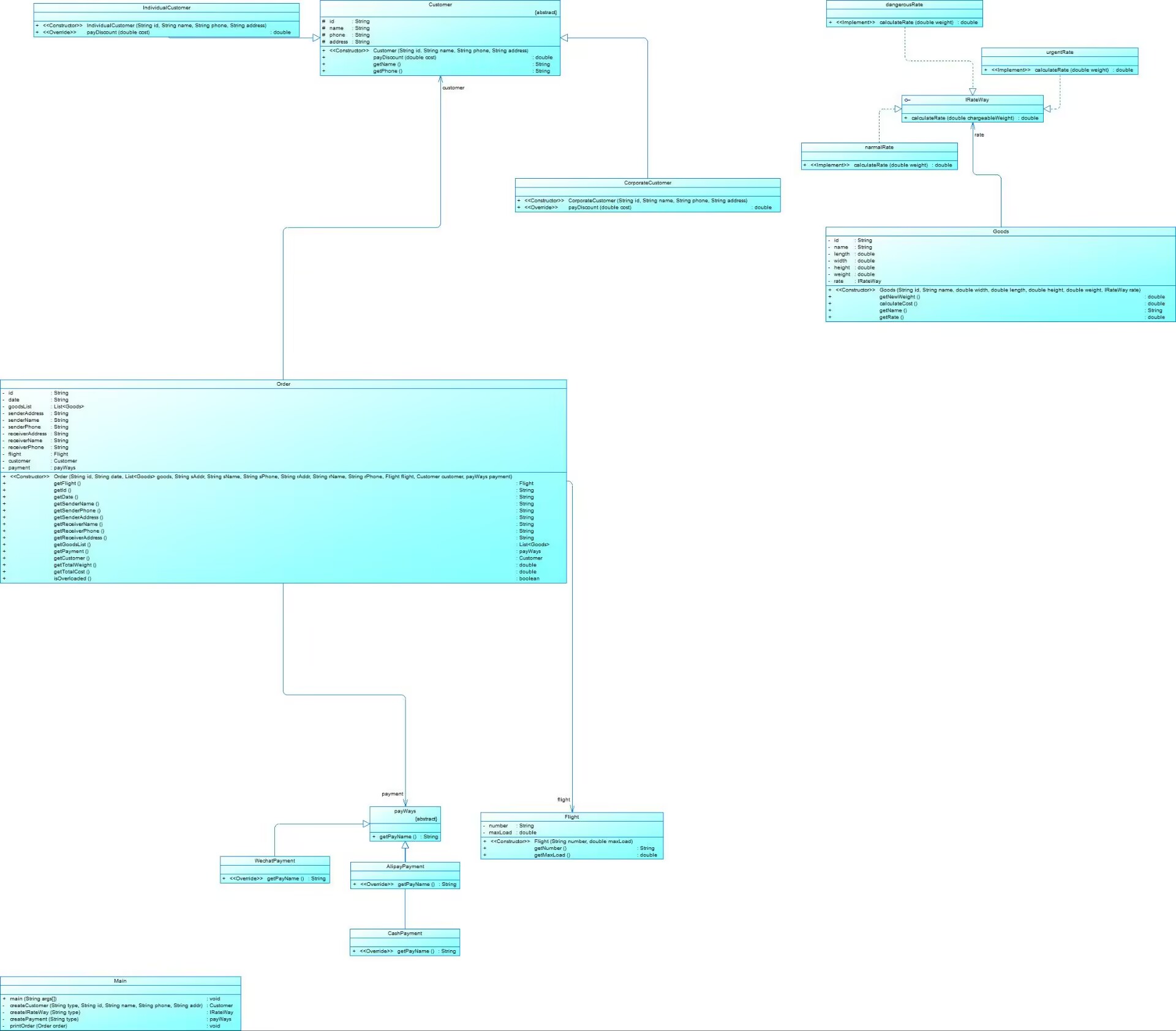
可以看到我定义了一个抽象类接口IRateWay和payWays分别作为三种不同货物类型计算费率的父类和三种支付方式的父类,而用户类下面也有个人用户和集团用户来继承它。通过继承,我切实能感受到继承很好用。
Souce Monitor分析结果:
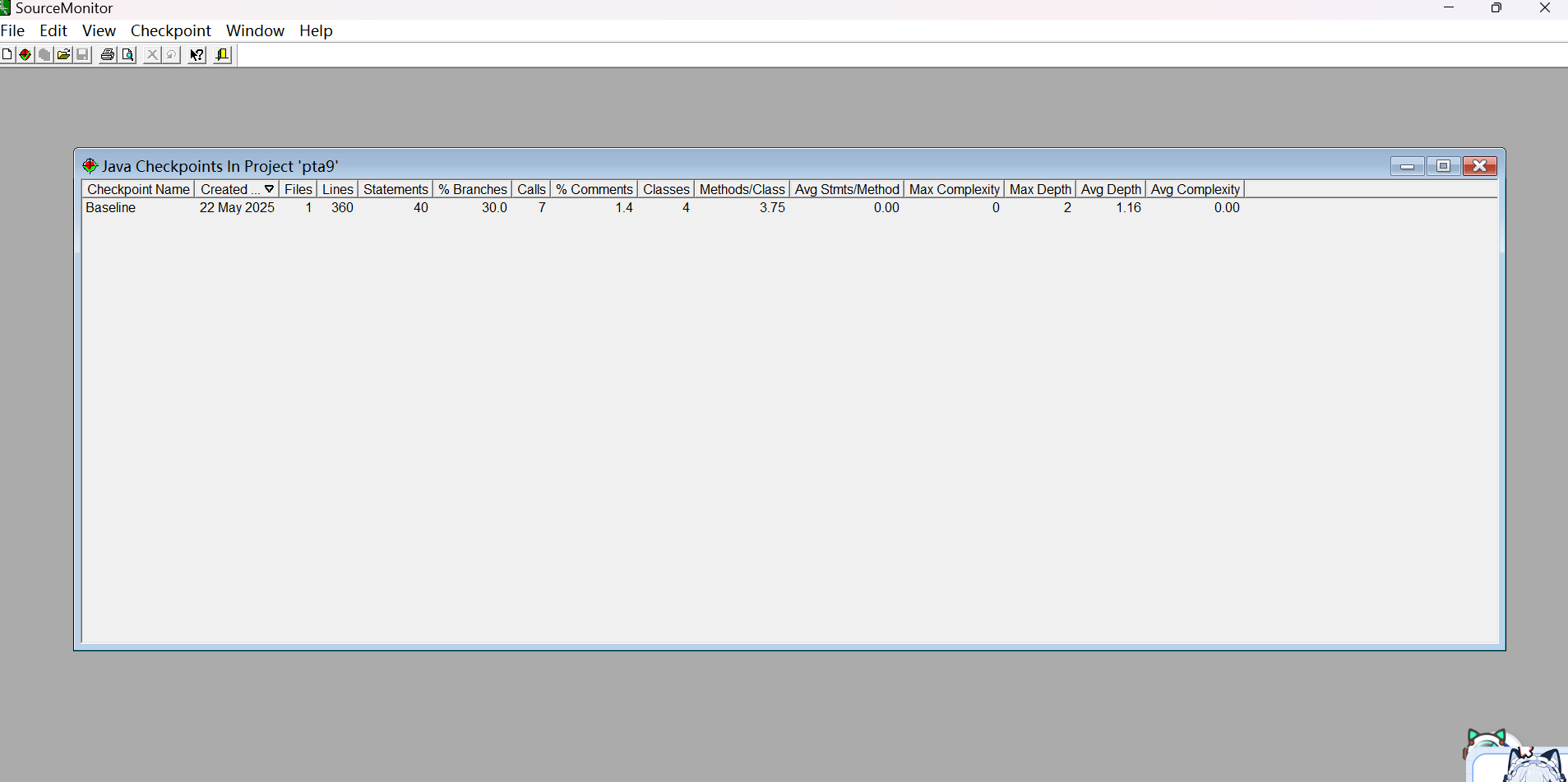
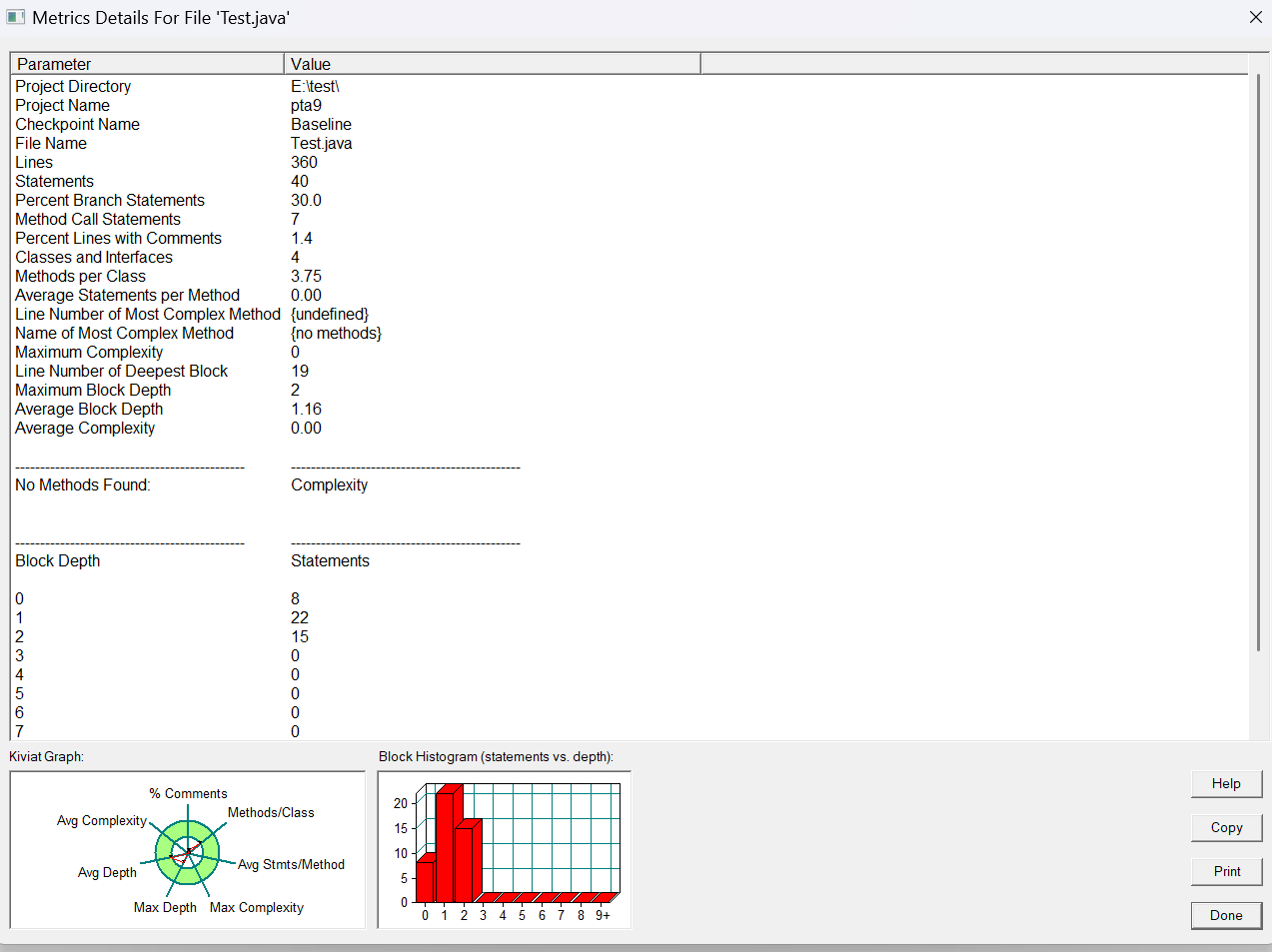
通过图片可以看到,我的代码分支覆盖率只有30%,也就是可能会存在没有被处理的逻辑路径,注释更是只有一点点,这个确实当时写完就提交了,确实没有养成写注释的习惯,下次尽量,然后复杂度很低,因为确实题目没什么算法。下面是题目代码。
点击查看代码
import java.util.*;
// 费率接口
interface IRateWay {
double calculateRate(double chargeableWeight);
}
// 普通货物费率
class narmalRate implements IRateWay {
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 35;
else if (weight < 50) return 30;
else if (weight < 100) return 25;
else return 15;
}
}
// 危险货物费率
class dangerousRate implements IRateWay {
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 80;
else if (weight < 50) return 50;
else if (weight < 100) return 30;
else return 20;
}
}
// 加急货物费率
class urgentRate implements IRateWay {
public double calculateRate(double weight) {
if (weight < 20) return 60;
else if (weight < 50) return 50;
else if (weight < 100) return 40;
else return 30;
}
}
// 支付方式抽象类
abstract class payWays {
public abstract String getPayName();
}
class WechatPayment extends payWays {
@Override
public String getPayName() {
return "微信";
}
}
class AlipayPayment extends payWays {
@Override
public String getPayName() {
return "支付宝";
}
}
class CashPayment extends payWays {
@Override
public String getPayName() {
return "现金";
}
}
// 货物类
class Goods {
private final String id;
private final String name;
private final double length;
private final double width;
private final double height;
private final double weight;
private final IRateWay rate;
public Goods(String id, String name, double width, double length,
double height, double weight, IRateWay rate) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.weight = weight;
this.rate = rate;
}
public double getNewWeight() {
double volume = (length * width * height) / 6000;
return Math.max(weight, volume);
}
public double calculateCost() {
return getNewWeight() * rate.calculateRate(getNewWeight());
}
public String getName() { return name; }
public double getRate() { return rate.calculateRate(getNewWeight()); }
}
// 客户抽象类
abstract class Customer {
protected final String id;
protected final String name;
protected final String phone;
protected final String address;
public Customer(String id, String name, String phone, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.address = address;
}
public abstract double payDiscount(double cost);
public String getName() { return name; }
public String getPhone() { return phone; }
}
// 个人客户类
class IndividualCustomer extends Customer {
public IndividualCustomer(String id, String name, String phone, String address) {
super(id, name, phone, address);
}
@Override
public double payDiscount(double cost) {
return cost * 0.9;
}
}
//集团客户类
class CorporateCustomer extends Customer {
public CorporateCustomer(String id, String name, String phone, String address) {
super(id, name, phone, address);
}
@Override
public double payDiscount(double cost) {
return cost * 0.8;
}
}
// 航班类
class Flight {
private final String number; //航班号
private final double maxLoad; //最大载重量
public Flight(String number, double maxLoad) {
this.number = number;
this.maxLoad = maxLoad;
}
public String getNumber() { return number; }
public double getMaxLoad() { return maxLoad; }
}
// 订单类
class Order {
private final String id;
private final String date;
private final List<Goods> goodsList;
private final String senderAddress;
private final String senderName;
private final String senderPhone;
private final String receiverAddress;
private final String receiverName;
private final String receiverPhone;
private final Flight flight;
private final Customer customer;
private final payWays payment;
public Order(String id, String date,List<Goods> goods,
String sAddr, String sName, String sPhone,
String rAddr,String rName, String rPhone,
Flight flight, Customer customer, payWays payment)
{
this.id = id;
this.goodsList = goods;
this.flight = flight;
this.customer = customer;
this.payment = payment;
this.date = date;
this.senderName = sName;
this.senderPhone = sPhone;
this.senderAddress = sAddr;
this.receiverName = rName;
this.receiverPhone = rPhone;
this.receiverAddress = rAddr;
}
// Getter方法
public Flight getFlight() { return flight; }
public String getId() { return id; }
public String getDate() { return date; }
public String getSenderName() { return senderName; }
public String getSenderPhone() { return senderPhone; }
public String getSenderAddress() { return senderAddress; }
public String getReceiverName() { return receiverName; }
public String getReceiverPhone() { return receiverPhone; }
public String getReceiverAddress() { return receiverAddress; }
public List<Goods> getGoodsList() { return goodsList; }
public payWays getPayment() { return payment; }
public Customer getCustomer() {
return this.customer;
}
public double getTotalWeight() {
double total = 0;
for (Goods g : goodsList) {
total += g.getNewWeight();
}
return total;
}
public double getTotalCost() {
double total = 0;
for (Goods g : goodsList) {
total += g.calculateCost();
}
total = customer.payDiscount(total);
return total;
}
public boolean isOverloaded() {
return getTotalWeight() > flight.getMaxLoad();
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 客户
String customerType = sc.nextLine();
String customerId = sc.nextLine();
String customerName = sc.nextLine();
String customerPhone = sc.nextLine();
String customerAddress = sc.nextLine();
Customer customer = createCustomer(customerType, customerId, customerName, customerPhone, customerAddress);
// 货物
String goodsType = sc.nextLine();
int count = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
List<Goods> goodsList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
String goodsId = sc.nextLine();
String goodsName = sc.nextLine();
double length = Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
double width = Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
double height = Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
double weight = Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine());
goodsList.add(new Goods(goodsId, goodsName, length, width, height, weight, createIRateWay(goodsType)));
}
// 航班
String flightNumber = sc.nextLine();
String startAirport = sc.nextLine();
String endAirport = sc.nextLine();
String flightDate = sc.nextLine();
double maxLoad = Double.parseDouble(sc.nextLine()); // 最大载重量
Flight flight = new Flight(flightNumber, maxLoad);
// 订单
String orderId = sc.nextLine();
String orderDate = sc.nextLine();
String senderAddress = sc.nextLine();
String senderName = sc.nextLine();
String senderPhone = sc.nextLine();
String recipientAddress = sc.nextLine();
String recipientName = sc.nextLine();
String recipientPhone = sc.nextLine();
payWays payment = createPayment(sc.nextLine());
Order order = new Order(orderId, orderDate, goodsList,
senderAddress, senderName, senderPhone,
recipientAddress, recipientName, recipientPhone,
flight, customer, payment);
// 检查载重
if (order.isOverloaded()) {
System.out.printf("The flight with flight number:%s has exceeded its load capacity and cannot carry the order.",
flight.getNumber());
return;
}
// 输出结果
printOrder(order);
}
private static Customer createCustomer(String type, String id, String name, String phone, String addr) {
switch (type) {
case "Individual":
return new IndividualCustomer(id, name, phone, addr);
case "Corporate":
return new CorporateCustomer(id, name, phone, addr);
default: return null;
}
}
private static IRateWay createIRateWay(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "Normal":
return new narmalRate();
case "Dangerous":
return new dangerousRate();
case "Expedite":
return new urgentRate();
default:return null;
}
}
private static payWays createPayment(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "Wechat":
return new WechatPayment();
case "ALiPay":
return new AlipayPayment();
case "Cash":
return new CashPayment();
default: return null;
}
}
private static void printOrder(Order order) {
Customer customer = order.getCustomer();
System.out.printf("客户:%s(%s)订单信息如下:\n", customer.getName(), customer.getPhone());
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("航班号:" + order.getFlight().getNumber());
System.out.println("订单号:" + order.getId());
System.out.println("订单日期:" + order.getDate());
System.out.println("发件人姓名:" + order.getSenderName());
System.out.println("发件人电话:" + order.getSenderPhone());
System.out.println("发件人地址:" + order.getSenderAddress());
System.out.println("收件人姓名:" + order.getReceiverName());
System.out.println("收件人电话:" + order.getReceiverPhone());
System.out.println("收件人地址:" + order.getReceiverAddress());
System.out.printf("订单总重量(kg):%.1f\n", order.getTotalWeight());
System.out.printf("%s支付金额:%.1f\n\n",
order.getPayment().getPayName(), order.getTotalCost());
System.out.println("货物明细如下:");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
System.out.println("明细编号\t货物名称\t计费重量\t计费费率\t应交运费");
int index = 1;
for (Goods goods : order.getGoodsList()) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%s\t%.1f\t%.1f\t%.1f\n",
index++,
goods.getName(),
goods.getNewWeight(),
goods.getRate(),
goods.calculateCost());
}
}
}
三、踩坑心得
一定要有完整的思路再去开始写代码
还是那句话,写代码一定要有“全局观”,我刚开始想到什么就写什么,想着先把题目要求先实现再来改,总是我以为我以为。但是这样如果算法难的话不仅会导致情况很可能考虑的不周到,还会影响编写其他代码的思路,最后的结果就是删删改改,可能还会越改越错。这次是算法不难所以可以写出来,如果像上次的电梯题目的话就很麻烦了,所以一定要谋而后动。
一定要仔细
不要盲目的去追求速度,如果速度上去了,因为粗心大意而调试找错的时间成本可能会大于仔细认真的敲,有时候一个中英文输错&&和||写错或者大小写拼写等等问题就很难发现,但又会影响你全部的代码。
题目需求极为重要
写之前一定要看清楚题目的要求,不管是算法部分,还是特殊情况的单独考虑,亦或是输入输出的格式问题都非常非常重要,因为这些都是会影响你的结果,不符合题目要求,测试就是不通过,就是没分,以后工作同样如此,一定要对需求敏感。
四、改进建议
1.代码有些地方写的还是不够好,还可以写简单一点。
2.就像前面分析的,代码的测试覆盖率低,可能有很多地方我没有考虑到的情况,只是这次题目没有测试。
3.在一些可能越界的地方加入判断更好的检测到问题出现在哪,快速定位和解决问题。对代码中可能存在的异常应该进行捕获,不然可能会导致运行时候错误,到时候很难找到代码错哪里
4.增加代码的注释,提高可读性,不然自己一段时间后重新看会很费劲,降低效率。这次是算法逻辑简单没什么注释也能看懂,如果是复杂方法逻辑不清晰不添加注释就会很难让别人理解,自己都可能看不懂。
五、总结
收获
通过这两次的迭代性题目集的综合性学习,我收获还是挺大的,首先就是我对面对对象程序设计原则有了更深的理解,然后是抽象类,接口的使用,切实体会到了如果遵循类设计原则确实有很多好处,提高效率,复用,代码可读性,可扩展性等等。
建议
希望老师迭代作业起步的时候能有更多的测试用例,比如如果有输入正确和输入错误给两个测试用例,有些时候不知道末尾加不加空格,有时候要输出输入错误的打印语句时会打错大小写中英文不小心打错的情况,如果有测试用例的话一下就能找到错误,像我这次的期中测验就是错在异常错误那里(生命值低于0),我想了半天不清楚为什么错误,因为我考虑了这个情况,后来才发现我是没有打印前面的“剩余生命值:”而只输出了“0.0”我也不知道当时怎么了没有状态这个都没有想到,导致浪费了很多很多的时间。所以还是希望老师用例尽量给多一点,考虑的情况多一点。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号