DebugInWasm3
- During installing wabt
- Port mapping
- Convert the binary wasm file to WebAssembly code file
- what is the dierctory of wasm3 mean?
- Set wasm3 to debug mode
- Set the debug environment in gdb
- Debug
hello.wasm- repl_load(): ParseModule
- repl_load(): LoadModule
- repl_load(): SetModuleName
- repl_load():Link all the modules
lazyCompile_Modules- repl_call(): Get and check every function, finally execute the function.
- repl_call(): Get Wasi context()
- repl_call(): Execute the main function
RunCode()function in repl_call()- Finally, free the Runtime and Environment
- Other details
- Performance Measurement Using Perf
During installing wabt
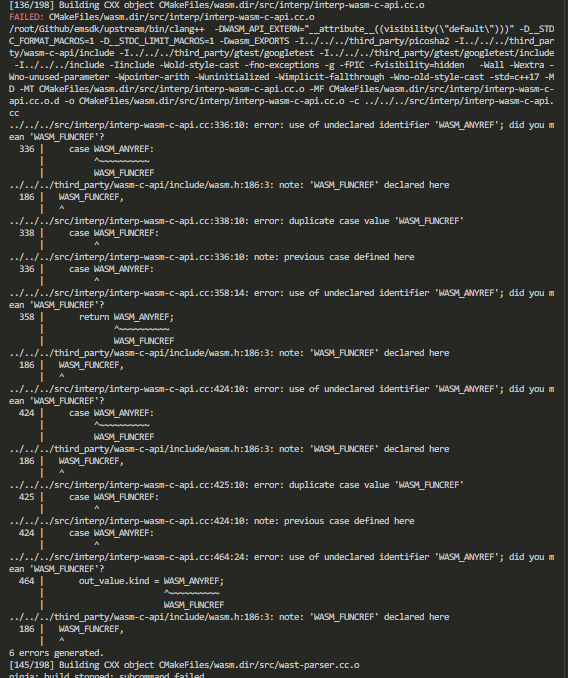
Port mapping
Connect to docker directly:
ssh [USER]@[IP] -p 50001
Convert the binary wasm file to WebAssembly code file
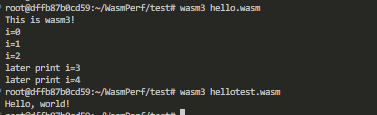
Check the differeces between two files
What is WebAssmebly format language and its detailed explanation, See here
what is the dierctory of wasm3 mean?
root@f5c6cb9f45b1:~/Github/wasm3# tree -L 2 .
.
|-- CMakeLists.txt
|-- LICENSE
|-- README.md
|-- build
| |-- CMakeCache.txt
| |-- CMakeFiles
| |-- Makefile
| |-- _deps
| |-- cmake_install.cmake
| |-- install_manifest.txt
| |-- source
| `-- wasm3
|-- build-cross.py
|-- build.zig
|-- docs
| |-- Cookbook.md
| |-- Demos.md
| |-- Development.md
| |-- Diagnostics.md
| |-- Hardware.md
| |-- Installation.md
| |-- Interpreter.md
| |-- Performance.md
| |-- Testing.md
| `-- Troubleshooting.md
|-- extra
| |-- button.png
| |-- disasm-func.sh
| |-- logo.png
| |-- logos
| |-- screenshot-android.png
| |-- screenshot-ios.png
| |-- testutils.py
| |-- utils.mk
| |-- wapm-package
| `-- wasm-symbol.svg
|-- platforms
| |-- android
| |-- app
| |-- app_fuzz
| |-- cosmopolitan
| |-- cpp
| |-- embedded
| |-- emscripten
| |-- emscripten_lib
| |-- ios
| |-- openwrt
| `-- python
|-- source
| |-- CMakeLists.txt
| |-- extensions
| |-- extra
| |-- m3_api_libc.c
| |-- m3_api_libc.h
| |-- m3_api_meta_wasi.c
| |-- m3_api_tracer.c
| |-- m3_api_tracer.h
| |-- m3_api_uvwasi.c
| |-- m3_api_wasi.c
| |-- m3_api_wasi.h
| |-- m3_bind.c
| |-- m3_bind.h
| |-- m3_code.c
| |-- m3_code.h
| |-- m3_compile.c
| |-- m3_compile.h
| |-- m3_config.h
| |-- m3_config_platforms.h
| |-- m3_core.c
| |-- m3_core.h
| |-- m3_env.c
| |-- m3_env.h
| |-- m3_exception.h
| |-- m3_exec.c
| |-- m3_exec.h
| |-- m3_exec_defs.h
| |-- m3_function.c
| |-- m3_function.h
| |-- m3_info.c
| |-- m3_info.h
| |-- m3_math_utils.h
| |-- m3_module.c
| |-- m3_parse.c
| |-- wasm3.h
| `-- wasm3_defs.h
`-- test
|-- fuzz
|-- internal
|-- lang
|-- run-spec-test.py
|-- run-wasi-test.py
|-- self-hosting
`-- wasi
29 directories, 64 files
Set wasm3 to debug mode
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug ..
Set the debug environment in gdb
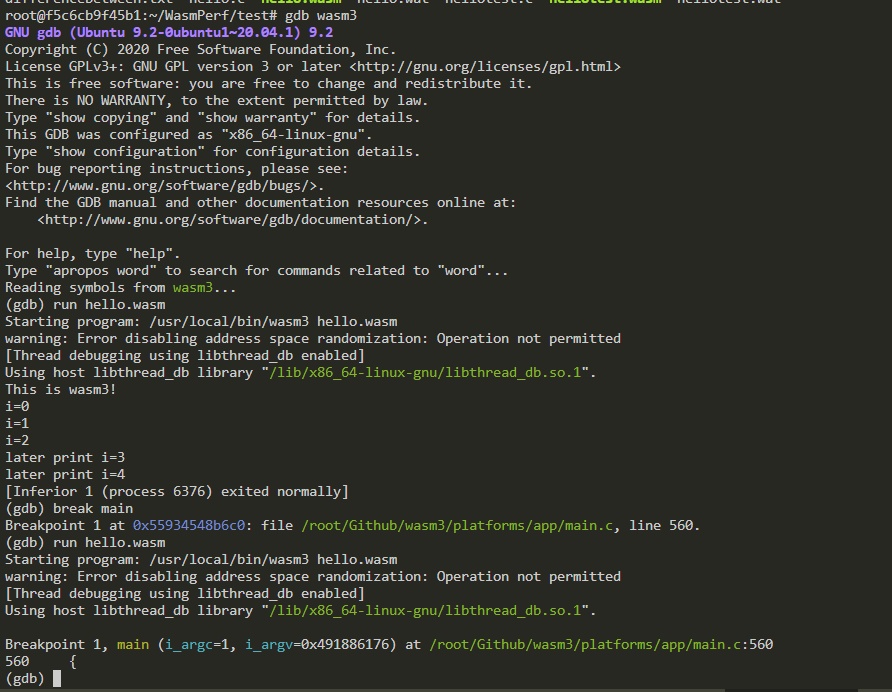
Debug hello.wasm
-
/root/Github/wasm3/platforms/appThis is the entry main function.int main (int i_argc, const char* i_argv[]){ M3Result result = m3Err_none; env = m3_NewEnvironment (); runtime = NULL; bool argRepl = false; bool argDumpOnTrap = false; bool argCompile = false; const char* argFile = NULL; const char* argFunc = "_start"; unsigned argStackSize = 64*1024; //... -
Set the environment in
m3_NewEnvironment()``m3_env.c: Setting an environment of the wasm3IM3Environment m3_NewEnvironment () { IM3Environment env = m3_AllocStruct (M3Environment); if (env) { _try { // create FuncTypes for all simple block return ValueTypes for (u8 t = c_m3Type_none; t <= c_m3Type_f64; t++) { IM3FuncType ftype; _ (AllocFuncType (& ftype, 1)); ftype->numArgs = 0; ftype->numRets = (t == c_m3Type_none) ? 0 : 1; ftype->types [0] = t; Environment_AddFuncType (env, & ftype); d_m3Assert (t < 5); env->retFuncTypes [t] = ftype; } } _catch: if (result) { m3_FreeEnvironment (env); env = NULL; } } return env; }DataType declared in the
wasm3.htypedef enum M3ValueType { c_m3Type_none = 0, c_m3Type_i32 = 1, c_m3Type_i64 = 2, c_m3Type_f32 = 3, c_m3Type_f64 = 4, c_m3Type_unknown } M3ValueType; typedef struct M3TaggedValue { M3ValueType type; union M3ValueUnion { uint32_t i32; uint64_t i64; float f32; double f64; } value; } -
Parses the arguments and load file
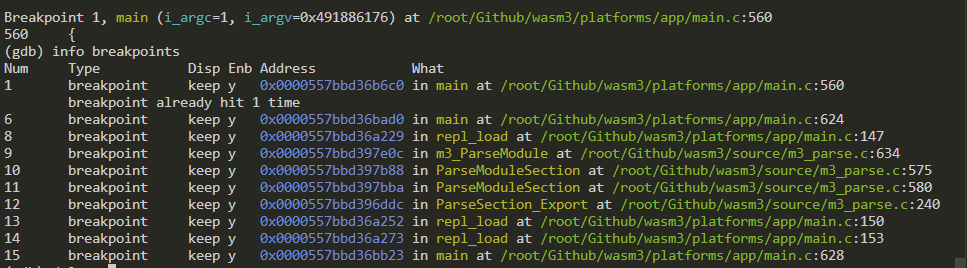
Breakpoint 5, main (i_argc=1, i_argv=0x7ffd79f86fe0) at /root/Github/wasm3/platforms/app/main.c:618 618 ARGV_SET(argFile); (gdb) step 620 result = repl_init(argStackSize); (gdb) n 621 if (result) FATAL("repl_init: %s", result); (gdb) n 623 if (argFile) { (gdb) n 624 result = repl_load(argFile); (gdb) print (char *) argFile $3 = 0x7ffd79f884ee "hello.wasm"
repl_load(): ParseModule
-
analyze the filenamein main function from 620 lines:
if (argFile) { result = repl_load(argFile); if (result) FATAL("repl_load: %s", result); if (argCompile) { repl_compile(); } if (argFunc and not argRepl) { if (!strcmp(argFunc, "_start")) { // When passing args to WASI, include wasm filename as argv[0] result = repl_call(argFunc, i_argc+1, i_argv-1); } else { result = repl_call(argFunc, i_argc, i_argv); } if (result) { if (argDumpOnTrap) { repl_dump(); } print_backtrace(); goto _onfatal; } } } -
"m3_ParseModule()" in function repl_load() in main.c
// Breakpoint 8, repl_load (fn=0x7ffc501104ee "hello.wasm") at /root/Github/wasm3/platforms/app/main.c:147 // 147 result = m3_ParseModule (env, &module, wasm, fsize); wasm = (u8*) malloc(fsize); if (!wasm) { result = "cannot allocate memory for wasm binary"; goto on_error; } if (fread (wasm, 1, fsize, f) != fsize) { result = "cannot read file"; goto on_error; } fclose (f); f = NULL; result = m3_ParseModule (env, &module, wasm, fsize); if (result) goto on_error; result = m3_LoadModule (runtime, module); if (result) goto on_error; m3_SetModuleName(module, modname_from_fn(fn)); result = link_all (module); if (result) goto on_error; if (wasm_bins_qty < MAX_MODULES) { wasm_bins[wasm_bins_qty++] = wasm; } return result; -
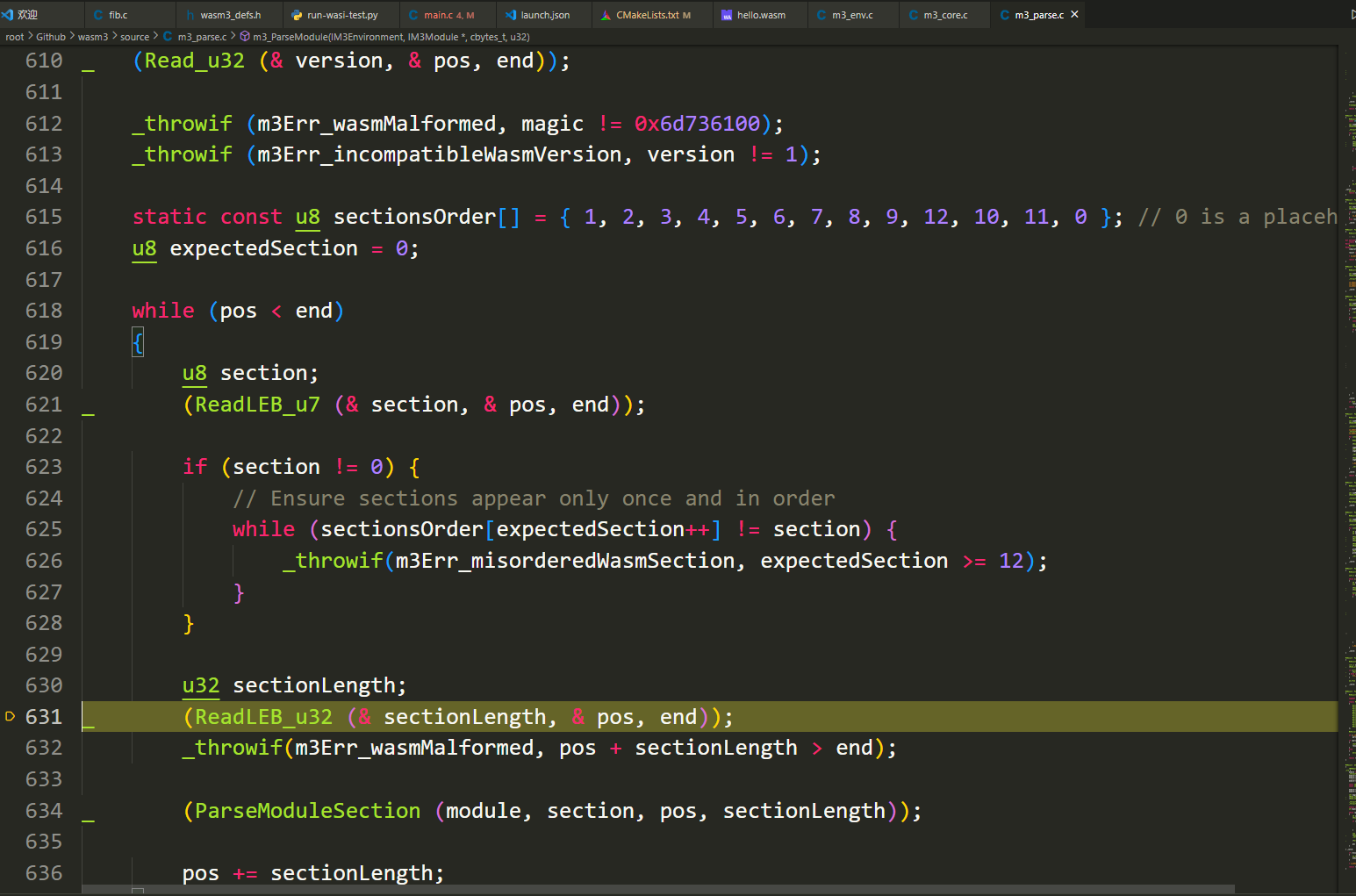
m3_ParseModule()in/root/Github/wasm3/source/m3_parse.callocate a space to a module, and read sections one by one to the structure till the end of the wasm file.M3Result m3_ParseModule (IM3Environment i_environment, IM3Module * o_module, cbytes_t i_bytes, u32 i_numBytes) { IM3Module module; m3log (parse, "load module: %d bytes", i_numBytes); _try { module = m3_AllocStruct (M3Module); _throwifnull (module); module->name = ".unnamed"; m3log (parse, "load module: %d bytes", i_numBytes); module->startFunction = -1; //module->hasWasmCodeCopy = false; module->environment = i_environment; const u8 * pos = i_bytes; const u8 * end = pos + i_numBytes; module->wasmStart = pos; module->wasmEnd = end; u32 magic, version; _ (Read_u32 (& magic, & pos, end)); _ (Read_u32 (& version, & pos, end)); _throwif (m3Err_wasmMalformed, magic != 0x6d736100); _throwif (m3Err_incompatibleWasmVersion, version != 1); static const u8 sectionsOrder[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 10, 11, 0 }; // 0 is a placeholder u8 expectedSection = 0; while (pos < end) { u8 section; _ (ReadLEB_u7 (& section, & pos, end)); if (section != 0) { // Ensure sections appear only once and in order while (sectionsOrder[expectedSection++] != section) { _throwif(m3Err_misorderedWasmSection, expectedSection >= 12); } } u32 sectionLength; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& sectionLength, & pos, end)); _throwif(m3Err_wasmMalformed, pos + sectionLength > end); _ (ParseModuleSection (module, section, pos, sectionLength)); pos += sectionLength; } } _catch: if (result) { m3_FreeModule (module); module = NULL; } * o_module = module; return result; } -
For each section, find its own sectionType and then for each sectionType from 12 different components, from external import :
-
function
Module_AddFunction()
-
table (annotated)
// result = ParseType_Table (& i_bytes, i_end);
-
memory
(ParseType_Memory (& io_module->memoryInfo, & i_bytes, i_end));
-
Kind_global
(Module_AddGlobal (io_module, & global, type, isMutable, true /* isImport */));
M3Result ParseModuleSection (M3Module * o_module, u8 i_sectionType, bytes_t i_bytes, u32 i_numBytes) { M3Result result = m3Err_none; typedef M3Result (* M3Parser) (M3Module *, bytes_t, cbytes_t); static M3Parser s_parsers [] = { ParseSection_Custom, // 0 ParseSection_Type, // 1 ParseSection_Import, // 2 ParseSection_Function, // 3 NULL, // 4: TODO Table ParseSection_Memory, // 5 ParseSection_Global, // 6 ParseSection_Export, // 7 ParseSection_Start, // 8 ParseSection_Element, // 9 ParseSection_Code, // 10 ParseSection_Data, // 11 NULL, // 12: TODO DataCount }; M3Parser parser = NULL; if (i_sectionType <= 12) parser = s_parsers [i_sectionType]; if (parser) { cbytes_t end = i_bytes + i_numBytes; result = parser (o_module, i_bytes, end); } else { m3log (parse, " skipped section type: %d", (u32) i_sectionType); } return result; } -
-
For example for
ParseSection_Import, Perform:M3Result ParseSection_Import (IM3Module io_module, bytes_t i_bytes, cbytes_t i_end) { M3Result result = m3Err_none; M3ImportInfo import = { NULL, NULL }, clearImport = { NULL, NULL }; u32 numImports; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& numImports, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, "** Import [%d]", numImports); _throwif("too many imports", numImports > d_m3MaxSaneImportsCount); // Most imports are functions, so we won't waste much space anyway (if any) _ (Module_PreallocFunctions(io_module, numImports)); for (u32 i = 0; i < numImports; ++i) { u8 importKind; _ (Read_utf8 (& import.moduleUtf8, & i_bytes, i_end)); _ (Read_utf8 (& import.fieldUtf8, & i_bytes, i_end)); _ (Read_u8 (& importKind, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, " kind: %d '%s.%s' ", (u32) importKind, import.moduleUtf8, import.fieldUtf8); switch (importKind) { case d_externalKind_function: { u32 typeIndex; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& typeIndex, & i_bytes, i_end)) _ (Module_AddFunction (io_module, typeIndex, & import)) import = clearImport; io_module->numFuncImports++; } break; case d_externalKind_table: // result = ParseType_Table (& i_bytes, i_end); break; case d_externalKind_memory: { _ (ParseType_Memory (& io_module->memoryInfo, & i_bytes, i_end)); io_module->memoryImported = true; } break; case d_externalKind_global: { i8 waType; u8 type, isMutable; _ (ReadLEB_i7 (& waType, & i_bytes, i_end)); _ (NormalizeType (& type, waType)); _ (ReadLEB_u7 (& isMutable, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, " global: %s mutable=%d", c_waTypes [type], (u32) isMutable); IM3Global global; _ (Module_AddGlobal (io_module, & global, type, isMutable, true /* isImport */)); global->import = import; import = clearImport; } break; default: _throw (m3Err_wasmMalformed); } FreeImportInfo (& import); } _catch: FreeImportInfo (& import); return result; } -
From Function : add all the functions into the Function one by one through
Module_AddFunctioin():AndModule_PreallocFunctions()function is used to allocate the space of the functions according to the number.M3Result ParseSection_Function (IM3Module io_module, bytes_t i_bytes, cbytes_t i_end) { M3Result result = m3Err_none; u32 numFunctions; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& numFunctions, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, "** Function [%d]", numFunctions); _throwif("too many functions", numFunctions > d_m3MaxSaneFunctionsCount); _ (Module_PreallocFunctions(io_module, io_module->numFunctions + numFunctions)); for (u32 i = 0; i < numFunctions; ++i) { u32 funcTypeIndex; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& funcTypeIndex, & i_bytes, i_end)); _ (Module_AddFunction (io_module, funcTypeIndex, NULL /* import info */)); } _catch: return result; } -
For memory section,
ParseSection_Memory():M3Result ParseSection_Memory (M3Module * io_module, bytes_t i_bytes, cbytes_t i_end) { M3Result result = m3Err_none; // TODO: MVP; assert no memory imported u32 numMemories; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& numMemories, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, "** Memory [%d]", numMemories); _throwif (m3Err_tooManyMemorySections, numMemories != 1); ParseType_Memory (& io_module->memoryInfo, & i_bytes, i_end); _catch: return result; } -
For Global Section, function is
ParseSection_Global(), usingModule_AddGlobal()function:M3Result ParseSection_Global (M3Module * io_module, bytes_t i_bytes, cbytes_t i_end) { M3Result result = m3Err_none; u32 numGlobals; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& numGlobals, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, "** Global [%d]", numGlobals); _throwif("too many globals", numGlobals > d_m3MaxSaneGlobalsCount); for (u32 i = 0; i < numGlobals; ++i) { i8 waType; u8 type, isMutable; _ (ReadLEB_i7 (& waType, & i_bytes, i_end)); _ (NormalizeType (& type, waType)); _ (ReadLEB_u7 (& isMutable, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, " global: [%d] %s mutable: %d", i, c_waTypes [type], (u32) isMutable); IM3Global global; _ (Module_AddGlobal (io_module, & global, type, isMutable, false /* isImport */)); global->initExpr = i_bytes; _ (Parse_InitExpr (io_module, & i_bytes, i_end)); global->initExprSize = (u32) (i_bytes - global->initExpr); _throwif (m3Err_wasmMissingInitExpr, global->initExprSize <= 1); } _catch: return result; } -
For Export Section,
ParseSection_Export(), export different kind between Global and functioin:if (exportKind == d_externalKind_function) { _throwif(m3Err_wasmMalformed, index >= io_module->numFunctions); IM3Function func = &(io_module->functions [index]); if (func->numNames < d_m3MaxDuplicateFunctionImpl) { func->names[func->numNames++] = utf8; func->export_name = utf8; utf8 = NULL; // ownership transferred to M3Function } } else if (exportKind == d_externalKind_global) { _throwif(m3Err_wasmMalformed, index >= io_module->numGlobals); IM3Global global = &(io_module->globals [index]); m3_Free (global->name); global->name = utf8; utf8 = NULL; // ownership transferred to M3Global } -
ParseSection for code function
ParseSection_Code()is like:M3Result ParseSection_Code (M3Module * io_module, bytes_t i_bytes, cbytes_t i_end) { M3Result result; u32 numFunctions; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& numFunctions, & i_bytes, i_end)); m3log (parse, "** Code [%d]", numFunctions); if (numFunctions != io_module->numFunctions - io_module->numFuncImports) { _throw ("mismatched function count in code section"); } for (u32 f = 0; f < numFunctions; ++f) { const u8 * start = i_bytes; u32 size; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& size, & i_bytes, i_end)); if (size) { const u8 * ptr = i_bytes; i_bytes += size; if (i_bytes <= i_end) { /* u32 numLocalBlocks; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& numLocalBlocks, & ptr, i_end)); m3log (parse, " code size: %-4d", size); u32 numLocals = 0; for (u32 l = 0; l < numLocalBlocks; ++l) { u32 varCount; i8 wasmType; u8 normalType; _ (ReadLEB_u32 (& varCount, & ptr, i_end)); _ (ReadLEB_i7 (& wasmType, & ptr, i_end)); _ (NormalizeType (& normalType, wasmType)); numLocals += varCount; m3log (parse, " %2d locals; type: '%s'", varCount, c_waTypes [normalType]); } */ IM3Function func = Module_GetFunction (io_module, f + io_module->numFuncImports); func->module = io_module; func->wasm = start; func->wasmEnd = i_bytes; //func->ownsWasmCode = io_module->hasWasmCodeCopy; // func->numLocals = numLocals; } else _throw (m3Err_wasmSectionOverrun); } } _catch: if (not result and i_bytes != i_end) result = m3Err_wasmSectionUnderrun; return result; }-
Checking Function Count Consistency: It checks if the number of functions read matches the count of function declarations in the module minus the number of function imports, and throws an error if there's a mismatch.
-
Parsing Function Bodies: It iterates through each function body:
- It records the start of the function body data.
- It reads the size of the function body.
- If the size is non-zero, it advances
i_bytesto point to the end of the function body data. - It checks if the end of the function body data is within bounds, and if not, it throws an
m3Err_wasmSectionOverrunerror.
-
Function Signature: The function takes three arguments:
M3Module * io_module: A pointer to a module structure where the parsed data will be stored.bytes_t i_bytes: A pointer to the beginning of the byte data for the Code section.cbytes_t i_end: A pointer to the end of the byte data for the Code section.
-
Variable Declarations:
M3Result result: A variable to hold the result of the parsing.u32 numFunctions: A variable to hold the number of functions in the Code section.
-
repl_load(): LoadModule
- In
m3_LoadModule()function, Init the memory, globals and DataSegements and elemets in the runtime and update the IM3Runtime:// TODO: deal with main + side-modules loading efforcement M3Result m3_LoadModule (IM3Runtime io_runtime, IM3Module io_module) { M3Result result = m3Err_none; if (M3_UNLIKELY(io_module->runtime)) { return m3Err_moduleAlreadyLinked; } io_module->runtime = io_runtime; M3Memory * memory = & io_runtime->memory; _ (InitMemory (io_runtime, io_module)); _ (InitGlobals (io_module)); _ (InitDataSegments (memory, io_module)); _ (InitElements (io_module)); // Start func might use imported functions, which are not liked here yet, // so it will be called before a function call is attempted (in m3_FindFunction) #ifdef DEBUG Module_GenerateNames(io_module); // only in debug mode, and generate names for unregistered functions(functions and imported function) and globals #endif io_module->next = io_runtime->modules; io_runtime->modules = io_module; return result; // ok _catch: io_module->runtime = NULL; return result; }
repl_load(): SetModuleName
- set module name using function
m3_SetModuleName()
repl_load():Link all the modules
- Link modules by function
link_all():M3Result link_all (IM3Module module) { M3Result res; res = m3_LinkSpecTest (module); if (res) return res; res = m3_LinkLibC (module); if (res) return res; #if defined(LINK_WASI) res = m3_LinkWASI (module); if (res) return res; #endif #if defined(d_m3HasTracer) res = m3_LinkTracer (module); if (res) return res; #endif #if defined(GAS_LIMIT) res = m3_LinkRawFunction (module, "metering", "usegas", "v(i)", &metering_usegas); if (!res) { fprintf(stderr, "Warning: Gas is limited to %0.4f\n", (double)(current_gas) / GAS_FACTOR); is_gas_metered = true; } if (res == m3Err_functionLookupFailed) { res = NULL; } #endif return res; }
lazy Compile_Modules
Lazy compile is a technique of delaying the compilation of a program or a part of it until it is actually needed. This can save time and resources, especially for large or complex codebases. Lazy compile can also enable some features that are not possible with eager compile, such as infinite data structures, partial definitions, and dynamic loading. However, lazy compile also has some drawbacks, such as indeterminacy, memory overhead, and difficulty in debugging12
- for this part, if
--compile disable lazy compilationis false, it will not be excuted
Breakpoint 14, repl_load (fn=0x7ffd7ba374ee "hello.wasm") at /root/Github/wasm3/platforms/app/main.c:153
153 m3_SetModuleName(module, modname_from_fn(fn));
(gdb) c
Continuing.
Breakpoint 16, main (i_argc=0, i_argv=0x7ffd7ba353a8) at /root/Github/wasm3/platforms/app/main.c:627
627 if (argCompile) {
(gdb) print argCompile
$26 = false
(gdb) print argFunc
$27 = 0x55a4851ac0fa "_start"
(gdb) print argRepl
$28 = false
repl_call(): Get and check every function, finally execute the function.
m3_FindFunction()for each module, find its functions and compile them usingCompileFunction()inside them3_FindFunction(), then judge every func's return status, return them as results.
M3Result m3_FindFunction (IM3Function * o_function, IM3Runtime i_runtime, const char * const i_functionName)
{
M3Result result = m3Err_none; d_m3Assert (o_function and i_runtime and i_functionName);
IM3Function function = NULL;
if (not i_runtime->modules) {
_throw ("no modules loaded");
}
function = (IM3Function) ForEachModule (i_runtime, (ModuleVisitor) v_FindFunction, (void *) i_functionName);
if (function)
{
if (not function->compiled)
{
_ (CompileFunction (function)) //
}
}
else _throw (ErrorModule (m3Err_functionLookupFailed, i_runtime->modules, "'%s'", i_functionName));
_catch:
if (result)
function = NULL;
* o_function = function;
return result;
}
repl_call(): Get Wasi context()
- in LinkWasi's process, there is a step to get the wasi's context:
if (!strcmp(name, "_start")) { #if defined(LINK_WASI) // Strip wasm file path if (argc > 0) { argv[0] = modname_from_fn(argv[0]); } m3_wasi_context_t* wasi_ctx = m3_GetWasiContext(); wasi_ctx->argc = argc; wasi_ctx->argv = argv; result = m3_CallArgv(func, 0, NULL); print_gas_used(); if (result == m3Err_trapExit) { exit(wasi_ctx->exit_code); } return result; #else return "WASI not linked"; #endif }
repl_call(): Execute the main function
- In
repl_call()function, execute them3_CallArgv()inm3_env.cto execute main function.
This function handles the entire process of preparing for, and making a call to a WebAssembly function within the Wasm3 interpreter. It ensures that arguments are correctly converted and placed on the stack, and that all necessary pre- and post- conditions are met for the function call. This is a crucial part of enabling interaction between the host environment and the WebAssembly code.M3Result m3_CallArgv (IM3Function i_function, uint32_t i_argc, const char * i_argv[]) { IM3FuncType ftype = i_function->funcType; IM3Runtime runtime = i_function->module->runtime; M3Result result = m3Err_none; u8* s = NULL; if (i_argc != ftype->numArgs) { return m3Err_argumentCountMismatch; } if (!i_function->compiled) { return m3Err_missingCompiledCode; } # if d_m3RecordBacktraces ClearBacktrace (runtime); # endif m3StackCheckInit(); _ (checkStartFunction(i_function->module)) s = GetStackPointerForArgs (i_function); for (u32 i = 0; i < ftype->numArgs; ++i) { switch (d_FuncArgType(ftype, i)) { case c_m3Type_i32: *(i32*)(s) = strtoul(i_argv[i], NULL, 10); s += 8; break; case c_m3Type_i64: *(i64*)(s) = strtoull(i_argv[i], NULL, 10); s += 8; break; # if d_m3HasFloat case c_m3Type_f32: *(f32*)(s) = strtod(i_argv[i], NULL); s += 8; break; // strtof would be less portable case c_m3Type_f64: *(f64*)(s) = strtod(i_argv[i], NULL); s += 8; break; # endif default: return "unknown argument type"; } } result = (M3Result) RunCode (i_function->compiled, (m3stack_t)(runtime->stack), runtime->memory.mallocated, d_m3OpDefaultArgs); ReportNativeStackUsage (); runtime->lastCalled = result ? NULL : i_function; _catch: return result; }
RunCode() function in repl_call()
// pc, sp, mem, r0
result = (M3Result) RunCode (i_function->compiled, (m3stack_t)(runtime->stack), runtime->memory.mallocated, d_m3OpDefaultArgs);
- Implementation in
m3_exec_defs.hd_m3RetSig RunCode (d_m3OpSig) { nextOpDirect(); } d_m30p(Entry)function inm3_exec.hd_m3Op (Entry) { d_m3ClearRegisters //# define d_m3ClearRegisters d_m3ExpClearRegisters (_fp0 = 0.;) d_m3TracePrepare IM3Function function = immediate (IM3Function); IM3Memory memory = m3MemInfo (_mem); #if d_m3SkipStackCheck if (true) #else if (M3_LIKELY ((void *) (_sp + function->maxStackSlots) < _mem->maxStack)) #endif { #if defined(DEBUG) function->hits++; #endif u8 * stack = (u8 *) ((m3slot_t *) _sp + function->numRetAndArgSlots); memset (stack, 0x0, function->numLocalBytes); stack += function->numLocalBytes; if (function->constants) { memcpy (stack, function->constants, function->numConstantBytes); } #if d_m3EnableStrace >= 2 d_m3TracePrint("%s %s {", m3_GetFunctionName(function), SPrintFunctionArgList (function, _sp + function->numRetSlots)); trace_rt->callDepth++; #endif m3ret_t r = nextOpImpl (); // #if d_m3EnableStrace >= 2 trace_rt->callDepth--; if (r) { d_m3TracePrint("} !trap = %s", (char*)r); } else { int rettype = GetSingleRetType(function->funcType); if (rettype != c_m3Type_none) { char str [128] = { 0 }; SPrintArg (str, 127, _sp, rettype); d_m3TracePrint("} = %s", str); } else { d_m3TracePrint("}"); } } #endif if (M3_UNLIKELY(r)) { _mem = memory->mallocated; fillBacktraceFrame (); } forwardTrap (r); } else newTrap (m3Err_trapStackOverflow); }- The Entry function is crucial as it sets up the environment for the WebAssembly function execution, handles the execution, and takes care of any traps (errors) that occur during execution. It's structured to handle various configurations and debugging scenarios, with conditional compilation for stack checking, tracing, and debug counting.
- _pc, _mem, _sp, _r0
- These parameters are central to the operation of the interpreter and are passed around to different operation functions to carry out the execution of WebAssembly instructions. They provide the necessary context for executing instructions, managing memory, and controlling the flow of the program.
- In the source code of Wasm3, these parameters being defined in macros like d_m3OpSig or d_m3BaseOpSig which are then used in the definition of operation functions. The exact macro definitions and how they are utilized might vary depending on the specific version of Wasm3 you are looking at, but generally, they set up the signature for operation functions, specifying the necessary parameters and their types.
- nextOpImpl()
Jump to different place, in Branch_if.d_m3Op (BranchIf_r) { i32 condition = (i32) _r0; pc_t branch = immediate (pc_t); if (condition) { jumpOp (branch); } else nextOp (); }
And Follow the next Op.
Finally, free the Runtime and Environment
Other details
pay attention to sectionsOrder[expectedSection++] != sectionin m3_ParseModule() in m3_parse.c , that means section order is consecutive and only once in order
Link_all(): m3_LinkeTracer() function
M3Result link_all (IM3Module module)
{
M3Result res;
res = m3_LinkSpecTest (module);
if (res) return res;
res = m3_LinkLibC (module);
if (res) return res;
#if defined(LINK_WASI)
res = m3_LinkWASI (module);
if (res) return res;
#endif
#if defined(d_m3HasTracer)
res = m3_LinkTracer (module);
if (res) return res;
#endif
#if defined(GAS_LIMIT)
res = m3_LinkRawFunction (module, "metering", "usegas", "v(i)", &metering_usegas);
if (!res) {
fprintf(stderr, "Warning: Gas is limited to %0.4f\n", (double)(current_gas) / GAS_FACTOR);
is_gas_metered = true;
}
if (res == m3Err_functionLookupFailed) { res = NULL; }
#endif
return res;
}
-
m3_LinkSpecTest()
-
m3_LinkLibc()
-
m3_LinWASI()
-
m3_LinkTracer()
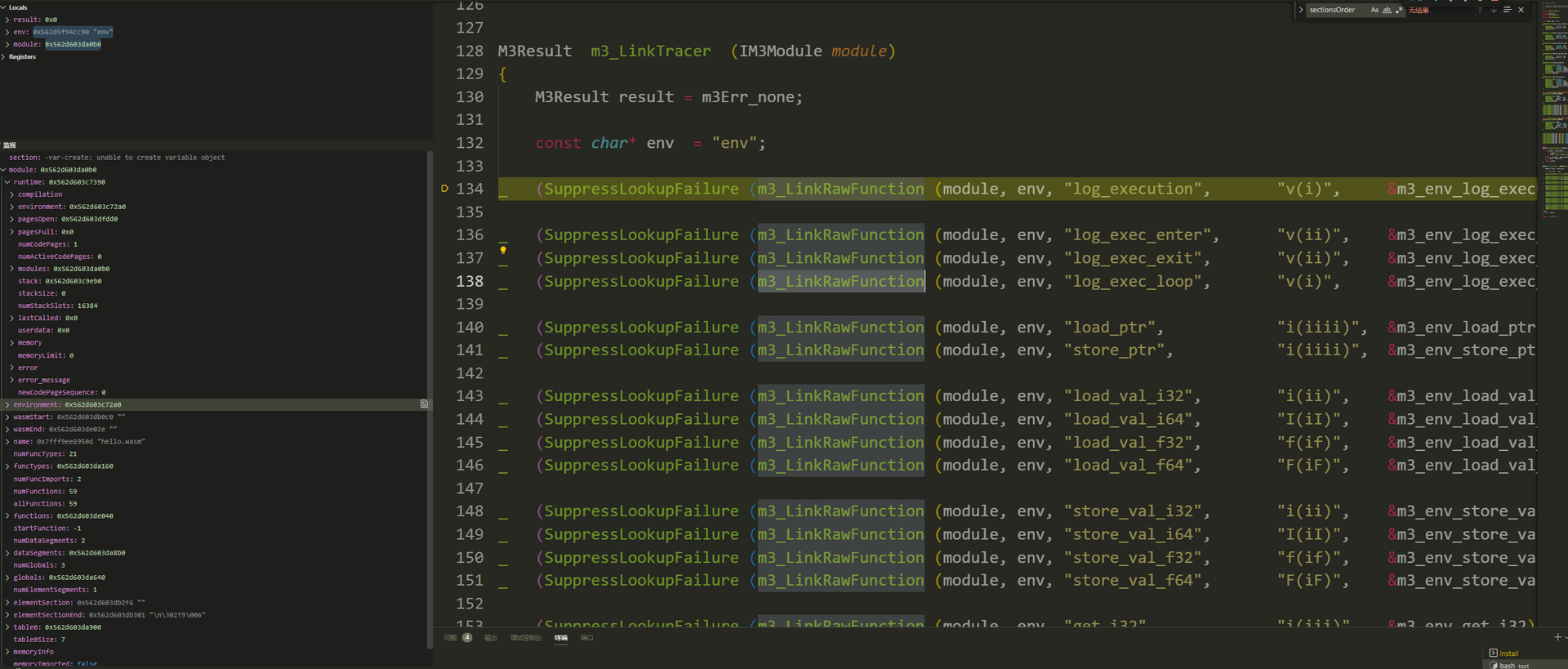
-
m3_LinkRawFunction()
M3Result m3_LinkRawFunction (IM3Module io_module, const char * const i_moduleName, const char * const i_functionName, const char * const i_signature, M3RawCall i_function) { return FindAndLinkFunction (io_module, i_moduleName, i_functionName, i_signature, (voidptr_t)i_function, NULL); }- FindAndLinkFunction()
M3Result FindAndLinkFunction (IM3Module io_module, ccstr_t i_moduleName, ccstr_t i_functionName, ccstr_t i_signature, voidptr_t i_function, voidptr_t i_userdata) { _try { _throwif(m3Err_moduleNotLinked, !io_module->runtime); const bool wildcardModule = (strcmp (i_moduleName, "*") == 0); result = m3Err_functionLookupFailed; for (u32 i = 0; i < io_module->numFunctions; ++i) { const IM3Function f = & io_module->functions [i]; if (f->import.moduleUtf8 and f->import.fieldUtf8) { if (strcmp (f->import.fieldUtf8, i_functionName) == 0 and (wildcardModule or strcmp (f->import.moduleUtf8, i_moduleName) == 0)) { if (i_signature) { _ (ValidateSignature (f, i_signature)); } _ (CompileRawFunction (io_module, f, i_function, i_userdata)); } } } } _catch: return result; }
- FindAndLinkFunction()
-
If
(GAS_LIMIT==Ture)then LinkRawFunction.m3_LinkRawFunction (module, "metering", "usegas", "v(i)", &metering_usegas); -
After all linkers, assign the current wasm to the
wasm_binsarrayif (wasm_bins_qty < MAX_MODULES) { wasm_bins[wasm_bins_qty++] = wasm; }
m3_FindFunction():CompileFunction()
M3Result CompileFunction (IM3Function io_function)
{
if (!io_function->wasm) return "function body is missing";
IM3FuncType funcType = io_function->funcType; m3log (compile, "compiling: [%d] %s %s; wasm-size: %d",
io_function->index, m3_GetFunctionName (io_function), SPrintFuncTypeSignature (funcType), (u32) (io_function->wasmEnd - io_function->wasm));
IM3Runtime runtime = io_function->module->runtime;
IM3Compilation o = & runtime->compilation; d_m3Assert (d_m3MaxFunctionSlots >= d_m3MaxFunctionStackHeight * (d_m3Use32BitSlots + 1)) // need twice as many slots in 32-bit mode
memset (o, 0x0, sizeof (M3Compilation));
o->runtime = runtime;
o->module = io_function->module;
o->function = io_function;
o->wasm = io_function->wasm;
o->wasmEnd = io_function->wasmEnd;
o->block.type = funcType;
_try {
// skip over code size. the end was already calculated during parse phase
u32 size;
_ (ReadLEB_u32 (& size, & o->wasm, o->wasmEnd)); d_m3Assert (size == (o->wasmEnd - o->wasm))
_ (AcquireCompilationCodePage (o, & o->page));
pc_t pc = GetPagePC (o->page);
u16 numRetSlots = GetFunctionNumReturns (o->function) * c_ioSlotCount;
for (u16 i = 0; i < numRetSlots; ++i)
MarkSlotAllocated (o, i);
o->function->numRetSlots = o->slotFirstDynamicIndex = numRetSlots;
u16 numArgs = GetFunctionNumArgs (o->function);
// push the arg types to the type stack
for (u16 i = 0; i < numArgs; ++i)
{
u8 type = GetFunctionArgType (o->function, i);
_ (PushAllocatedSlot (o, type));
// prevent allocator fill-in
o->slotFirstDynamicIndex += c_ioSlotCount;
}
o->slotMaxAllocatedIndexPlusOne = o->function->numRetAndArgSlots = o->slotFirstLocalIndex = o->slotFirstDynamicIndex;
_ (CompileLocals (o));
u16 maxSlot = GetMaxUsedSlotPlusOne (o);
o->function->numLocalBytes = (maxSlot - o->slotFirstLocalIndex) * sizeof (m3slot_t);
o->slotFirstConstIndex = o->slotMaxConstIndex = maxSlot;
// ReserveConstants initializes o->firstDynamicSlotNumber
_ (ReserveConstants (o)); // reserve all the constants find in the
// start tracking the max stack used (Push() also updates this value) so that op_Entry can precisely detect stack overflow
o->maxStackSlots = o->slotMaxAllocatedIndexPlusOne = o->slotFirstDynamicIndex;
o->block.blockStackIndex = o->stackFirstDynamicIndex = o->stackIndex; m3log (compile, "start stack index: %d",
(u32) o->stackFirstDynamicIndex);
_ (EmitOp (o, op_Entry));
EmitPointer (o, io_function);
_ (CompileBlockStatements (o));
// TODO: validate opcode sequences
_throwif(m3Err_wasmMalformed, o->previousOpcode != c_waOp_end);
io_function->compiled = pc;
io_function->maxStackSlots = o->maxStackSlots;
u16 numConstantSlots = o->slotMaxConstIndex - o->slotFirstConstIndex; m3log (compile, "unique constant slots: %d; unused slots: %d",
numConstantSlots, o->slotFirstDynamicIndex - o->slotMaxConstIndex);
io_function->numConstantBytes = numConstantSlots * sizeof (m3slot_t);
if (numConstantSlots)
{
io_function->constants = m3_CopyMem (o->constants, io_function->numConstantBytes);
_throwifnull(io_function->constants);
}
} _catch:
ReleaseCompilationCodePage (o);
return result;
}
In summary, CompileFunction is responsible for translating the Wasm bytecode of a single function into a form that can be executed by the Wasm3 interpreter, handling all necessary preparations such as reserving stack slots for return values, arguments, local variables, and constants, and performing some basic validation on the bytecode.
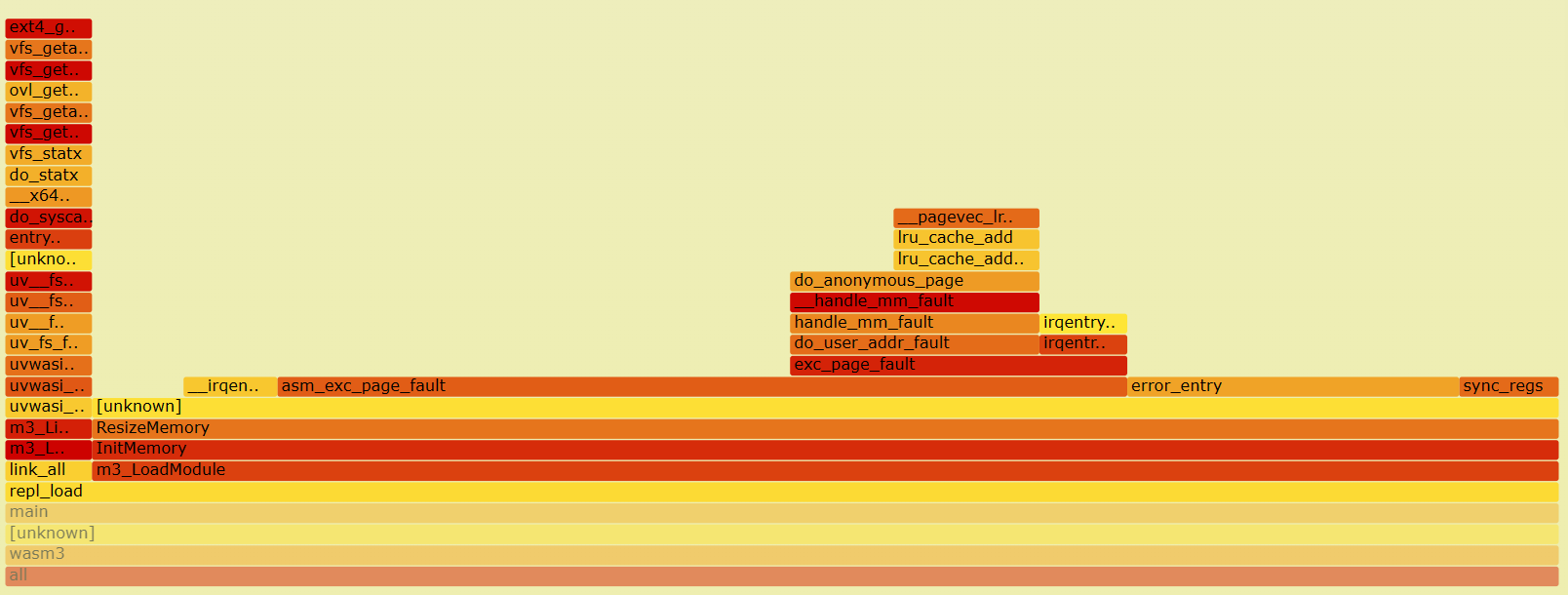
Performance Measurement Using Perf
Usage using tool perf > blog
repl_loadoccupies the most of the resources
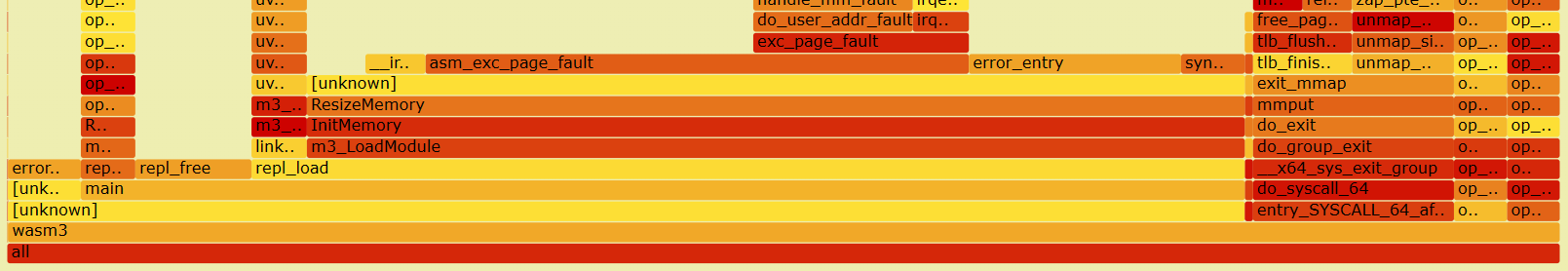
ResizeMemoryfunction called byInitMmorywhich is insidem3_LoadMoudlefunction inrepl_loadtake the most of the resources.
M3Result ResizeMemory (IM3Runtime io_runtime, u32 i_numPages) { M3Result result = m3Err_none; u32 numPagesToAlloc = i_numPages; M3Memory * memory = & io_runtime->memory; #if 0 // Temporary fix for memory allocation if (memory->mallocated) { memory->numPages = i_numPages; memory->mallocated->end = memory->wasmPages + (memory->numPages * c_m3MemPageSize); return result; } i_numPagesToAlloc = 256; #endif if (numPagesToAlloc <= memory->maxPages) { size_t numPageBytes = numPagesToAlloc * d_m3MemPageSize; #if d_m3MaxLinearMemoryPages > 0 _throwif("linear memory limitation exceeded", numPagesToAlloc > d_m3MaxLinearMemoryPages); #endif // Limit the amount of memory that gets actually allocated if (io_runtime->memoryLimit) { numPageBytes = M3_MIN (numPageBytes, io_runtime->memoryLimit); } size_t numBytes = numPageBytes + sizeof (M3MemoryHeader); size_t numPreviousBytes = memory->numPages * d_m3MemPageSize; if (numPreviousBytes) numPreviousBytes += sizeof (M3MemoryHeader); void* newMem = m3_Realloc ("Wasm Linear Memory", memory->mallocated, numBytes, numPreviousBytes); _throwifnull(newMem); memory->mallocated = (M3MemoryHeader*)newMem; # if d_m3LogRuntime M3MemoryHeader * oldMallocated = memory->mallocated; # endif memory->numPages = numPagesToAlloc; memory->mallocated->length = numPageBytes; memory->mallocated->runtime = io_runtime; memory->mallocated->maxStack = (m3slot_t *) io_runtime->stack + io_runtime->numStackSlots; m3log (runtime, "resized old: %p; mem: %p; length: %zu; pages: %d", oldMallocated, memory->mallocated, memory->mallocated->length, memory->numPages); } else result = m3Err_wasmMemoryOverflow; _catch: return result; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号