set学习笔记
set的特性是,所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序,set的元素不像map那样可以同时拥有实值(value)和键值(key),set元素的键值就是实值,实值就是键值。set不允许两个元素有相同的键值(multiset可以)。
set的各成员函数列表如下:
begin()--返回指向第一个元素的迭代器
insert()--在集合中插入元素
end()--返回指向最后一个元素的迭代器
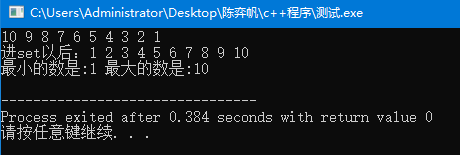
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n = 10; 4 multiset<int>s; 5 int main(){ 6 for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){ 7 cout << i << ' '; 8 s.insert(i); 9 } 10 set<int>::iterator i = s.begin(); 11 cout << endl << "进set以后:"; 12 for(; i != s.end(); i++) cout << *i << ' '; 13 cout << endl; 14 cout << "最小的数是:" << *s.begin() << ' ' << "最大的数是:" << *prev(s.end()) << endl; 15 return 0; 16 }
clear()--清除所有元素
empty()--如果集合为空,返回true
size()--集合中元素的数目
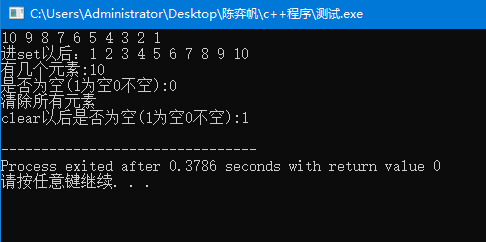
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n = 10; 4 multiset<int>s; 5 int main(){ 6 for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){ 7 cout << i << ' '; 8 s.insert(i); 9 } 10 set<int>::iterator i = s.begin(); 11 cout << endl << "进set以后:"; 12 for(; i != s.end(); i++) cout << *i << ' '; 13 cout << endl << "有几个元素:" << s.size() << endl << "是否为空(1为空0不空):" << s.empty(); 14 s.clear(); 15 cout << endl << "清除所有元素"; 16 cout << endl << "clear以后是否为空(1为空0不空):" << s.empty() << endl; 17 return 0; 18 }
count()--返回某个值元素的个数
erase()--删除集合中的元素
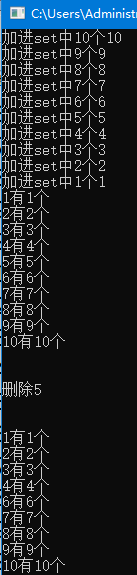
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n = 10; 4 multiset<int>s; 5 int main(){ 6 for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){ 7 cout << "加进set中" << i << "个" << i << endl; 8 for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++) s.insert(i); 9 } 10 set<int>::iterator i = s.begin(); 11 int x = INT_MAX; 12 for(; i != s.end(); i++){ 13 if(*i != x) 14 x = *i, cout << *i << "有" << s.count(*i) << "个" << endl; 15 } 16 cout << endl << endl << "删除5" << endl << endl << endl; 17 s.erase(5); 18 for(i = s.begin(); i != s.end(); i++){ 19 if(*i != x) 20 x = *i, cout << *i << "有" << s.count(*i) << "个" << endl; 21 } 22 return 0; 23 }
find()--返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器
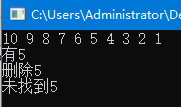
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n = 10; 4 multiset<int>s; 5 int main(){ 6 for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--){ 7 cout << i << ' '; 8 s.insert(i); 9 } 10 cout << endl; 11 set<int>::iterator it = s.find(5); 12 if(it != s.end()) cout << "有5" << endl; 13 else cout << "未找到5" << endl; 14 s.erase(5); 15 cout << "删除5" << endl; 16 it = s.find(5); 17 if(it != s.end()) cout << "有5" << endl; 18 else cout << "未找到5" << endl; 19 return 0; 20 }
max_size()--返回集合能容纳的元素的最大限值
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 multiset<int>s; 4 int main(){ 5 cout << s.max_size() << endl; 6 return 0; 7 }
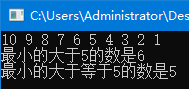
upper_bound()--返回大于某个值元素的迭代器
lower_bound()--返回指向大于等于某值的第一个元素的迭代器
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 multiset<int>s; 4 int n = 10; 5 int main(){ 6 for(int i = 10; i >= 1; i--){ 7 s.insert(i); 8 cout << i << ' '; 9 } 10 cout << endl; 11 cout << "最小的大于5的数是" << *s.upper_bound(5) << endl << "最小的大于等于5的数是" << *s.lower_bound(5) << endl; 12 return 0; 13 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号