设计模式6 插件模式 Plugin Pattern
代码地址:https://github.com/showkawa/springBoot_2017/tree/master/spb-demo/spb-script
插件模式不属于经典设计模式的范畴,但是在项目开放中也会碰到,特别是做微前端(Micro-Frontend)开发的小伙伴会对插件化插件模式体会更深。我这边写这个插件模式是因为我这边项目有一些工具型的项目开发,需要做到可插拔和方便其他业务项目定制自己的插件。
下面是我的插件模式的UML (关于UML类图的基础知识可以查看博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/hlkawa/p/12854562.html)。这边的插件模式核心有三个,分别是Plugin接口,PluginRegister接口和实现类SimplePluginRegister.
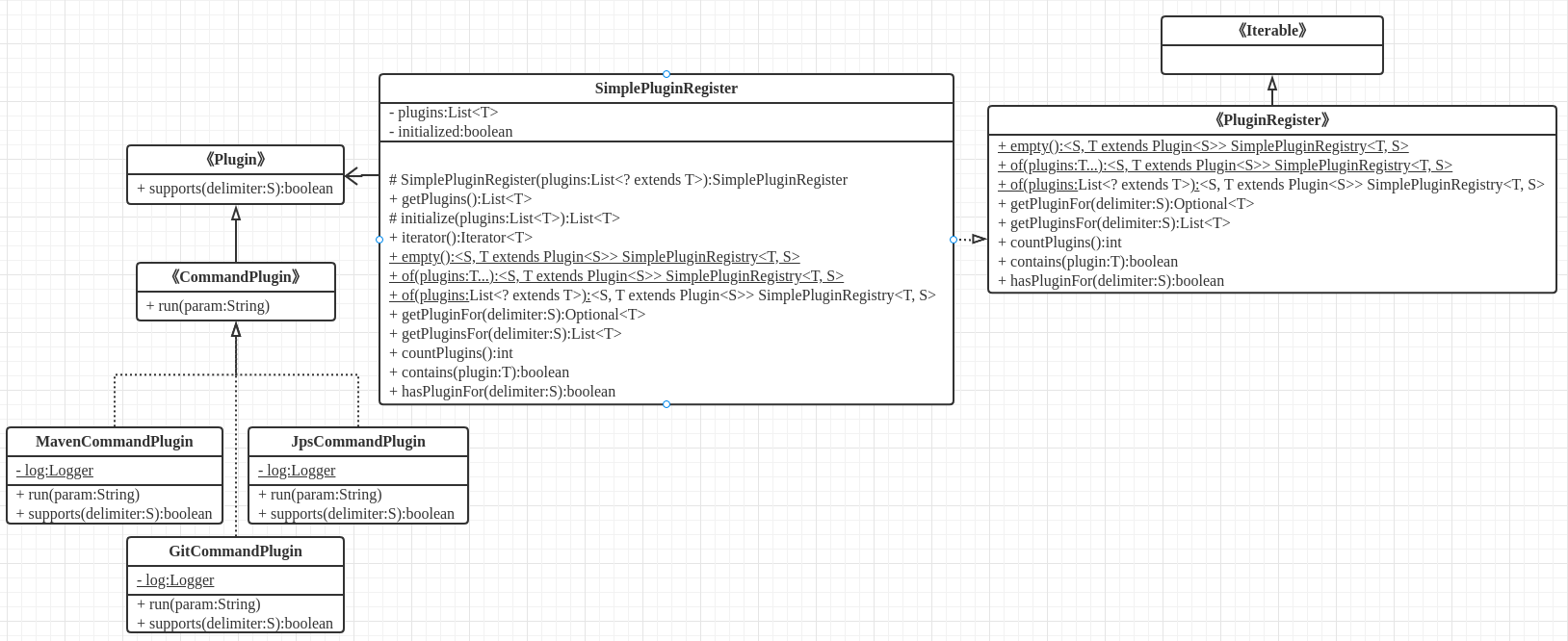
1. Plugin接口
Plugin定义了方法suppotrs根据入参delimiter来判断是否激活和使用当前插件
public interface Plugin<S> { boolean supports(S delimiter); }
2. PluginRegister接口
PluginRegister接口主要定义了一些初始化插件,以及获取插件和统计插件的方法
public interface PluginRegistry<T extends Plugin<S>, S> extends Iterable<T> { public static <S, T extends Plugin<S>> PluginRegistry<T, S> empty() { return of(Collections.emptyList()); } @SafeVarargs public static <S, T extends Plugin<S>> PluginRegistry<T, S> of(T... plugins) { return of(Arrays.asList(plugins)); } public static <S, T extends Plugin<S>> PluginRegistry<T, S> of(List<? extends T> plugins) { return of(plugins); } Optional<T> getPluginFor(S delimiter); List<T> getPluginsFor(S delimiter); int countPlugins(); boolean contains(T plugin); boolean hasPluginFor(S delimiter); List<T> getPlugins(); }
3. SimplePluginRegister类
SimplePluginRegister的实现类是PluginRegister的默认实现类,如果不想使用默认的实现也可以根据自己业务去实现和扩展PluginRegister接口,下面具体的方法我就不多做介绍了代码逻辑很简单
package com.kawa.script; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import java.util.*; import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class SimplePluginRegistry<T extends Plugin<S>, S> implements PluginRegistry<T, S>, Iterable<T> { private List<T> plugins; private boolean initialized; protected SimplePluginRegistry(List<? extends T> plugins) { Assert.notNull(plugins, "Plugins must not be null!"); this.plugins = plugins == null ? new ArrayList<>() : (List<T>) plugins; this.initialized = false; } public List<T> getPlugins() { if (!initialized) { this.plugins = initialize(this.plugins); this.initialized = true; } return plugins; } protected synchronized List<T> initialize(List<T> plugins) { Assert.notNull(plugins, "Plugins must not be null!"); return plugins.stream() .filter(it -> it != null) .collect(Collectors.toList()); } @Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return getPlugins().iterator(); } public static <S, T extends Plugin<S>> SimplePluginRegistry<T, S> empty() { return of(Collections.emptyList()); } @SafeVarargs public static <S, T extends Plugin<S>> SimplePluginRegistry<T, S> of(T... plugins) { return of(Arrays.asList(plugins)); } public static <S, T extends Plugin<S>> SimplePluginRegistry<T, S> of(List<? extends T> plugins) { return new SimplePluginRegistry<>(plugins); } @Override public Optional<T> getPluginFor(S delimiter) { Assert.notNull(delimiter, "Delimiter must not be null!"); return getPlugins().stream() .filter(it -> it.supports(delimiter)) .findFirst(); } @Override public List<T> getPluginsFor(S delimiter) { Assert.notNull(delimiter, "Delimiter must not be null!"); return getPlugins().stream() .filter(it -> it.supports(delimiter)) .collect(Collectors.toList()); } @Override public int countPlugins() { return getPlugins().size(); } @Override public boolean contains(T plugin) { return getPlugins().contains(plugin); } @Override public boolean hasPluginFor(S delimiter) { return getPluginFor(delimiter).isPresent(); } }
下面就是如何激活和利用插件功能,这边我以MavenCommandPlugin为例,依赖关系如下图
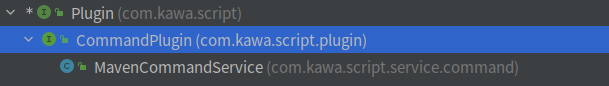
其中CommandPlugin定义了方法run(),就是具体的插件的功能逻辑
package com.kawa.script.plugin; import com.kawa.script.Plugin; public interface CommandPlugin extends Plugin<String> { void run(String parma); }
MavenCommnadService对应maven的插件功能,下面的run()方法代码逻辑不用太关注(就是实现java调用maven指令),主要是关注supports()方法决定该插件是否被激活
package com.kawa.script.service.command; import com.kawa.script.plugin.CommandPlugin; import org.apache.maven.shared.invoker.*; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.nio.file.Path; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.util.Collections; public class MavenCommandService implements CommandPlugin { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MavenCommandService.class); @Override public void run(String parma) { log.info("parma:{}", parma); ClassLoader classLoader = MavenCommandService.class.getClassLoader(); String classPath = classLoader.getResource("").getPath(); Path path = Paths.get(classPath.replace("/target/classes/", "/pom.xml")); InvocationRequest invocationRequest = new DefaultInvocationRequest(); invocationRequest.setPomFile(path.toFile()); invocationRequest.setGoals(Collections.singletonList(parma)); InvocationResult result = null; try { result = new DefaultInvoker() .setMavenHome(Paths.get("/usr/share/maven").toFile()) .execute(invocationRequest); } catch (MavenInvocationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } int exitCode = result.getExitCode(); if (exitCode != 0) { log.info(">>>>>>>>>>> maven run command hit error <<<<<<<<<<"); } log.info(result.toString()); } @Override public boolean supports(String s) { return s.equals("maven"); } }
现在开始初始话插件, 可以看到在静态代码块中通过 new SimplePluginRegistry<>() 初始化三个插件 (JpsCommandService, MavenCommandService, GitCommandService)
package com.kawa.script; import com.kawa.script.plugin.CommandPlugin; import com.kawa.script.service.command.GitCommandService; import com.kawa.script.service.command.JpsCommandService; import com.kawa.script.service.command.MavenCommandService; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Optional; public class BrianScriptApplication { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BrianScriptApplication.class); private static SimplePluginRegistry<CommandPlugin, String> simplePluginRegistry; static { simplePluginRegistry = new SimplePluginRegistry<>(Arrays.asList( new JpsCommandService(), new MavenCommandService(), new GitCommandService())); } public static void main(String[] args) { if (args == null || args.length <= 0) { log.info(">>>>>>>>> no args, exit!!!"); return; } String value = null; String command = args[0]; if (args.length > 1) { value = args[1]; } Optional<CommandPlugin> pluginFor = simplePluginRegistry.getPluginFor(command); String finalValue = value; pluginFor.ifPresentOrElse(cp -> { log.info(">>>>>>>>>> {} run <<<<<<<<<<", cp.getClass().getSimpleName()); cp.run(finalValue); }, new Thread(() -> log.info(">>>>>>>>>> invalid command <<<<<<<<<<"))); } }
然后在方法 simplePluginRegistry.getPluginFor(command) 中获取和激活插件,在这个方法里面回调supports()来判断激活哪个插件
@Override public Optional<T> getPluginFor(S delimiter) { Assert.notNull(delimiter, "Delimiter must not be null!"); return getPlugins().stream() .filter(it -> it.supports(delimiter)) .findFirst(); }
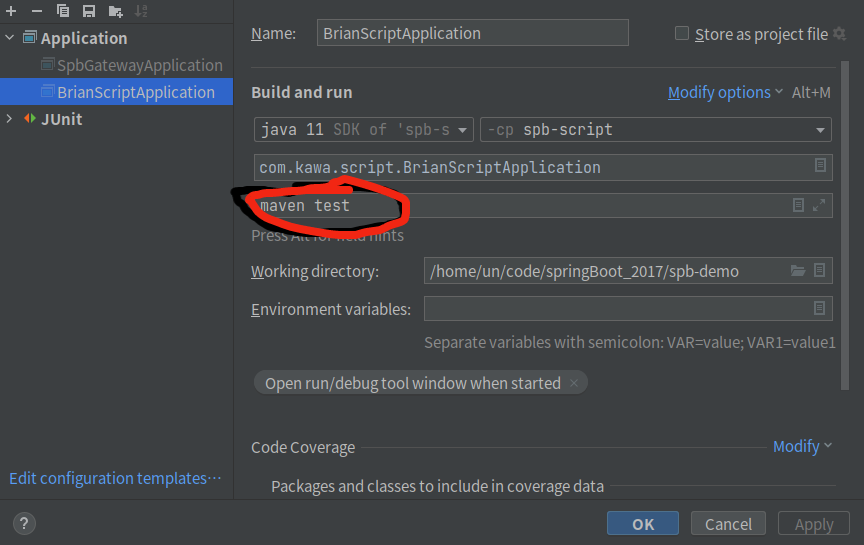
OK,现在演示下java程序使用maven插件功能, 在Idea测试 带上参数 maven test
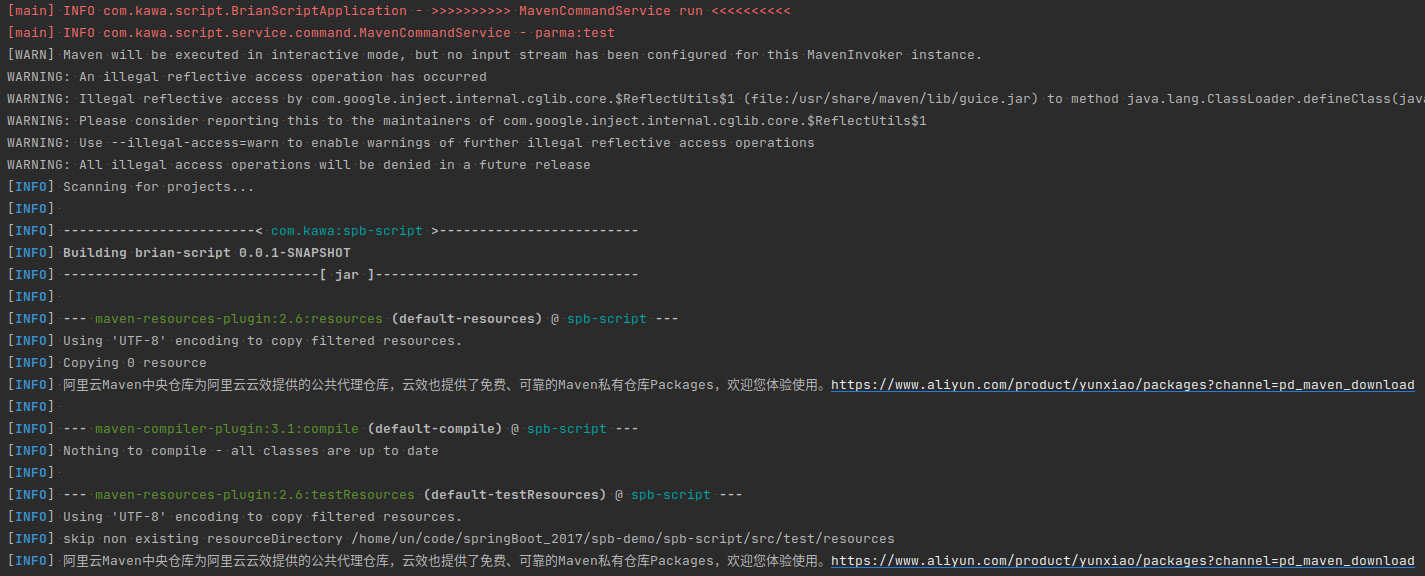
会发现有调用到maven插件并执行test指令(当然这不是重点,重点是通过插件的设计模式的去初始化插件,以及根据入参条件去激活对应的激活插件然后运行创建对应的业务逻辑)
到此插件模式讲完.
插件模式的好处:
1、提供了扩展程序的可能
2、增加插件也很方便
参考来源:spring-plugin (https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-plugin)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号