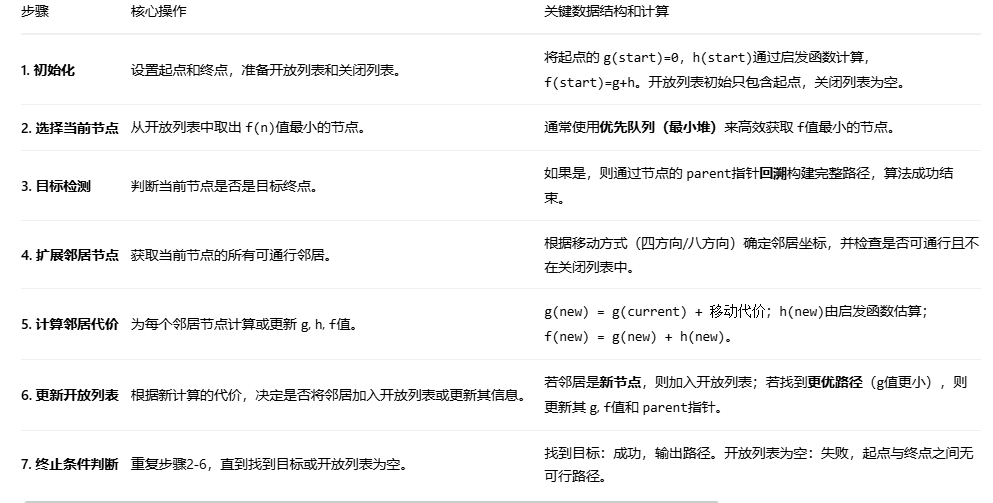
C# AStar 算法 - 基本实现
算法实现代码:
代码由AI生成的

1 namespace Utils.AStarHelp 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// 计算两个点之间的路径-现有路径计算 5 /// </summary> 6 public class AStarPathHelp 7 { 8 public static void GetPaht() 9 { 10 // 1.初始化 11 12 // 创建路径点网格 13 List<Node> allNodes = new List<Node>(); 14 for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++) 15 { 16 for (int y = 0; y < 5; y++) 17 { 18 allNodes.Add(new Node(x, y)); 19 } 20 } 21 22 // 设置障碍物(示例) 23 allNodes.Find(n => n.X == 2 && n.Y == 2).IsWalkable = false; 24 allNodes.Find(n => n.X == 1 && n.Y == 1).IsWalkable = false; 25 26 // 定义起点和终点 27 Node start = allNodes.Find(n => n.X == 0 && n.Y == 0); 28 Node goal = allNodes.Find(n => n.X == 4 && n.Y == 4); 29 30 // 执行A*寻路 31 AStarPathfinder pathfinder = new AStarPathfinder(); 32 List<Node> path = pathfinder.FindPath(allNodes, start, goal, "manhattan"); 33 34 // 输出结果 35 pathfinder.PrintPathInfo(path, start, goal); 36 } 37 } 38 39 // 节点类,表示路径规划中的每个位置点 40 public class Node : IComparable<Node> 41 { 42 public int X { get; } // 节点X坐标 43 public int Y { get; } // 节点Y坐标 44 public float G { get; set; } // 从起点到当前节点的实际代价 45 public float H { get; set; } // 当前节点到终点的预估代价 46 public float F => G + H; // 总评估代价 47 public Node Parent { get; set; } // 父节点,用于路径回溯 48 public bool IsWalkable { get; set; } = true; // 是否可通行 49 50 public Node(int x, int y) 51 { 52 X = x; 53 Y = y; 54 } 55 56 // 重写Equals和GetHashCode,便于在集合中比较节点 57 public override bool Equals(object obj) => obj is Node other && X == other.X && Y == other.Y; 58 public override int GetHashCode() => HashCode.Combine(X, Y); 59 60 // 实现IComparable接口,用于优先队列排序 61 public int CompareTo(Node other) => F.CompareTo(other.F); 62 63 64 } 65 66 public class AStarPathfinder 67 { 68 // 启发式函数:曼哈顿距离(适用于四方向移动) 69 private float ManhattanHeuristic(Node a, Node b) => Math.Abs(a.X - b.X) + Math.Abs(a.Y - b.Y); 70 71 // 启发式函数:欧几里得距离(适用于任意方向移动) 72 private float EuclideanHeuristic(Node a, Node b) => 73 (float)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(a.X - b.X, 2) + Math.Pow(a.Y - b.Y, 2)); 74 75 // 启发式函数:切比雪夫距离(适用于八方向移动) 76 private float ChebyshevHeuristic(Node a, Node b) => 77 Math.Max(Math.Abs(a.X - b.X), Math.Abs(a.Y - b.Y)); 78 79 // 获取当前节点的所有邻居节点(四方向) 80 private List<Node> GetNeighbors(Node node, List<Node> allNodes) 81 { 82 List<Node> neighbors = new List<Node>(); 83 int[] dx = { -1, 1, 0, 0 }; // 左右上下 84 int[] dy = { 0, 0, -1, 1 }; 85 86 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) 87 { 88 int newX = node.X + dx[i]; 89 int newY = node.Y + dy[i]; 90 91 // 查找是否存在该邻居节点 92 Node neighbor = allNodes.Find(n => n.X == newX && n.Y == newY); 93 if (neighbor != null && neighbor.IsWalkable) 94 { 95 neighbors.Add(neighbor); 96 } 97 } 98 return neighbors; 99 } 100 101 102 // A*寻路主算法 103 public List<Node> FindPath(List<Node> allNodes, Node start, Node goal, string heuristicType = "manhattan") 104 { 105 // 2. 选择当前节点 106 107 // 开放列表:存储待探索节点(按F值排序的优先队列) 108 var openList = new PriorityQueue<Node, float>(); 109 // 关闭列表:存储已探索节点 110 var closedSet = new HashSet<Node>(); 111 // 节点信息字典:记录每个节点的最佳G值和父节点 112 var nodeInfo = new Dictionary<Node, (float g, Node parent)>(); 113 114 // 初始化起点 115 start.G = 0; 116 start.H = GetHeuristic(start, goal, heuristicType); 117 openList.Enqueue(start, start.F); 118 nodeInfo[start] = (0, null); 119 120 // 7. 终止条件判断 重复步骤2 - 6,直到找到目标或开放列表为空。 121 while (openList.Count > 0) 122 { 123 // 从开放列表中取出F值最小的节点作为当前节点[1](@ref) 124 Node current = openList.Dequeue(); 125 126 // 3. 目标检测 127 128 // 如果到达终点,回溯构建完整路径 129 if (current.Equals(goal)) 130 { 131 return ReconstructPath(current); 132 } 133 134 // 将当前节点移至关闭列表,标记为已探索 135 closedSet.Add(current); 136 137 // 4. 扩展邻居节点 138 139 // 遍历当前节点的所有邻居节点 140 foreach (Node neighbor in GetNeighbors(current, allNodes)) 141 { 142 // 跳过已在关闭列表中的节点 143 if (closedSet.Contains(neighbor)) 144 continue; 145 146 // 计算从起点经过当前节点到达邻居的新G值 147 float tentativeG = nodeInfo[current].g + 1; // 假设每步代价为1 148 149 // 5. 计算邻居代价 150 // 如果找到更优路径或邻居节点尚未探索 151 if (!nodeInfo.ContainsKey(neighbor) || tentativeG < nodeInfo[neighbor].g) 152 { 153 // 更新邻居节点的父节点和代价值 154 neighbor.Parent = current; 155 neighbor.G = tentativeG; 156 neighbor.H = GetHeuristic(neighbor, goal, heuristicType); 157 158 nodeInfo[neighbor] = (tentativeG, current); 159 160 // 如果邻居不在开放列表中,则加入 161 if (!openList.UnorderedItems.Any(item => item.Element.Equals(neighbor))) 162 { 163 // 6. 更新开放列表 164 openList.Enqueue(neighbor, neighbor.F); 165 } 166 } 167 } 168 } 169 170 return null; // 未找到路径 171 } 172 173 private float GetHeuristic(Node a, Node b, string type) 174 { 175 return type.ToLower() switch 176 { 177 "euclidean" => EuclideanHeuristic(a, b), 178 "chebyshev" => ChebyshevHeuristic(a, b), 179 _ => ManhattanHeuristic(a, b) 180 }; 181 } 182 183 184 // 从终点回溯构建完整路径 185 private List<Node> ReconstructPath(Node endNode) 186 { 187 List<Node> path = new List<Node>(); 188 Node current = endNode; 189 190 while (current != null) 191 { 192 path.Add(current); 193 current = current.Parent; 194 } 195 196 path.Reverse(); // 反转路径,从起点到终点 197 return path; 198 } 199 200 // 打印路径和算法统计信息 201 public void PrintPathInfo(List<Node> path, Node start, Node goal) 202 { 203 if (path == null) 204 { 205 Console.WriteLine("未找到可行路径!"); 206 return; 207 } 208 209 Console.WriteLine($"找到路径!路径长度:{path.Count - 1}步"); 210 Console.WriteLine("路径点序列:"); 211 212 foreach (Node node in path) 213 { 214 string nodeType = node.Equals(start) ? "[起点]" : 215 node.Equals(goal) ? "[终点]" : ""; 216 Console.WriteLine($" ({node.X}, {node.Y}) {nodeType}"); 217 } 218 219 Console.WriteLine($"起点: ({start.X}, {start.Y})"); 220 Console.WriteLine($"终点: ({goal.X}, {goal.Y})"); 221 Console.WriteLine($"总代价G: {goal.G}"); 222 } 223 } 224 225 }
复制完直接用就可以了 调用 AStarPathHelp.GetPaht(); 即可。代码中已经标识了具体的流程和步骤。
流程说明:
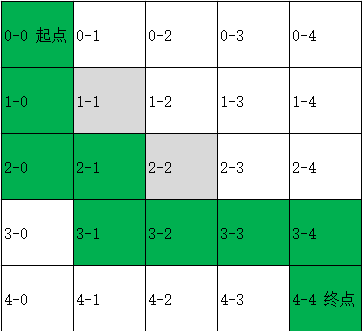
最终路径为:
关于距离计算方式: 默认采用 曼哈顿距离,根据实际情况 改变对应的计算方式
1. 曼哈顿距离
-
何时使用:当你的单位只能像国际象棋里的“车”一样,上下左右移动时。
-
例子:经典益智游戏《华容道》、一些简单的2D网格RPG游戏。
-
计算:从点 (1,1) 到 (4,5) 的曼哈顿距离是
|1-4| + |1-5| = 3 + 4 = 7。
2. 切比雪夫距离
-
何时使用:当你的单位可以像国际象棋里的“王”一样,向周围8个方向移动,并且对角线移动的成本与直线移动相同时。
-
例子:许多战略游戏(如《文明》系列)中的单位移动。
-
计算:从点 (1,1) 到 (4,5) 的切比雪夫距离是
max(|1-4|, |1-5|) = max(3, 4) = 4。
3. 欧几里得距离
-
何时使用:当你的单位可以在一个连续的平面上向任意方向自由移动时。这是最符合现实世界直觉的距离。
-
例子:无人机路径规划、RTS游戏(如《星际争霸》)中单位的真实移动、物理模拟。
-
计算:从点 (1,1) 到 (4,5) 的欧几里得距离是
√((1-4)² + (1-5)²) = √(9 + 16) = 5。 -
注意:在实际编程中,为了节省计算平方根的开销,有时会使用平方欧几里得距离(即
dx² + dy²)进行比较,只要保证所有h(n)使用相同的标准,且满足可采纳性(不高估)即可。
选择的核心原则是:你选择的 h(n) 应该尽可能接近实际成本,并且绝对不能高估实际成本。
-
看移动规则:
-
只能走四方向? -> 曼哈顿距离
-
可以走八方向,且对角线成本与直线相同? -> 切比雪夫距离
-
可以走八方向,但对角线成本更高(例如 √2)? -> 可能需要使用对角距离(一种对角线和直线混合的优化距离)。
-
可以任意方向移动? -> 欧几里得距离
-
-
看地图类型:
-
网格化地图:优先考虑曼哈顿或切比雪夫。
-
导航网格或连续空间:使用欧几里得距离。
-
距离参考: 欧式距离、曼哈顿距离、切比雪夫距离三种距离的可视化展示
以上内容仅仅为学习留存使用。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号