使用while循环分别对两个vector进行赋值,该怎么做
问题
在写程序的时候遇到了这样一个问题,见代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool isequal(vector<int> vshort, vector<int> vlong)
{
for (int index = 0; index != vshort.size(); index++)
if (vshort[index] != vlong[index])
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
int n;
while (cin >> n)
v1.push_back(n);
while (cin >> n)
v2.push_back(n);
if (v1.size() <= v2.size())
cout << isequal(v1, v2) << endl;
else
cout << isequal(v2, v1) << endl;
return 0;
}
结果没有达到想要的效果(即正确对两个vector赋值)
可以看下这篇博客应该能明白为什么是错误的写什么代码来清空缓冲区
这段代码目前在接受输入时,将所有的用户输入依次存储到v1 和 v2 中,但它会因为 cin 连续输入的问题导致输入难以区分,造成逻辑错误。如果想要正确设置 v1 和 v2 的值,可以通过以下方式修改代码:
改进方法
方法 1:指定每组的长度
让用户先输入每组数据的长度,然后依次读取指定数量的数据。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool isequal(vector<int> vshort, vector<int> vlong)
{
for (int index = 0; index != vshort.size(); index++)
if (vshort[index] != vlong[index])
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1, v2;
int n, size1, size2;
// 输入第一组数据的长度和内容
cout << "输入第一组数据的长度:";
cin >> size1;
cout << "输入第一组数据:";
for (int i = 0; i < size1; ++i)
{
cin >> n;
v1.push_back(n);
}
// 输入第二组数据的长度和内容
cout << "输入第二组数据的长度:";
cin >> size2;
cout << "输入第二组数据:";
for (int i = 0; i < size2; ++i)
{
cin >> n;
v2.push_back(n);
}
if (v1.size() <= v2.size())
isequal(v1, v2) ? cout << "v1是v2的前缀" << endl
: cout << "v1 和 v2 之间不存在前缀关系" << endl;
else
isequal(v1, v2) ? cout << "v2是v1的前缀" << endl
: cout << "v1 和 v2 之间不存在前缀关系" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出如下:
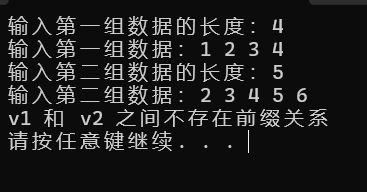
方法 2:使用特殊分隔符
用一个非整数值(如 end)或其他特定分隔符来标记输入结束。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool isequal(vector<int> vshort, vector<int> vlong)
{
for (int index = 0; index != vshort.size(); index++)
if (vshort[index] != vlong[index])
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1, v2;
int n;
string input;
// 输入第一组数据
cout << "输入第一组数据(以 end 结束):";
while (cin >> input && input != "end")
{
n = stoi(input);
v1.push_back(n);
}
// 输入第二组数据
cout << "输入第二组数据(以 end 结束):";
while (cin >> input && input != "end")
{
n = stoi(input);
v2.push_back(n);
}
if (v1.size() <= v2.size())
isequal(v1, v2) ? cout << "v1是v2的前缀" << endl
: cout << "v1 和 v2 之间不存在前缀关系" << endl;
else
isequal(v1, v2) ? cout << "v2是v1的前缀" << endl
: cout << "v1 和 v2 之间不存在前缀关系" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出如下:
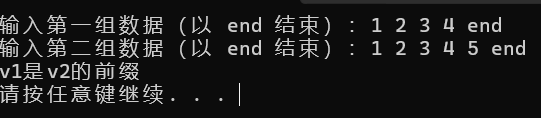
想了解下stio函数的话,可以看下这篇博客stoi函数介绍
方法 3:使用分行输入
通过每组数据分行输入,每行数据代表一个向量。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
bool isequal(vector<int> vshort, vector<int> vlong)
{
for (int index = 0; index != vshort.size(); index++)
if (vshort[index] != vlong[index])
return false;
return true;
}
vector<int> parseLine(const string& line)
{
vector<int> vec;
int num;
stringstream ss(line);
while (ss >> num)
vec.push_back(num);
return vec;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1, v2;
string line;
// 输入第一组数据
cout << "输入第一组数据(单独一行):";
getline(cin, line);
v1 = parseLine(line);
// 输入第二组数据
cout << "输入第二组数据(单独一行):";
getline(cin, line);
v2 = parseLine(line);
if (v1.size() <= v2.size())
isequal(v1, v2) ? cout << "v1是v2的前缀" << endl
: cout << "v1 和 v2 之间不存在前缀关系" << endl;
else
isequal(v1, v2) ? cout << "v2是v1的前缀" << endl
: cout << "v1 和 v2 之间不存在前缀关系" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出如下:

关于streamstring的介绍,可以看下这篇博客 streamstring类介绍
总结
-
指定长度法(方法 1):适合输入大小固定的情况。
-
特殊分隔符法(方法 2):适合不定长输入,但要求用户清楚规则。
-
分行输入法(方法 3):最通用且直观,推荐用于实际开发中。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号