Set容器
一、简介:
参考链接:http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/set/
https://www.cnblogs.com/caiyishuai/p/8646345.html
关于set,必须说明的是set关联式容器。set作为一个容器也是用来存储同一数据类型的数据类型,并且能从一个数据集合中取出数据,在set中每个元素的值都唯一,而且系统能根据元素的值自动进行排序。应该注意的是set中数元素的值不能直接被改变。C++ STL中标准关联容器set, multiset, map, multimap内部采用的就是一种非常高效的平衡检索二叉树:红黑树,也成为RB树(Red-Black Tree)。RB树的统计性能要好于一般平衡二叉树,所以被STL选择作为了关联容器的内部结构。
二、常用方法:
集合(Set)是一种包含已排序对象的关联容器
|
begin() |
返回指向第一个元素的迭代器 |
|
clear() |
清除所有元素 |
|
count() |
返回某个值元素的个数 |
|
empty() |
如果集合为空,返回true |
|
end() |
返回指向最后一个元素的迭代器 |
|
equal_range() |
返回集合中与给定值相等的上下限的两个迭代器 |
|
erase() |
删除集合中的元素 |
|
find() |
返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器 |
|
get_allocator() |
返回集合的分配器 |
|
insert() |
在集合中插入元素 |
|
lower_bound() |
返回指向大于(或等于)某值的第一个元素的迭代器 |
|
key_comp() |
返回一个用于元素间值比较的函数 |
|
max_size() |
返回集合能容纳的元素的最大限值 |
|
rbegin() |
返回指向集合中最后一个元素的反向迭代器 |
|
rend() |
返回指向集合中第一个元素的反向迭代器 |
|
size() |
集合中元素的数目 |
|
swap() |
交换两个集合变量 |
|
upper_bound() |
返回大于某个值元素的迭代器 |
|
value_comp() |
返回一个用于比较元素间的值的函数 |
三、 示例
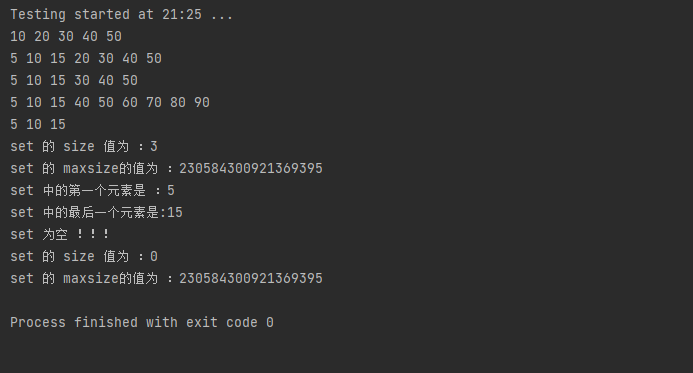
bool fncomp (int lhs, int rhs) { return lhs<rhs; } struct classcomp { bool operator()(const int &lhs, const int &rhs) const { return lhs < rhs; } }; class SetExample { public: void Show(const set<int>& val) { for (auto item : val) { cout << item << " "; } cout << endl; } void Example() { std::set<int> first; // empty set of ints int myints[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; std::set<int> second(myints, myints + 5); // range std::set<int> third(second); // a copy of second std::set<int> fourth(second.begin(), second.end()); // iterator ctor. std::set<int, classcomp> fifth; // class as Compare bool (*fn_pt)(int, int) = fncomp; std::set<int, bool (*)(int, int)> sixth(fn_pt); // function pointer as Compar set<int> myset; set<int>::iterator it; for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) { myset.insert(i * 10); } // 10 20 30 40 50 Show(myset); int temp[] = {5, 10, 15}; myset.insert(temp, temp + 3); // 10已经存在,只插入了 5 15 // 5 10 15 20 30 40 50 Show(myset); // 删除20 myset.erase(20); // 5 10 15 30 40 50 Show(myset); // 删除30 it = myset.find(30); // 5 10 15 40 50 myset.erase(it); int temp2[] = {60, 70, 80, 90}; myset.insert(temp2, temp2 + 4); // 5 10 15 40 50 60 70 80 90 Show(myset); it = myset.find(40); myset.erase(it, myset.end()); // 5 10 15 Show(myset); cout << "set 的 size 值为 :" << myset.size() << endl; cout << "set 的 maxsize的值为 :" << myset.max_size() << endl; cout << "set 中的第一个元素是 :" << *myset.begin() << endl; cout << "set 中的最后一个元素是:" << *(--myset.end()) << endl; myset.clear(); if (myset.empty()) { cout << "set 为空 !!!" << endl; } cout << "set 的 size 值为 :" << myset.size() << endl; cout << "set 的 maxsize的值为 :" << myset.max_size() << endl; } };
输出:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号