一:继承条件下的构造方法调用
运行示例,观察输出回答相关问题
package reserve; class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } }
测试截图:
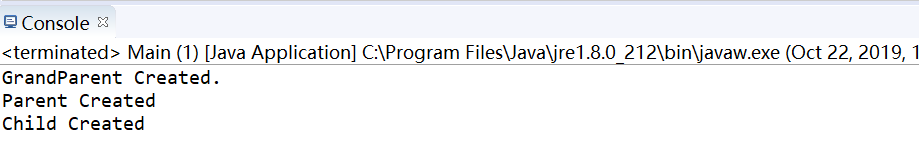
问题:为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?
构造函数是一种特殊的方法。主要用来在创建对象时初始化对象,即为对象成员变量赋值初始值,总与new运算符一起使用在创建对象的语句中。特别的一个类可以有多个构造函数,可其参数个数的不同或参数类型的不同来区分它们,即构造函数的重载。构造函数的功能主要用于在类的对象创建时定义初始化的状态。
构造一个对象,先调用其构造方法,来初始化其成员函数和成员变量。
子类拥有父类的成员变量和成员方法,如果不调用,则从父类继承而来的成员变量和成员方法得不到正确的初始化。
不能反过来调用也是这的原因,因为父类根本不知道子类有什么变量而且这样一来子类也得不到初始化 的父类变量,导致程序运行出错。
二:何为“不可变的类”?
不可变类是指,一旦一个类的对象被创建出来,在其整个生命周期中,它的成员变量就不能被修改,java平台的类库中包含许多不可变的类,比如说String,基本类型的包装类,BigInteger和BigDecimal,存在不可变的类有许多理由:不可变的类比可变的类更加容易设计,实现和使用,它们不容易出错,而且冯家安全。
不可变的“类”的作用:
1.便于实现String常量池。只有当字符串是不可变的,字符串池才有可能实现。
2.便于网络安全问题
3.使多线程安全
4.避免本地安全性问题
5.加快字符串处理速度
三:请自行编写代码测试特性:在子类中若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字
package reserve; class Fu{ public void show() { System.out.println("我是父类"); } } class Child extends Fu{ public void show(){ super.show(); System.out.println("我是子类"); } } public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Child child=new Child(); child.show(); } }
测试截图:
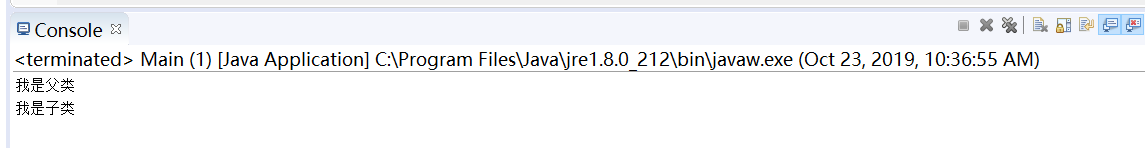
四:下列语句哪一个将引起编译错误?为什么?哪一个会引起运行时错误?为什么?
m=d; d=m; d=(Dog)m; d=c; c=(Cat)m;
先进行自我判断,得出结论后,运行相关代码,看看你的判断是否正确。
自我判断:"d=m","d=c"引起编译错误
“c=(Cat)m”引起运行是错误
原因:“d=m”编译错误是因为Mammal类是Dog类的父类,子类中的成员比父类的多,父类无法将子类初始化;
“d=c”编译错误是因为两者代表不同的类,不能给对方赋值;
“c=(Cat)m”会引起运行时错误是因为Dog类的对象d已将Mammal类的对象m初始化,m被转换为Dog类后不能再转换为Cat类。
五:运行下列示例代码,回答问题
package reserve; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
测试截图:
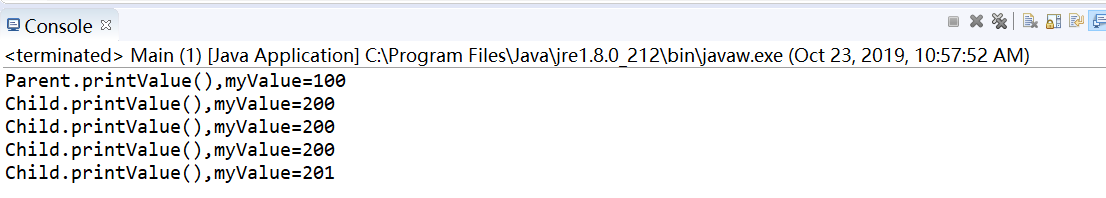
收获和总结:
当子类与父类有一样的方法时,对象是子类型的,它就调用子类型的方法,是父类型的它就调用父类型的方法。
如果子类与父类中有相同的字段,则子类中的字段就会代替或者隐藏父类中的字段。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号